Simple Screening of Listeria monocytogenes Based on a Fluorescence Assay via a Laminated Lab-On-Paper Chip
- PMID: 29182562
- PMCID: PMC5746779
- DOI: 10.3390/bios7040056
Simple Screening of Listeria monocytogenes Based on a Fluorescence Assay via a Laminated Lab-On-Paper Chip
Abstract
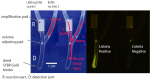
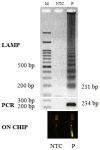
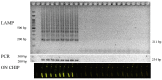
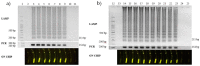
Monitoring food safety is essential for protecting the health and safety of consumers. Conventional methods used are time consuming and laborious, requiring anywhere from three to seven days to obtain results. Thus, better monitoring methods are required. In this study, a laminated lab-on-paper chip was developed, and its use for the screening of ready-to-eat seafood was demonstrated. The assay on a chip was based on loop-mediated isothermal DNA amplification (LAMP) of the hly gene of Listeria monocytogenes and fluorescence signal detection via SYBR GoldTM. Overall assay processes were completed in 4.5 h., (including 3.5 h. incubation for the bacteria enrichment, direct DNA amplification with no DNA extraction, and signal detection), without relying on standard laboratory facilities. Only positive samples induced fluorescence signals on chip upon illumination with UV light (λ = 460). The method has a limit of detection of 100 copies of L. monocytogenes DNA per 50 g of sample. No cross-reactivity was observed in samples contaminated with other bacteria. On-site monitoring of the seafood products using this chip revealed that one of 30 products from low sanitation vendors (3.33%) were contaminated, and these agreed with the results of PCR. The results demonstrated a benefit of this chip assay for practical on-site monitoring.
Keywords: Detection; LAMP; Lab-on-paper chip; Listeria monocytogenes; frozen seafood; hly gene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Application and evaluation of loop-mediated isothermal amplification method for detecting of Listeria monocytogenes in food].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Mar;48(3):213-7. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24844836 Chinese.
-
Reverse transcription - loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the rapid detection of pathogenic Listeria monocytogenes in meat products.Can J Microbiol. 2019 Dec;65(12):913-921. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2019-0114. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Can J Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31491332
-
Sensitive colorimetric detection of Listeria monocytogenes based on isothermal gene amplification and unmodified gold nanoparticles.Methods. 2013 Dec 15;64(3):260-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2013.08.003. Epub 2013 Aug 12. Methods. 2013. PMID: 23948710
-
Fluorescence-Free Biosensor Methods in Detection of Food Pathogens with a Special Focus on Listeria monocytogenes.Biosensors (Basel). 2017 Dec 20;7(4):63. doi: 10.3390/bios7040063. Biosensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29261134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Development of molecular detection of food-borne pathogenic bacteria using miniaturized microfluidic devices].Orv Hetil. 2015 Dec 20;156(51):2082-8. doi: 10.1556/650.2015.30325. Orv Hetil. 2015. PMID: 26654545 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
Development of a Novel Phagomagnetic-Assisted Isothermal DNA Amplification System for Endpoint Electrochemical Detection of Listeria monocytogenes.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Apr 7;13(4):464. doi: 10.3390/bios13040464. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37185539 Free PMC article.
-
Paper-based sensors for bacteria detection.Nat Rev Bioeng. 2023;1(3):180-192. doi: 10.1038/s44222-023-00024-w. Epub 2023 Feb 14. Nat Rev Bioeng. 2023. PMID: 36937095 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization [WHO], Initiative to Estimate the Global Burden of Foodborne Diseases: Information and Publications. [(accessed on 26 November 2016)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/foodsafety/publications/foodborne_disease/fergreport/en/
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

