Palliative chemotherapy and targeted therapies for esophageal and gastroesophageal junction cancer
- PMID: 29182797
- PMCID: PMC6486200
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004063.pub4
Palliative chemotherapy and targeted therapies for esophageal and gastroesophageal junction cancer
Abstract
Background: Almost half of people with esophageal or gastroesophageal junction cancer have metastatic disease at the time of diagnosis. Chemotherapy and targeted therapies are increasingly used with a palliative intent to control tumor growth, improve quality of life, and prolong survival. To date, and with the exception of ramucirumab, evidence for the efficacy of palliative treatments for esophageal and gastroesophageal cancer is lacking.
Objectives: To assess the effects of cytostatic or targeted therapy for treating esophageal or gastroesophageal junction cancer with palliative intent.
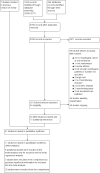
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), MEDLINE, Embase, the Web of Science, PubMed Publisher, Google Scholar, and trial registries up to 13 May 2015, and we handsearched the reference lists of studies. We did not restrict the search to publications in English. Additional searches were run in September 2017 prior to publication, and they are listed in the 'Studies awaiting assessment' section.
Selection criteria: We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on palliative chemotherapy and/or targeted therapy versus best supportive care or control in people with esophageal or gastroesophageal junction cancer.
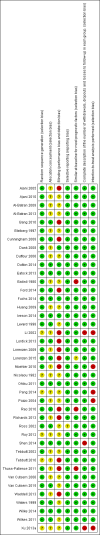
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently extracted data. We assessed the quality and risk of bias of eligible studies according to the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. We calculated pooled estimates of effect using an inverse variance random-effects model for meta-analysis.
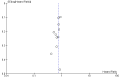
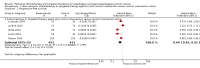
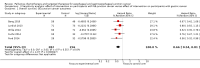
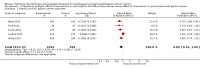
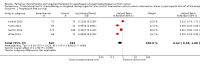
Main results: We identified 41 RCTs with 11,853 participants for inclusion in the review as well as 49 ongoing studies. For the main comparison of adding a cytostatic and/or targeted agent to a control arm, we included 11 studies with 1347 participants. This analysis demonstrated an increase in overall survival in favor of the arm with an additional cytostatic or targeted therapeutic agent with a hazard ratio (HR) of 0.75 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.68 to 0.84, high-quality evidence). The median increased survival time was one month. Five studies in 750 participants contributed data to the comparison of palliative therapy versus best supportive care. We found a benefit in overall survival in favor of the group receiving palliative chemotherapy and/or targeted therapy compared to best supportive care (HR 0.81, 95% CI 0.71 to 0.92, high-quality evidence). Subcomparisons including only people receiving second-line therapies, chemotherapies, targeted therapies, adenocarcinomas, and squamous cell carcinomas all showed a similar benefit. The only individual agent that more than one study found to improve both overall survival and progression-free survival was ramucirumab. Palliative chemotherapy and/or targeted therapy increased the frequency of grade 3 or higher treatment-related toxicity. However, treatment-related deaths did not occur more frequently. Quality of life often improved in the arm with an additional agent.
Authors' conclusions: People who receive more chemotherapeutic or targeted therapeutic agents have an increased overall survival compared to people who receive less. These agents, administered as both first-line or second-line treatments, also led to better overall survival than best supportive care. With the exception of ramucirumab, it remains unclear which other individual agents cause the survival benefit. Although treatment-associated toxicities of grade 3 or more occurred more frequently in arms with an additional chemotherapy or targeted therapy agent, there is no evidence that palliative chemotherapy and/or targeted therapy decrease quality of life. Based on this meta-analysis, palliative chemotherapy and/or targeted therapy can be considered standard care for esophageal and gastroesophageal junction carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
VTJ: none known.
EWS: none known.
AvdG: none known.
RHJM: none known.
MJB: none known.
MPP: none known.
EJK: none known.
MCWS: none known.
Figures



















Update of
-
WITHDRAWN: Chemotherapy for metastatic carcinoma of the esophagus and gastro-esophageal junction.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 May 12;(5):CD004063. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004063.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 28;11:CD004063. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004063.pub4. PMID: 20464727 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Ajani 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ajani JA, Fodor MB, Tjulandin SA, Moiseyenko VM, Chao Y, Cabral Filho S, et al. Phase II multi‐institutional randomized trial of docetaxel plus cisplatin with or without fluorouracil in patients with untreated, advanced gastric, or gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(24):5660‐7. - PubMed
Ajani 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ajani JA, Buyse M, Lichinitser M, Gorbunova V, Bodoky G, Douillard JY, et al. Combination of cisplatin/S‐1 in the treatment of patients with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: results of noninferiority and safety analyses compared with cisplatin/5‐fluorouracil in the First‐Line Advanced Gastric Cancer Study. European Journal of Cancer 2013;49(17):3616‐24. - PubMed
-
- Ajani JA, Rodriguez W, Bodoky G, Moiseyenko V, Lichinitser M, Gorbunova V, et al. Multicenter phase III comparison of cisplatin/S‐1 with cisplatin/infusional fluorouracil in advanced gastric or gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma study: the FLAGS trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2010;28(9):1547‐53. - PubMed
-
- Bodoky G, Scheulen ME, Rivera F, Jassem J, Carrato A, Moiseyenko V, et al. Clinical benefit and health‐related quality of life assessment in patients treated with cisplatin/S‐1 versus Cisplatin/5‐FU: secondary end point results from the first‐line advanced gastric cancer study (FLAGS). Journal of Gastrointestinal Cancer 2015;46(2):109‐17. - PubMed
Al‐Batran 2008 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Batran SE, Hartmann JT, Probst S, Schmalenberg H, Hollerbach S, Hofheinz R, et al. Phase III trial in metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with fluorouracil, leucovorin plus either oxaliplatin or cisplatin: a study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2008;26(9):1435‐42. - PubMed
Al‐Batran 2013 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Batran SE, Pauligk C, Homann N, Hartmann JT, Moehler M, Probst S, et al. The feasibility of triple‐drug chemotherapy combination in older adult patients with oesophagogastric cancer: a randomised trial of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie (FLOT65+). European Journal of Cancer 2013;49(4):835‐42. - PubMed
Bang 2010 {published data only}
-
- Bang YJ, Cutsem E, Feyereislova A, Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, et al. Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2‐positive advanced gastric or gastro‐oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): a phase 3, open‐label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2010;376(9742):687‐97. - PubMed
-
- Sawaki A, Ohashi Y, Omuro Y, Satoh T, Hamamoto Y, Boku N, et al. Efficacy of trastuzumab in Japanese patients with HER2‐positive advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: a subgroup analysis of the Trastuzumab for Gastric Cancer (ToGA) study. Gastric Cancer 2012;15(3):313‐22. - PMC - PubMed
Bleiberg 1997 {published data only}
-
- Bleiberg H, Conroy T, Paillot B, Lacave AJ, Blijham G, Jacob JH, et al. Randomised phase II study of cisplatin and 5‐fluorouracil (5‐Fu) versus cisplatin alone in advanced squamous cell oesophageal cancer. European Journal of Cancer 1997;33(8):1216‐20. - PubMed
Cunningham 2008 {published data only}
-
- Cunningham D, Starling N, Rao S, Iveson T, Nicolson M, Coxon F, et al. Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;358(1):36‐46. - PubMed
-
- Sumpter K, Harper‐Wynne C, Cunningham D, Rao S, Tebbutt N, Norman AR, et al. Report of two protocol planned interim analyses in a randomised multicentre phase III study comparing capecitabine with fluorouracil and oxaliplatin with cisplatin in patients with advanced oesophagogastric cancer receiving ECF. British Journal of Cancer 2005;92(11):1976‐83. - PMC - PubMed
Dank 2008 {published data only}
-
- Curran D, Pozzo C, Zaluski J, Dank M, Barone C, Valvere V, et al. Quality of life of palliative chemotherapy naive patients with advanced adenocarcinoma of the stomach or esophagogastric junction treated with irinotecan combined with 5‐fluorouracil and folinic acid: results of a randomised phase III trial. Quality of Life Research 2009;18(7):853‐61. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dank M, Zaluski J, Barone C, Valvere V, Yalcin S, Peschel C, et al. Randomized phase III study comparing irinotecan combined with 5‐fluorouracil and folinic acid to cisplatin combined with 5‐fluorouracil in chemotherapy naive patients with advanced adenocarcinoma of the stomach or esophagogastric junction. Annals of Oncology 2008;19(8):1450‐7. - PubMed
Duffour 2006 {published data only}
-
- Duffour J, Bouche O, Rougier P, Milan C, Bedenne L, Seitz JF, et al. Safety of cisplatin combined with continuous 5‐FU versus bolus 5‐FU and leucovorin, in metastatic gastrointestinal cancer (FFCD 9404 randomised trial). Anticancer Research 2006;26(5 B):3877‐83. - PubMed
Dutton 2014 {published data only}
-
- Dutton SJ, Ferry DR, Blazeby JM, Abbas H, Dahle‐Smith A, Mansoor W, et al. Gefitinib for oesophageal cancer progressing after chemotherapy (COG): aA phase 3, multicentre, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled randomised trial. Lancet Oncology 2014;15(8):894‐904. - PubMed
Eatock 2013 {published data only}
-
- Eatock MM, Tebbutt NC, Bampton CL, Strickland AH, Valladares‐Ayerbes M, Swieboda‐Sadlej A, et al. Phase II randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of AMG 386 (trebananib) in combination with cisplatin and capecitabine in patients with metastatic gastro‐oesophageal cancer. Annals of Oncology 2013;24(3):710‐8. - PubMed
Ezdinli 1980 {published data only}
-
- Ezdinli EZ, Gelber R, Desai DV, Falkson G, Moertel CG, Hahn RG. Chemotherapy of advanced esophageal carcinoma. Cancer 1980;46(10):2149‐53. - PubMed
Ford 2014 {published data only}
-
- Ford HER, Marshall A, Bridgewater JA, Janowitz T, Coxon FY, Wadsley J, et al. Docetaxel versus active symptom control for refractory oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma (COUGAR‐02): an open‐label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncology 2014;15(1):78‐86. - PubMed
Fuchs 2014 {published data only}
-
- Fuchs CS, Tomasek J, Yong CJ, Dumitru F, Passalacqua R, Goswami C, et al. Ramucirumab monotherapy for previously treated advanced gastric or gastro‐oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (REGARD): an international, randomised, multicentre, placebo‐controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2014;383(9911):31‐9. - PubMed
-
- Muro K, Cho JY, Bodoky G, Goswami C, Chao Y, Dos Santos LV, et al. Efficacy and safety of ramucirumab (RAM) for metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma across age subgroups in two global phase 3 trials. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2017 Feb [Epub ahead of print]; Vol. 35, issue 4 Suppl 3. [DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.35.4_suppl.3] - DOI
Huang 2009 {published data only}
-
- Huang JY, Sun Y, Fan QX, Zhang YQ. Efficacy of Shenyi Capsule combined with gemcitabine plus cisplatin in treatment of advanced esophageal cancer: A randomized controlled trial. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine 2009;7(11):1047‐51. - PubMed
Iveson 2014 {published data only}
-
- Iveson T, Donehower RC, Davidenko I, Tjulandin S, Deptala A, Harrison M, et al. Rilotumumab in combination with epirubicin, cisplatin, and capecitabine as first‐line treatment for gastric or oesophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma: an open‐label, dose de‐escalation phase 1b study and a double‐blind, randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncology 2014;15(9):1007‐18. - PubMed
Levard 1998 {published data only}
-
- Levard H, Pouliquen X, Hay J‐M, Fingerhut A, Langlois‐Zantain O, Huguier M, et al. 5‐Fluorouracil and cisplatin as palliative treatment of advanced oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. European Journal of Surgery 1998;164(11):849‐57. - PubMed
-
- Pouliquen X, Levard H, Hay J‐M, McGee K, Fingerhut A, Langlois‐Zantin O. 5‐Fluorouracil and cisplatin therapy after palliative surgical resection of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. A multicenter randomized trial. French Associations for Surgical Research. Annals of Surgery 1996;223(2):127. - PMC - PubMed
Li 2002 {published data only}
-
- Li Q, Feng FY, Han J, Sui GJ, Zhu YG, Zhang Y, et al. Phase III clinical study of a new anticancer drug atofluding. Ai Zheng 2002;21(12):1350‐3. - PubMed
Lordick 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lordick F, Kang YK, Chung HC, Salman P, Oh SC, Bodoky G, et al. Capecitabine and cisplatin with or without cetuximab for patients with previously untreated advanced gastric cancer (EXPAND): a randomised, open‐label phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncology 2013;14(6):490‐9. - PubMed
Lorenzen 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lorenzen S, Schuster T, Porschen R, Al‐Batran SE, Hofheinz R, Thuss‐Patience P, et al. Cetuximab plus cisplatin‐5‐fluorouracil versus cisplatin‐5‐fluorouracil alone in first‐line metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: a randomized phase II study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. Annals of Oncology 2009;20(10):1667‐73. - PubMed
Lorenzen 2015 {published data only}
-
- Lorenzen S, Riera Knorrenschild J, Haag GM, Pohl M, Thuss‐Patience P, Bassermann F, et al. Lapatinib versus lapatinib plus capecitabine as second‐line treatment in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2‐amplified metastatic gastro‐oesophageal cancer: a randomised phase II trial of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. European Journal of Cancer 2015;51(5):569‐76. - PubMed
Moehler 2010 {published data only}
-
- Moehler M, Kanzler S, Geissler M, Raedle J, Ebert MP, Daum S, et al. A randomized multicenter phase II study comparing capecitabine with irinotecan or cisplatin in metastatic adenocarcinoma of the stomach or esophagogastric junction. Annals of Oncology 2010;21(1):71‐7. - PubMed
Nicolaou 1982 {published data only}
-
- Nicolaou N, Conlan AA. Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin and celetin intubation for inoperable oesophageal carcinoma. South African Medical Journal 1982;61(12):428‐31. - PubMed
Ohtsu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Ohtsu A, Shah MA, Cutsem E, Rha SY, Sawaki A, Park SR, et al. Bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy as first‐line therapy in advanced gastric cancer: a randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled phase III study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2011 2011;29(30):3968‐76. - PubMed
Pang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Pang LN, Wang F, He W, Zhou R, Cao L, Fan QX. Efficacy and safety of S‐1 or fluorouracil combined with cisplatin in treatment of advanced esophagus cancer. World Chinese Journal of Digestology 2014;22(3):383‐8.
Pozzo 2004 {published data only}
-
- Pozzo C, Barone C, Szanto J, Padi E, Peschel C, Bukki J, et al. Irinotecan in combination with 5‐fluorouracil and folinic acid or with cisplatin in patients with advanced gastric or esophageal‐gastric junction adenocarcinoma: results of a randomized phase II study. Annals of Oncology 2004;15(12):1773‐81. - PubMed
Rao 2010 {published data only}
-
- Rao S, Starling N, Cunningham D, Sumpter K, Gilligan D, Ruhstaller T, et al. Matuzumab plus epirubicin, cisplatin and capecitabine (ECX) compared with epirubicin, cisplatin and capecitabine alone as first‐line treatment in patients with advanced oesophago‐gastric cancer: a randomised, multicentre open‐label phase II study. Annals of Oncology 2010;21(11):2213‐9. - PubMed
Richards 2013 {published data only}
-
- Richards D, Kocs DM, Spira AI, David McCollum A, Diab S, Hecker LI, et al. Results of docetaxel plus oxaliplatin (DOCOX) (plus or minus) cetuximab in patients with metastatic gastric and/or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma: results of a randomised phase 2 study. European Journal of Cancer 2013;49(13):2823‐31. - PubMed
Ross 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ross P, Nicolson M, Cunningham D, Valle J, Seymour M, Harper P, et al. Prospective randomized trial comparing mitomycin, cisplatin, and protracted venous‐infusion fluorouracil (PVI 5‐FU) with epirubicin, cisplatin, and PVI 5‐FU in advanced esophagogastric cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2002;20(8):1996‐2004. - PubMed
Roy 2012 {published data only}
Shen 2014 {published data only}
-
- Shen L, Li J, Xu J, Pan H, Dai G, Qin S, et al. Bevacizumab plus capecitabine and cisplatin in Chinese patients with inoperable locally advanced or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer: randomized, double‐blind, phase III study (AVATAR study). Gastric Cancer 2014;18(1):168‐76. - PMC - PubMed
Tebbutt 2002 {published data only}
-
- Tebbutt NC, Norman A, Cunningham D, Iveson T, Seymour M, Hickish T, et al. A muticentre, randomised phase III trial comparing protracted venous infusion (PVI) 5‐fluorouracil (5‐FU) with PVI 5‐FU plus mitomycin C in patients with inoperable oesophago‐gastric cancer. Annals of Oncology 2002;13(10):1568‐75. - PubMed
Tebbutt 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tebbutt NC, Cummins MM, Sourjina T, Strickland A, Hazel G, Ganju V, et al. Randomised, non‐comparative phase II study of weekly docetaxel with cisplatin and 5‐fluorouracil or with capecitabine in oesophagogastric cancer: the AGITG ATTAX trial. British Journal of Cancer 2010;102(3):475‐81. - PMC - PubMed
Thuss‐Patience 2011 {published data only}
Van Cutsem 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ajani JA, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S, Majlis A, Constenla M, Boni C, et al. Clinical benefit with docetaxel plus fluorouracil and cisplatin compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil in a phase III trial of advanced gastric or gastroesophageal cancer adenocarcinoma: the V‐325 study group. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2007;25(22):3205‐9. - PubMed
-
- Ajani JA, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S, Majlis A, Constenla M, Boni C, et al. Quality of life with docetaxel plus cisplatin and fluorouracil compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil from a phase III trial for advanced gastric or gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: the V‐325 study group. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2007;25(22):3210‐6. - PubMed
-
- Cutsem E, Moiseyenko VM, Tjulandin S, Majlis A, Constenla M, Boni C, et al. Phase III study of docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first‐line therapy for advanced gastric cancer: a report of the V325 study group. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2006 Nov;24(31):4991‐7. - PubMed
Van Cutsem 2015 {published data only}
-
- Cutsem E, Boni C, Tabernero J, Massuti B, Middleton G, Dane F, et al. Docetaxel plus oxaliplatin with or without fluorouracil or capecitabine in metastatic or locally recurrent gastric cancer: a randomized phase II study. Annals of Oncology 2015;26(1):149‐56. - PubMed
Waddell 2013 {published data only}
-
- Waddell TS, Chau I, Barbachano Y, Castro DG, Wotherspoon A, Saffery C, et al. A randomized multicenter trial of epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and capecitabine (EOC) plus panitumumab in advanced esophagogastric cancer (REAL3). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2012;30(6):18.
-
- Waddell TS, Chau I, Peckitt C, Gonzalez D, Wotherspoon A, Patel B, et al. Quality of life (QoL) analysis from the randomized phase III REAL3 trial of epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and capecitabine (EOC) with or without panitumumab (P) in advanced esophagogastric adenocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2014;32(15):4067.
Waters 1999 {published data only}
-
- Webb A, Cunningham D, Scarffe JH, Harper P, Norman A, Joffe JK, et al. Randomized trial comparing epirubicin, cisplatin, and fluorouracil versus fluorouracil, doxorubicin, and methotrexate in advanced esophagogastric cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 1997;15(1):261‐7. - PubMed
Wilke 2014 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Batran SE, Cutsem E, Oh SC, Bodoky G, Shimada Y, Hironaka S, et al. Quality‐of‐life and performance status results from the phase III RAINBOWstudy of ramucirumab plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel in patients with previously treated gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. Annals of Oncology 2016;27(4):673‐9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Muro K, Cho JY, Bodoky G, Goswami C, Chao Y, Dos Santos LV, et al. Efficacy and safety of ramucirumab (RAM) for metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma across age subgroups in two global phase 3 trials. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2017 Feb [Epub ahead of print]; Vol. 35, issue 4 Suppl 3. [DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.35.4_suppl.3] - DOI
-
- Muro K, Oh SC, Shimada Y, Lee KW, Yen CJ, Chao Y, et al. Subgroup analysis of East Asians in RAINBOW: A phase 3 trial of ramucirumab plus paclitaxel for advanced gastric cancer. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2016;31(3):581‐9. - PubMed
-
- Shitara K, Muro K, Shimada Y, Hironaka S, Sugimoto N, Komatsu Y, et al. Subgroup analyses of the safety and efficacy of ramucirumab in Japanese and Western patients in RAINBOW: a randomized clinical trial in second‐line treatment of gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2016;19(3):927‐38. - PubMed
-
- Wilke H, Muro K, Cutsem E, Oh SC, Bodoky G, Shimada Y, et al. Ramucirumab plus paclitaxel versus placebo plus paclitaxel in patients with previously treated advanced gastric or gastro‐oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (RAINBOW): a double‐blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncology 2014;15(11):1224‐35. - PubMed
Wilkes 2011 {published data only}
-
- Wilkes EA, Selby AL, Cole AT, Freeman JG, Rennie MJ, Khan ZH. Poor tolerability of thalidomide in end‐stage oesophageal cancer. European Journal of Cancer Care 2011;20(5):593‐600. - PubMed
Xu 2013a {published data only}
-
- Xu Z, Chen J, Tao M. Nimotuzumab combined with cisplatin and 5‐FU in treatment of patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Journal of Practical Oncology 2013;28(6):650‐3.
References to studies excluded from this review
Adenis 2010 {published data only}
-
- Adenis A, Penel N, Horn S, Dominguez S, Vanhuyse M, Mirabel X. Palliative chemotherapy does not improve survival in metastatic esophageal cancer. Oncology 2010;79(1‐2):46‐54. - PubMed
Al‐Batran 2010 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Batran SE, Ajani JA. Impact of chemotherapy on quality of life in patients with metastatic esophagogastric cancer. Cancer 2010;116(11):2511‐8. - PubMed
Albertsson 2007 {published data only}
-
- Albertsson M, Johansson B, Friesland S, Kadar L, Letocha H, Frykholm G, et al. Phase II studies on docetaxel alone every third week, or weekly in combination with gemcitabine in patients with primary locally advanced, metastatic, or recurrent esophageal cancer. Medical Oncology (Northwood, London, England) 2007;24(4):407‐12. - PubMed
Boku 2009 {published data only}
-
- Boku N, Yamamoto S, Fukuda H, Shirao K, Doi T, Sawaki A, et al. Fluorouracil versus combination of irinotecan plus cisplatin versus S‐1 in metastatic gastric cancer: a randomised phase 3 study. Lancet Oncology 2009;10(11):1063‐9. - PubMed
Brell 2009 {published data only}
Burris 2017 {published data only}
-
- Burris HA, Kurkjian CD, Hart L, Pant S, Murphy PB, Jones SF, et al. TAK‐228 (formerly MLN0128), an investigational dual TORC1/2 inhibitor plus paclitaxel, with/without trastuzumab, in patients with advanced solid malignancies. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology 2017;80(2):261‐73. - PubMed
Cascinu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Cascinu S, Galizia E, Labianca R, Ferrau F, Pucci F, Silva RR, et al. Pegylated liposomal doxorubicin, 5‐fluorouracil and cisplatin versus mitomycin‐C, 5‐fluorouracil and cisplatin for advanced gastric cancer: a randomized phase II trial. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology 2011;68(1):37‐43. - PubMed
Du 2015 {published data only}
Eichhorst 2016 {published data only}
-
- Eichhorst B, Fink AM, Bahlo J, Busch R, Kovacs G, Maurer C, et al. First‐line chemoimmunotherapy with bendamustine and rituximab versus fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab in patients with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL10): an international, open‐label, randomised, phase 3, non‐inferiority trial. Lancet Oncology 2016;17(7):928‐42. - PubMed
Font 2008 {published data only}
-
- Font A, Salazar R, Maurel J, Taron M, Ramirez JL, Tabernero J, et al. Cisplatin plus weekly CPT‐11/docetaxel in advanced esophagogastric cancer: a phase I study with pharmacogenetic assessment of XPD, XRCC3 and UGT1A1 polymorphisms. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology 2008;62(6):1075‐83. - PubMed
Grunberger 2007 {published data only}
-
- Grunberger B, Raderer M, Schmidinger M, Hejna M. Palliative chemotherapy for recurrent and metastatic esophageal cancer. Anticancer Research 2007;27(4 C):2705‐14. - PubMed
Gubanski 2010 {published data only}
-
- Gubanski M, Johnsson A, Fernebro E, Kadar L, Karlberg I, Flygare P, et al. Randomized phase II study of sequential docetaxel and irinotecan with 5‐fluorouracil/folinic acid (leucovorin) in patients with advanced gastric cancer: the GATAC trial. Gastric Cancer 2010;13(3):155‐61. - PubMed
Gubanski 2014 {published data only}
-
- Gubanski M, Glimelius B, Lind PA. Quality of life in patients with advanced gastric cancer sequentially treated with docetaxel and irinotecan with 5‐fluorouracil and folinic acid (leucovin). Medical Oncology (Northwood, London) 2014;31(4):906. - PubMed
Hironaka 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hironaka S, Ueda S, Yasui H, Nishina T. Randomized, open‐label, phase III study comparing irinotecan with paclitaxel in patients with advanced gastric cancer without severe peritoneal metastasis after failure of prior combination chemotherapy using fluoropyrimidine plus platinum: WJOG 4007 trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2013;31(35):4438‐44. - PubMed
Horgan 2011 {published data only}
Ilhan‐Mutlu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Ilhan‐Mutlu A, Preusser M, Schoppmann SF, Asari R, Ba‐Ssalamah A, Schwameis K, et al. Comparison between DCF (Docetaxel, Cisplatin and 5‐Fluorouracil) and modified EOX (Epirubicin, Oxaliplatin and Capecitabine) as palliative first‐line chemotherapy for adenocarcinoma of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Anticancer Research 2013;33(8):3455‐9. - PubMed
Imazawa 2009 {published data only}
-
- Imazawa M, Kojima T, Boku N, Onozawa Y, Hironaka S, Fukutomi A, et al. Efficacy of sequential methotrexate and 5‐fluorouracil (MTX/5FU) in improving oral intake in patients with advanced gastric cancer with severe peritoneal dissemination. Gastric Cancer 2009;12(3):153‐7. - PubMed
Jeung 2011 {published data only}
-
- Jeung HC, Rha SY, Im CK, Shin SJ, Ahn JB, Yang WI, et al. A randomized phase 2 study of docetaxel and S‐1 versus docetaxel and cisplatin in advanced gastric cancer with an evaluation of SPARC expression for personalized therapy. Cancer 2011 May 15;117(10):2050‐7. - PubMed
Kang 2009 {published data only}
-
- Kang YK, Kang WK, Shin DB, Chen J, Xiong J, Wang J, et al. Capecitabine/cisplatin versus 5‐fluorouracil/cisplatin as first‐line therapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer: a randomised phase III noninferiority trial. Annals of Oncology 2009;20(4):666‐73. - PubMed
Kerkar 2009 {published data only}
Kim 2014 {published data only}
-
- Kim YS, Sym SJ, Park SH, Park I, Hong J, Ahn HK, et al. A randomized phase II study of weekly docetaxel/cisplatin versus weekly docetaxel/oxaliplatin as first‐line therapy for patients with advanced gastric cancer. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology 2014;73(1):163‐9. - PubMed
Koizumi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Koizumi W, Tanabe S, Azuma M, Ishido K, Nishimura K, Sasaki T, et al. Impacts of fluorouracil‐metabolizing enzymes on the outcomes of patients treated with S‐1 alone or S‐1 plus cisplatin for first‐line treatment of advanced gastric cancer. International Journal of Cancer [Journal International du Cancer] 2010;126(1):162‐70. - PubMed
Koizumi 2014 {published data only}
Komatsu 2011 {published data only}
-
- Komatsu Y, Takahashi Y, Kimura Y, Oda H, Tajima Y, Tamura S, et al. Randomized phase II trial of first‐line treatment with tailored irinotecan and S‐1 therapy versus S‐1 monotherapy for advanced or recurrent gastric carcinoma (JFMC31‐0301). Anticancer Drugs 2011;22(6):576‐83. - PubMed
Konings 2010 {published data only}
-
- Konings IR, Gaast A, Wijk LJ, Jongh FE, Eskens FA, Sleijfer S. The addition of pravastatin to chemotherapy in advanced gastric carcinoma: a randomised phase II trial. European Journal of Cancer 2010;46(18):3200‐4. - PubMed
Le Tourneau 2015 {published data only}
-
- Tourneau C, Delord JP, Gonçalves A, Gavoille C, Dubot C, Isambert N, et al. Molecularly targeted therapy based on tumour molecular profiling versus conventional therapy for advanced cancer (SHIVA): A multicentre, open‐label, proof‐of‐concept, randomised, controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncology 2015;16(13):1324‐34. - PubMed
Li 2011 {published data only}
Lim 2010 {published data only}
Lim 2017 {published data only}
-
- Lim SH, Shim YM, Park SH, Kim HK, Choi YS, Ahn MJ, et al. A randomized phase II study of leucovorin/5‐fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin (LV5FU2 vs. FOLFOX) for curatively‐resected, node‐positive esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Research and Treatment 2017;49(3):816‐23. - PMC - PubMed
Lissoni 2009 {published data only}
-
- Lissoni P, Rovelli F, Brivio F, Zago R, Colciago M, Messina G, et al. A randomized study of chemotherapy versus biochemotherapy with chemotherapy plus Aloe arborescens in patients with metastatic cancer. In Vivo 2009;23(1):171‐5. - PubMed
Lu 2014 {published data only}
-
- Lu YM, Liu ZC, Zhang J. S‐1 plus oxaliplatin vs. S‐1 as first‐line treatment in patients with previously untreated advanced gastric cancer: a randomized phase II study. Journal of Chemotherapy (Florence) 2014;26(3):159‐64. - PubMed
Lundholm 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lundholm K, Gunnebo L, Korner U, Iresjo BM, Engstrom C, Hyltander A, et al. Effects by daily long term provision of ghrelin to unselected weight‐losing cancer patients: a randomized double‐blind study. Cancer 2010;116(8):2044‐52. - PubMed
Lustberg 2010 {published data only}
-
- Lustberg MB, Bekaii‐Saab T, Young D, Otterson G, Burak W, Abbas A, et al. Phase II randomized study of two regimens of sequentially administered mitomycin C and irinotecan in patients with unresectable esophageal and gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2010;5(5):713‐8. - PMC - PubMed
Macedo 2009 {published data only}
-
- Macedo A, Pereira C, Goncalves J, Sousa C. Economic evaluation of capecitabine use as first line treatment in patients with advanced gastric carcinoma in Portugal. Acta Medica Portuguesa 2009;22(6):827‐32. - PubMed
Mizota 2011 {published data only}
-
- Mizota A, Shitara K, Kondo C, Nomura M, Yokota T, Takahari D, et al. A retrospective comparison of docetaxel and paclitaxel for patients with advanced or recurrent esophageal cancer who previously received platinum‐based chemotherapy. Oncology (Switzerland) 2011;81(3‐4):237‐42. - PubMed
Moehler 2016b {published data only}
-
- Moehler M, Gepfner‐Tuma I, Maderer A, Thuss‐Patience PC, Ruessel J, Hegewisch‐Becker S, et al. Sunitinib added to FOLFIRI versus FOLFIRI in patients with chemorefractory advanced adenocarcinoma of the stomach or lower esophagus: A randomized, placebo‐controlled phase II AIO trial with serum biomarker program. BMC Cancer 2016;16(1):699. [DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2736-9] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Moon 2010 {published data only}
-
- Moon YW, Rha SY, Jeung HC, Kim C, Hong MH, Chang H, et al. Outcomes of multiple salvage chemotherapy for advanced gastric cancer: implications for clinical practice and trial design. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology 2010;66(4):797‐805. - PubMed
Nakashima 2008 {published data only}
-
- Nakashima K, Hironaka S, Boku N, Onozawa Y, Fukutomi A, Yamazaki K, et al. Irinotecan plus cisplatin therapy and S‐1 plus cisplatin therapy for advanced or recurrent gastric cancer in a single institution. Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology 2008;38(12):810‐5. - PubMed
Narahara 2011 {published data only}
Ochenduszko 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ochenduszko S, Konopka K, Puskulluoglu M, Urbanczyk K, Budzynski A, Matlok M, et al. Comparison of efficacy and tolerance of first‐line palliative chemotherapy EOX and mDCF regimens in patients with locally advanced inoperable or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma without overexpression of HER2 receptors. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2015;33(3 Suppl):135. - PMC - PubMed
Ohtsu 2013 {published data only}
Ojima 2016 {published data only}
-
- Ojima T, Nakamori M, Nakamura M, Katsuda M, Hayata K, Kato T, et al. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy with divided‐dose docetaxel, cisplatin and fluorouracil for patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Anticancer Research 2016;36(2):829‐34. - PubMed
Okines 2008 {published data only}
-
- Okines AFC, Norman AR, McCloud PI, Kang Y, Cunningham D. Meta‐analysis of the real 2 and ML17032 trials comparing capecitabine with 5‐fluorouracil (5‐Fu) in advanced oesophago‐gastric cancer. Annals of Oncology 2008;19(S8):viii169. - PubMed
Okines 2010a {published data only}
-
- Okines AFC, Ashley SE, Cunningham D, Oates J, Turner A, Webb J, et al. Epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and capecitabine with or without panitumumab for advanced esophagogastric cancer: Dose‐finding study for the prospective multicenter, randomized, phase II/III REAL‐3 trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2010;28(25):3945‐50. - PubMed
Okines 2010b {published data only}
-
- Okines AFC, Asghar U, Cunningham D, Ashley S, Ashton J, Jackson K, et al. Rechallenge with platinum plus fluoropyrimidine +/‐ Epirubicin in patients with oesophagogastric cancer. Oncology (Switzerland) 2010;79(1‐2):150‐8. - PubMed
Park 2006 {published data only}
-
- Park SH, Lee WK, Chung M, Lee Y, Han SH, Bang SM, et al. Paclitaxel versus docetaxel for advanced gastric cancer: a randomized phase II trial in combination with infusional 5‐fluorouracil. Anti‐cancer Drugs 2006;17(2):225‐9. - PubMed
Park 2014 {published data only}
-
- Park JW, Yoon J, Cho CK, Lee YW, Yoo HS. Survival analysis of stage IV metastatic gastric cancer patients treated with HangAm‐Plus. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine 2014;20(1):49‐55. - PubMed
Roth 2007 {published data only}
-
- Roth AD, Fazio N, Stupp R, Falk S, Bernhard J, Saletti P, et al. Docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil; Docetaxel and cisplatin; and epirubicin, cisplatin, and fluorouracil as systemic treatment for advanced gastric carcinoma: A randomized phase II trial of the Swiss Group for Clinical Cancer Research. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2007;25(22):3217‐23. - PubMed
Sadighi 2006 {published data only}
Sakamoto 2010 {published data only}
-
- Sakamoto T, Yasui H, Boku N, Onozawa Y, Hironaka S, Fukutomi A, et al. Comparison of combination chemotherapy with irinotecan and cisplatin regimen administered every 2 or 4 weeks in pretreated patients with unresectable or recurrent gastric cancer: retrospective analysis. International Journal of Clinical Oncology 2010;15(3):287‐93. - PubMed
Satoh 2014 {published data only}
-
- Satoh T, Xu RH, Chung HC, Sun GP, Doi T. Lapatinib plus paclitaxel versus paclitaxel alone in the second‐line treatment of HER2‐amplified advanced gastric cancer in Asian populations: TyTAN—a randomized, phase III study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2014;32(19):2039‐49. - PubMed
Satoh 2015 {published data only}
Seol 2009 {published data only}
-
- Seol YM, Song MK, Choi YJ, Kim GH, Shin HJ, Song GA, et al. Oral fluoropyrimidines (capecitabine or S‐1) and cisplatin as first line treatment in elderly patients with advanced gastric cancer: a retrospective study. Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology 2009;39(1):43‐8. - PubMed
Sgourakis 2012 {published data only}
Shenfine 2009 {published data only}
-
- Shenfine J, McNamee P, Steen N, Bond J, Griffin SM. A randomized controlled clinical trial of palliative therapies for patients with inoperable esophageal cancer. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2009;104(7):1674‐85. - PubMed
Shirao 2013 {published data only}
-
- Shirao K, Boku N, Yamada Y, Yamaguchi K, Doi T, Goto M, et al. Randomized phase III study of 5‐fluorouracil continuous infusion vs. sequential methotrexate and 5‐fluorouracil therapy in far advanced gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis (JCOG0106). Japanese Journal of Clinical Oncology 2013;43(10):972‐80. - PubMed
Shitara 2011 {published data only}
-
- Shitara K, Matsuo K, Mizota A, Kondo C, Nomura M, Takahari D, et al. Association of fluoropyrimidines, platinum agents, taxanes, and irinotecan in any line of chemotherapy with survival in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2011;14(2):155‐60. - PubMed
Shu 2017 {published data only}
-
- Shu ZB, Ding DY, Li YC. Adjuvant chemotherapy for chemotherapy‐naive advanced gastric cancer patients with oxaliplatin plus tegafur versus oxaliplatin plus S‐1. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2017;10(6):9322‐9.
Sun 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sun J, Sheng ZJ. Clinical study on efficacy of Aidi injection combined with PT chemotherapy protocol in advanced esophageal cancer patients. Cancer Research and Clinic 2013;25(8):547‐9.
Takashima 2010 {published data only}
Tanaka 2010 {published data only}
-
- Tanaka T, Fujita H, Matono S, Nagano T, Nishimura K, Murata K, et al. Outcomes of multimodality therapy for stage IVB esophageal cancer with distant organ metastasis (M1‐Org). Diseases of the Esophagus 2010;23(8):646‐51. - PubMed
Thuss‐Patience 2005 {published data only}
-
- Thuss‐Patience PC, Kretzschmar A, Repp M, Kingreen D, Hennesser D, Micheel S, et al. Docetaxel and continuous‐infusion fluorouracil versus epirubicin, cisplatin, and fluorouracil for advanced gastric adenocarcinoma: a randomized phase II study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2005;23(3):494‐501. - PubMed
Whistance 2011 {published data only}
-
- Whistance RN, Blazeby JM. Systematic review: quality of life after treatment for upper gastrointestinal cancer. Current Opinion in Supportive and Palliative Care 2011;5(1):37‐46. - PubMed
Xu 2013b {published data only}
-
- Xu Y, Zhao AG, Li ZY, Zhao G, Cai Y, Zhu XH, et al. Survival benefit of traditional Chinese herbal medicine (a herbal formula for invigorating spleen) for patients with advanced gastric cancer. Integrative Cancer Therapies 2013;12(5):414‐22. - PubMed
Yamada 2015 {published data only}
-
- Yamada Y, Higuchi K, Nishikawa K, Gotoh M, Fuse N, Sugimoto N, et al. Phase III study comparing oxaliplatin plus S‐1 with cisplatin plus S‐1 in chemotherapy‐naive patients with advanced gastric cancer. Annals of Oncology 2015;26(1):141‐8. - PubMed
Yamazaki 2008 {published data only}
-
- Yamazaki K, Hironaka S, Boku N, Yasui H, Fukutomi A, Yoshino T, et al. A retrospective study of second‐line chemotherapy for unresectable or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus refractory to chemotherapy with 5‐fluorouracil plus platinum. International Journal of Clinical Oncology 2008;13(2):150‐5. - PubMed
Yu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Yu J, Wang BH, Zhang XZ. Clinical study of paclitaxel plus nedaplatin versus paclitaxel plus cisplatin in treatment of patients with advanced esophageal carcinoma. Chinese Journal of Cancer Prevention and Treatment 2010;17(9):693‐5.
Yun 2010 {published data only}
-
- Yun J, Lee J, Park SH, Park JO, Park YS, Lim HY, et al. A randomised phase II study of combination chemotherapy with epirubicin, cisplatin and capecitabine (ECX) or cisplatin and capecitabine (CX) in advanced gastric cancer. European Journal of Cancer 2010;46(5):885‐91. - PubMed
Zhang 2006 {published data only}
-
- Zhang P, Feng FY, Wu LY, Hu Y, Liu JW, Gao YJ, et al. Phase II multicenter clinical trial of nedaplatin in the treatment of malignant tumors. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2006;28(3):230‐4. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Ajani 2017 {published data only}
-
- Ajani JA, Abramov M, Bondarenko I, Shparyk Y, Gorbunova V, Hontsa A, et al. A phase III trial comparing oral S‐1/cisplatin and intravenous 5‐fluorouracil/cisplatin in patients with untreated diffuse gastric cancer. Annals of Oncology 2017;28(9):2142‐8. - PubMed
Al‐Batran 2017 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Batran SE, Riera‐Knorrenschild J, Pauligk C, Goetze TO, Hegewisch‐Becker S, Seraphin J, et al. A randomized, double‐blind, multicenter phase III study evaluating paclitaxel with and without RAD001 in patients with gastric cancer who have progressed after therapy with a fluoropyrimidine/platinum‐containing regimen (RADPAC). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2017;35(4 Suppl):4. [DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.35.4_suppl.4] - DOI
Bang 2017 {published data only}
-
- Bang YJ, Cho JY, Kim YH, Kim JW, Bartolomeo M, Ajani JA, et al. Efficacy of sequential ipilimumab monotherapy versus best supportive care for unresectable locally advanced/metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer. Clinical Cancer Research 2017;23(19):5671‐8. - PubMed
Bi 2011 {published data only}
-
- Bi F, Li Q, Zhou C, Yu J, Cai X, Qiu M, et al. Preliminary results of a randomized phase II study: Treatment of Chinese patients with advanced gastric cancer with FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX7 or the reverse sequence. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2011;29(15):Supplement.
Cohen 2013 {published data only}
-
- Cohen DJ, Christos PJ, Kindler HL, Catenacci DVT, Bekaii‐Saab TB, Tahiri S, et al. Vismodegib (V), a hedgehog (HH) pathway inhibitor, combined with FOLFOX for first‐line therapy of patients (pts) with advanced gastric and gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) carcinoma: a New York Cancer Consortium led phase II randomized study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2013;31(15):4011.
Denlinger 2016 {published data only}
-
- Denlinger CS, Maqueda MA, Watkins DJ, Sym SJ, Bendell JC, Park SH, et al. Randomized phase 2 study of paclitaxel (PTX), trastuzumab (T) with or without MM‐111 in HER2 expressing gastroesophageal cancers (GEC). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016;34(15 Suppl):4043.
Enzinger 2016 {published data only}
-
- Enzinger PC, Burtness BA, Niedzwiecki D, Ye X, Douglas K, Ilson DH, et al. CALGB 80403 (Alliance)/E1206: a randomized phase II study of three chemotherapy regimens plus cetuximab in metastatic esophageal and gastroesophageal junction cancers. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016;34(23):2736‐42. - PMC - PubMed
Hall 2017 {published data only}
Hecht 2016 {published data only}
-
- Hecht JR, Bang YJ, Qin SK, Chung HC, Xu JM, Park JO, et al. Lapatinib in combination with capecitabine plus oxaliplatin in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2‐positive advanced or metastatic gastric, esophageal, or gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: TRIO‐013/LOGiC ‐ A randomized phase III trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016;34(5):443‐51. - PubMed
Huang 2016 {published data only}
-
- Huang J, Liu Y, Dai S, Lu P, Ba Y, Wu L, et al. Randomized, open‐label, phase III study comparing irinotecan plus S‐1 with S‐1 alone in patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after failure of prior platinum‐ or taxane‐based chemotherapy: Results of an interim analysis. Annals of Oncology 2016;27(6 Suppl):LBA27. [DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdw435.18] - DOI
Iqbal 2017 {published data only}
-
- Iqbal S, McDonough S, Lenz HJ, Ilson DH, Burtness B, Nangia CS, et al. A randomized phase II pilot study prospectively evaluating treatment for patients based on ERCC1 for advanced/ metastatic esophageal, gastric, or gastroesophageal junction cancer: SWOG S1201. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2017;35(15 Suppl):4009. - PMC - PubMed
Janjigian 2017 {published data only}
-
- Janjigian YY, Bendell JC, Calvo E, Kim JW, Ascierto PA, Sharma P, et al. CheckMate‐032: Phase I/II, open‐label study of safety and activity of nivolumab (nivo) alone or with ipilimumab (ipi) in advanced and metastatic (A/M) gastric cancer (GC). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016;34(14 Suppl):4010.
Kang 2017 {published data only}
-
- Kang YK, Satoh T, Ryu MH, Chao Y, Kato K, Chung HC, et al. Nivolumab (ONO‐4538/BMS‐936558) as salvage treatment after second or later‐line chemotherapy for advanced gastric or gastro‐esophageal junction cancer (AGC): A double‐blinded, randomized, phase III trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2017;35(4 Suppl):2.
Lee 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lee KH, Baba E, Ryu MH, Boku N, Park YI, Hyodo I, et al. Phase III trial of a 3‐weekly vs. 5‐weekly schedule of S‐1 plus cisplatin (SP) combination chemotherapy for first‐line treatment of advanced gastric cancer (AGC): SOS study. European Journal of Cancer 2013;49(14):S614‐5.
Lee 2015 {published data only}
Li 2015 {published data only}
Li 2016a {published data only}
-
- Li J, Qin S, Xu J, Xiong J, Wu C, Bai Y, et al. Randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled phase III trial of apatinib in patients with chemotherapy‐refractory advanced or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016;34(13):1448‐54. - PubMed
Li 2016b {published data only}
-
- Li K, Liu J. Clinical efficacy and safety of nedaplatin combined with paclitaxel liposome in treatment of advanced esophageal cancer. Cancer Research and Clinic 2016;28(11):748‐51. [10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006‐9801.2016.11.007]
Liu 2016 {published data only}
Luelmo 2008 {published data only}
-
- Luelmo S, Polee M, Bochove A, Pruijt H, Ouwerkerk J, Sleeboom H, et al. Randomized phase II study of cisplatin and high dose 5‐fluorouracil/leucovorin or paclitaxel and high‐dose 5‐fluorouracil/leucovorin in locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer and adenocarcinomas of the gastrooesophageal junction. Annals of Oncology 2008;19(S8):viii173‐viii174.
Moehler 2013 {published data only}
-
- Moehler MH, Thuss‐Patience PC, Schmoll HJ, Hegewisch‐Becker S, Wilke H, Al‐Batran SE, et al. FOLFIRI plus sunitinib versus FOLFIRI alone in advanced chemorefractory esophagogastric cancer patients: A randomized placebo‐controlled multicentric AIO phase II trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2013;31(15 Suppl):4086.
Moehler 2016a {published data only}
-
- Moehler MH, Cho JY, Kim YH, Kim JW, Bartolomeo M, Ajani JA, et al. A randomized, open‐label, two‐arm phase II trial comparing the efficacy of sequential ipilimumab (ipi) versus best supportive care (BSC) following first‐line (1L) chemotherapy in patients with unresectable, locally advanced/metastatic (A/M) gastric or gastro‐esophageal junction (G/GEJ) cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016;34(Suppl):4011.
Moehler 2017 {published data only}
-
- Moehler MH, Thuss‐Patience PC, Brenner B, Longo F, Meiler J, Ettrich TJ, et al. Cisplatin/5‐FU (CF) +/‐ panitumumab (P) for patients (pts) with non‐resectable, advanced, or metastatic esophageal squamous cell cancer (ESCC): An open‐label, randomized AIO/TTD/BDGO/EORTC phase III trial (POWER). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2017;35(15 Suppl):4011.
Pavlakis 2015 {published data only}
-
- Pavlakis N, Sjoquist KM, Tsobanis E, Martin AJ, Kang YK, Bang YJ, et al. INTEGRATE: A randomized, phase II, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study of regorafenib in refractory advanced oesophagogastric cancer (AOGC): A study by the Australasian Gastrointestinal Trials Group (AGITG)‐Final overall and subgroup results. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2015;33(15 Suppl):4003.
Ryu 2016 {published data only}
-
- Ryu MH, Park YI, Chung IJ, Lee KW, Oh HS, Lee KH, et al. Phase III trial of s‐1 plus oxaliplatin (SOX) vs s‐1 plus cisplatin (SP) combination chemotherapy for first‐line treatment of advanced gastric cancer (AGC): SOPP study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016;34(15 Suppl):4015.
Sahin 2015 {published data only}
-
- Sahin U, Al‐Batran SE, Hozaeel W, Zvirbule Z, Freiberg‐Richter J, Lordick F, et al. IMAB362 plus zoledronic acid (ZA) and interleukin2 (IL2) in patients (pts) with advanced gastroesophageal cancer (GEC): Clinical activity and safety data from the PILOT phase I trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2015 [Epub ahead of print]; Vol. 33, issue 15 Suppl. [DOI: 10.1200/jco.2015.33.15_suppl.e15079] - DOI
Schuler 2016 {published data only}
-
- Schuler M, Al‐Batran SE, Zvirbule Z, Manikhas G, Lordick F, Rusyn A, et al. Final results of the FAST study, an international, multicenter, randomized, phase II trial of epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and capecitabine (EOX) with or without the anti‐CLDN18.2 antibody IMAB362 as first‐line therapy in patients with advanced CLDN18.2+ gastric and gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma. Annals of Oncology 2016 Oct 11 [Epub ahead of print]; Vol. 27, issue 6 Suppl. [DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdw371.06] - DOI
Shah 2015 {published data only}
-
- Shah MA, Janjigian YY, Stoller R, Shibata S, Kemeny M, Krishnamurthi S, et al. Randomized multicenter phase II study of modified docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil (DCF) versus DCF plus growth factor support in patients with metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma: A study of the US gastric cancer consortium. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2015;33(33):3874‐9. - PubMed
Shah 2016 {published data only}
Shah 2017a {published data only}
Smyth 2011 {published data only}
-
- Smyth EC, Enzinger PC, Li J, Vincitore M, Lacy J, El‐Rayes BF, et al. Bevacizumab (Bev) plus chemotherapy for advanced gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma (GC): combined U.S. experience. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2011;29(15 Suppl):4056.
Song 2016 {published data only}
-
- Song L. Effect of S‐1 maintenance chemotherapy following first‐line regimen in patients with advanced esophageal cancer. Diseases of the Esophagus 2016;29:130A‐131A.
Tebbutt 2013 {published data only}
-
- Tebbutt NC, Price TJ, Sjoquist KM, Veillard AS, Hall M, Ferraro DA, et al. Final results of AGITG ATTAX 3 study: Randomized phase II study of weekly docetaxel (T), cisplatin, and fluoropyrimidine (F) with or without panitumumab (P) in advanced esophagogastric (OG) cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2013;31(15 Suppl):4081.
Tebutt 2016 {published data only}
Thuss‐Patience 2015 {published data only}
-
- Thuss‐Patience PC, Al‐Batran SE, Siveke JT, Homann N, Malfertheiner P, Glaeser D, et al. Pazopanib and 5‐FU/ oxaliplatin as first‐line treatment in advanced gastric cancer: PaFLO, a randomized phase II study from the AIO (Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2015;33(15 Suppl):4033.
Thuss‐Patience 2017 {published data only}
-
- Thuss‐Patience PC, Shah MA, Ohtsu A, Cutsem E, Ajani JA, Castro H, et al. Trastuzumab emtansine versus taxane use for previously treated HER2‐positive locally advanced or metastatic gastric or gastro‐oesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (GATSBY): an international randomised, open‐label, adaptive, phase 2/3 study. Lancet Oncology 2017;18(5):640‐53. - PubMed
Wang 2010 {published data only}
-
- Wang X‐Q, Yang F. Clinical effects of Zhisheng capsule combined with chemotherapy on patients with middle or advanced stage oesophageal cancer. Drugs & Clinic 2010;25(4):297‐9.
Wang 2016 {published data only}
-
- Wang JW, Xu RH, Li J, Bai YX, Liu TS, Jiao SC, et al. Randomized multicenter phase III study of a modified docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil regimen compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first‐line therapy for advanced or locally recurrent gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2016;19(1):234‐44. - PMC - PubMed
Wang 2017 {published data only}
-
- Wang F, Fan QX, Wang HH, Han DM, Song NS, Lu H. Efficacy and safety of Xiaoaiping combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced esophageal cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu za Zhi [Chinese Journal of Oncology] 2017;39(6):453‐7. - PubMed
Wu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Wu J, Long GX. Clinical observation on Aidi injection supplemental to chemotherapy in treatment of advanced oesophageal carcinoma. Journal of Internal Intensive Medicine 2013;19(2):100‐15.
Xie 2016 {published data only}
-
- Xie C, Shi Y, Zhu Z, Li Z, Yu X. The efficacy and adverse reaction of docetaxel combined with oxaliplatin in the treatment of advanced esophageal cancer. Anti‐Tumor Pharma 2016;6(5):361‐5.
Yeh 2012 {published data only}
-
- Yeh KH, Chen JS, Sobrero A, Singhal N, Dosso S, Kang YK, et al. Safety and tolerability data from a phase II study of AUY922 compared with chemotherapy in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Annals of Oncology 2012;23(4):118.
Yoon 2016 {published data only}
-
- Yoon HH, Bendell JC, Braiteh FS, Firdaus I, Philip PA, Cohn AL, et al. Ramucirumab combined with FOLFOX as front‐line therapy for advanced esophageal, gastroesophageal junction, or gastric adenocarcinoma: a randomized, double‐blind, multicenter Phase II trial. Annals of Oncology 2016;27(12):2196‐203. - PMC - PubMed
Zaanan 2015 {published data only}
-
- Zaanan A, Bennouna J, Hiret S, Douillard JY, Bouche O, Tougeron D, et al. Masitinib plus irinotecan for second line treatment of esophagogastric adenocarcinoma: An open label phase Ib/II trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2015;33(15 Suppl):4027.
Zhang 2015 {published data only}
-
- Zhang X, Shen L, Lu Z, Liu W, Liu T, Hu B, et al. Comparison of efficacy and safety of paclitaxel and capecitabine followed by capecitabine as maintenance therapy versus cisplatin and capecitabine therapy for advanced gastric cancer: A multicentre, randomised, active‐controlled phase III study. Annals of Oncology 2015;26(9 Suppl):ix44. [DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdv523.05] - DOI
Zhou 2016 {published data only}
-
- Zhou Y, Liu C, Tang Y, Wang S. Clinical observation of S‐l in the maintenance treatment of advanced esophageal cancer. Cancer Research and Clinic 2016;28(7):452‐4.
References to ongoing studies
Aanur 2017 {published data only}
-
- Aanur P, Gutierrez M, Kelly RJ, Ajani JA, Ku GY, Denlinger CS, et al. FRACTION (Fast Real‐time Assessment of Combination Therapies in Immuno‐ONcology)‐gastric cancer (GC): A randomized, open‐label, adaptive, phase 2 study of nivolumab in combination with other immuno‐oncology (IO) agents in patients with advanced GC. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2017 [Epub ahead of print]; Vol. 35, issue 15 Suppl. [DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.35.15_suppl.TPS4137] - DOI
Bang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Bang YJ, Kang YK, Alsina M, Wainberg ZA, Chau I, Zhu J, et al. JAGUAR: a randomized phase II study of the AKT inhibitor ipatasertib (GDC‐0068) versus placebo in combination with mFOLFOX6 chemotherapy in patients (pts) with locally advanced or metastatic HER2‐negative gastric (G) or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2014;32(15 Suppl):TPS4147.
Bendell 2017 {published data only}
-
- Bendell JC, Starodub A, Huang X, Maltzman JD, Wainberg ZA, Shah MA. A phase 3 randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of GS‐5745 combined with mFOLFOX6 as first‐line treatment in patients with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2017 [Epub ahead of print]; Vol. 35, issue 15 Suppl. [DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.35.15_suppl.TPS4139] - DOI
Cafferkey 2016 {published data only}
-
- Cafferkey C, Chau I, Thistlethwaite F, Petty RD, Starling N, Watkins D, et al. PLATFORM: Planning treatment of oesophago‐gastric (OG) cancer randomised maintenance therapy trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016 [Epub ahead of print]; Vol. 34, issue 4 Suppl. [DOI: 10.1200/jco.2016.34.4_suppl.tps187; NCT02678182] - DOI
CTRI/2016/01/006474 {published data only}
-
- CTRI/2016/01/006474. Palliative chemotherapy in esophageal cancer for survival [A randomized clinical trial of best supportive care compared with best supportive care with chemotherapy in advanced unresectable or metastatic esophageal cancer]. ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials/pmaindet2.php?trialid=13694 (first received 1 January 2016).
Doi 2016 {published data only}
-
- Doi T, Bennouna J, Shen L, Enzinger PC, Wang R, Csiki I, et al. KEYNOTE‐181: Phase 3, open‐label study of second‐line pembrolizumab vs single‐agent chemotherapy in patients with advanced/metastatic esophageal adenocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016 [Epub ahead of print]; Vol. 34, issue 15 Suppl. [DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2016.34.15_suppl.TPS4140] - DOI
Esaki 2017 {published data only}
-
- Esaki T, Makiyama A, Kashiwada T, Hosokawa A, Kawada J, Moriwaki T, et al. ACT (WJOG7112G): A randomized phase II study of weekly paclitaxel ± trastuzumab in patients with HER2‐positive advanced gastric or gastro‐esophageal junction cancer refractory to trastuzumab combined with fluoropyrimidine and platinum. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2017 [Epub ahead of print]; Vol. 35, issue 4 Suppl. [DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.35.4_suppl.TPS218] - DOI
EUCTR 2016‐001514‐20 {published data only}
-
- EUCTR 2016‐001514‐20. A randomized phase 3 study of nivolumab plus ipilimumab or nivolumab combined with fluorouracil plus cisplatin versus fluorouracil plus cisplatin in subjects with unresectable advanced, recurrent or metastatic previously untreated esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. clinicaltrialsregister.eu/ctr‐search/trial/2016‐001514‐20 (first received 17 October 2016).
Haag 2017 {published data only}
Malka 2011 {published data only}
-
- Malka D, Gourgou‐Bourgade S, Emile J, Laurent‐Puig P, Taieb J. Met or EGFR Inhibition in Gastroesophageal Adenocarcinoma (MEGA): FOLFOX alone or in combination with AMG 102 or panitumumab as first‐line treatment in patients with advanced gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: FNCLCC‐FFCD‐AGEO‐GERCOR PRODIGE 17‐ACCORD 20 randomized phase II trial. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2011;29(15 Suppl):TPS178.
NCT00515411 {published data only}
-
- NCT00515411. Study of modified docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil (mDCF) in unresectable or metastatic gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma [A phase II study of modified docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil (mDCF) in patients with unresectable or metastatic gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00515411 (first received 10 August 2007).
NCT00680901 {published data only}
-
- NCT00680901. LOGiC ‐ lapatinib optimization study in ErbB2 (HER2) positive gastric cancer: a phase III global, blinded study designed to evaluate clinical endpoints and safety of chemotherapy plus lapatinib [A phase III study for ErbB2 positive advanced or metastatic gastric, esophageal, or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma treated with capecitabine plus oxaliplatin with or without lapatinib]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00680901 (first received 15 May 2008).
NCT00816634 {published data only}
-
- NCT00816634. Efficacy comparison study of combination regimens to treat advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (XP versus XT) [A randomized phase II trial of capecitabine plus cisplatin (XP) versus capecitabine plus paclitaxel (XT) as a first‐line treatment for advanced or recurrent esophageal squamous cell carcinoma]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00816634 (first received 30 December 2008).
NCT00824785 {published data only}
-
- NCT00824785. REAL3 trial of efficacy of EOX with/without panitumumab in previously untreated adv OG cancer (REAL3) [REAL 3: a randomised open‐labelled multicentre trial of the efficacy of epirubicin, oxaliplatin and capecitabine (EOX) with or without panitumumab in previously untreated advanced oesophago‐gastric cancer]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00824785 (first received 16 January 2009).
NCT00982592 {published data only}
-
- NCT00982592. Combination chemotherapy with or without vismodegib in treating patients with advanced stomach cancer or gastroesophageal junction cancer [A randomized, double blind placebo controlled phase 2 study of FOLFOX plus or minus GDC‐0449 in patients with advanced gastric and gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) carcinoma]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00982592 (first received 22 September 2009).
NCT00991952 {published data only}
-
- NCT00991952. Irinotecan hydrochloride with or without alvocidib in treating patients with advanced stomach or gastroesophageal junction cancer that cannot be removed by surgery [A multicenter random assignment phase II study of irinotecan and alvocidib (flavopiridol) versus irinotecan alone for patients with p53 wild type gastric adenocarcinoma]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00991952 (first received 7 October 2009).
NCT01020630 {published data only}
-
- NCT01020630. Sunitinib in patients with advanced gastric cancer and treated with FOLFIRI (SUN‐CASE) [A randomized, placebo‐controlled phase II trial investigating SUNITINIB versus placebo in patients with chemorefractory advanced adenocarcinoma of the stomach or lower esophagus treated with chemotherapy FOLFIRI]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01020630 (first received 23 November 2009).
NCT01246960 {published data only}
-
- NCT01246960. A study of ramucirumab in participants with gastric, esophageal, and gastroesophageal cancer [Randomized, placebo‐controlled, double‐blind phase 2 study of mFOLFOX6 chemotherapy plus ramucirumab drug product(IMC‐1121B) versus mFOLFOX6 plus placebo for advanced adenocarcinoma of the esophagus, gastroesophageal junction or stomach]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01246960 (first received 8 November 2010).
NCT01474642 {published data only}
-
- NCT01474642. Phase II trial of XP versus XG in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [A randomized phase II trial of capecitabine plus cisplatin (XP) versus capecitabine plus genexol (XG) as a first‐line treatment for advanced or recurrent esophageal squamous cell carcinoma]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01474642 (first received 18 November 2011).
NCT01498289 {published data only}
-
- NCT01498289. S1201: combination chemo for patients w/advanced or metastatic esophageal, gastric, or gastroesophageal junction cancer [A randomized phase II pilot study prospectively evaluating treatment for patients based on ERCC1(excision repair cross‐complementing 1) for advanced/metastatic esophageal, gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01498289 (first received 22 December 2011).
NCT01503372 {published data only}
-
- NCT01503372. FLO +/‐ pazopanib as first‐line treatment in advanced gastric cancer (PaFLO) [Pazopanib with 5‐fluorouracil, leucovorin and oxaliplatin (FLO) as 1st‐line treatment in advanced gastric cancer; a randomized phase‐ii‐study of the arbeitsgemeinschaft internistische onkologie]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01503372 (first received 22 December 2011).
NCT01627379 {published data only}
-
- NCT01627379. Cisplatin and 5‐FU +/‐ panitumumab for patients with nonresectable,advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell cancer (POWER) [An open‐label, randomized phase III trial of cisplatin and 5‐fluorouracil with or without panitumumab for patients with nonresectable, advanced or metastatic esophageal squamous cell cancer]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01627379 (first received 13 June 2012).
NCT01704690 {published data only}
-
- NCT01704690. Combination treatment of S‐1 with paclitaxel in advanced esophageal cancer [Combination treatment of S‐1 with paclitaxel versus paclitaxel+cisplatin and 5‐Fu+cisplatin as first‐line treatment in advanced esophageal cancer]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01704690 (first received 4 October 2012).
NCT01747551 {published data only}
-
- NCT01747551. FOLFOX +/‐ ziv‐aflibercept for esophageal and gastric cancer [Randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled phase II study of FOLFOX +/‐ ziv‐aflibercept in patients with advanced esophageal and gastric cancer]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01747551 (first received 5 December 2012).
NCT01896531 {published data only}
-
- NCT01896531. A study of GDC‐0068 in combination with fluoropyrimidine plus oxaliplatin in participants with advanced or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer [A randomized, phase II, placebo controlled study of GDC‐0068, an inhibitor to Akt, in combination with fluoropyrimidine plus oxaliplatin in patients with locally advanced or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01896531 (first received 8 July 2013).
NCT02137343 {published data only}
-
- NCT02137343. A phase 3 study of rilotumumab (AMG 102) with cisplatin and capecitabine (CX) as first‐line therapy in gastric cancer (RILOMET‐2) [A phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled study of rilotumumab (AMG 102) with cisplatin and capecitabine (CX) as first‐line therapy in advanced MET‐positive gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma]. Clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02137343 (first received 28 April 2014).
NCT02177552 {published data only}
-
- NCT02177552. Study assessing the effects of chemotherapy in advanced esophagogastric adenocarcinoma (SEED) [Study assessing the effects of chemotherapy in advanced esophagogastric adenocarcinoma ‐ carboplatin, docetaxel and capecitabine (CTX) or epirubicin, oxaliplatin and capecitabine: a randomised phase 2 trial]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02177552 (first received 18 June 2014).
NCT02178956 {published data only}
-
- NCT02178956. A study of BBI608 plus weekly paclitaxel to treat gastric and gastro‐esophageal junction cancer (BRIGHTER) [A phase III clinical trial of BBI608 plus weekly paclitaxel vs. placebo plus weekly paclitaxel in adult patients with advanced, previously treated gastric and gastro‐esophageal junction adenocarcinoma]. clincaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02178956 (first received 27 June 2014).
NCT02344810 {published data only}
-
- NCT02344810. C‐Met inhibitor AMG 337, oxaliplatin, leucovorin calcium, and fluorouracil in treating patients with advanced stomach or esophageal cancer [A phase I and randomized phase II double blinded placebo controlled study of mFOLFOX6 +/‐ AMG 337 in the first line treatment of patients with Her2/Neu negative and high MET expressing advanced gastric and esophageal adenocarcinoma]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02344810 (first received 16 January 2015).
NCT02409849 {published data only}
-
- NCT02409849. Octreotide LAR as maintenance treatment for patients with NEC [Randomized phase II study of octreotide LAR as maintenance treatment after first‐line chemotherapy for patients with unresectable or metastatic gastro‐entero‐pancreatic or esophageal neuroendocrine carcinomas]. clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02409849 (first received 1 April 2015).
NCT02569242 {published data only}
-
- NCT02569242. Study of nivolumab in unresectable advanced or recurrent esophageal cancer [ONO‐4538 phase III study a multicenter, randomized, open‐label study in patients with unresectable advanced or recurrent esophageal cancer]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02569242 (first received 6 October 2015).
NCT02625610 {published data only}
-
- Julien T, Maria DB, Antonio C, Jayne G, Deborah W, Huiling X, et al. Avelumab in first‐line maintenance gastric gancer (JAVELIN Gastric 100). Annals of Oncology 2015;27:ii81‐ii82.
-
- NCT02625610. Avelumab in first‐line maintenance gastric cancer (JAVELIN Gastric 100) [A phase III open‐label, multicenter trial of maintenance therapy with avelumab (MSB0010718C) versus continuation of first‐line chemotherapy in subjects with unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic, adenocarcinoma of the stomach, or of the gastro‐esophageal junction]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02625610 (first received 9 December 2015).
NCT02625623 {published data only}
-
- Eric VC, Lucjan W, Keun‐Wook L, Fortunato C, Rosine G, Julien T, et al. JAVELIN gastric 300: phase 3 trial of avelumab (anti‐PD‐L1 antibody) + best supportive care (BSC) vs BSC ± chemotherapy as third‐line treatment for advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer. Annals of Oncology 2015;27:ii82.
NCT02743494 {published data only}
-
- NCT02743494. An investigational immuno‐therapy study of nivolumab or placebo in patients with resected esophageal or gastroesophageal junction cancer (CheckMate 577) [A randomized, multicenter, double blind, phase iii study of adjuvant nivolumab or placebo in subjects with resected esophageal, or gastroesophageal junction cancer]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT02743494 (first received 19 April 2016).
NCT02773524 {published data only}
-
- Sjoquist KM, Pavlakis N, Martin AJ, Tsobanis E, Yip S, Bang YJ, et al. Integrate II: A randomised phase 3 double‐blind placebo‐controlled study of regorafenib in refractory advanced gastro‐oesophageal cancer (AGOC) An international study organized by the Australasian Gastrointestinal Trials Group (AGITG). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016 [Epub ahead of print]; Vol. 35, issue 15. [DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.35.15_suppl.TPS4136] - DOI
NCT02872116 {published data only}
-
- Moehler MH, Janjigian YY, Adenis A, Aucoin JS, Boku N, Chau I, et al. CheckMate 649: A randomized, multicenter, open‐label, phase 3 study of nivolumab (nivo) + ipilimumab (ipi) or nivo + chemotherapy (CTX) vs CTX alone in pts with previously untreated advanced (adv) gastric (G) or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology 19 Aug 2016 [Epub ahead of print]; Vol. 35, issue 15. [DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.35.4_suppl.TPS213] - DOI
NCT03002064 {published data only}
-
- NCT03002064. Docetaxol plus cisplatin versus 5‐Fu plus cisplatin as 1st‐line chemotherapy in advanced ESCC patients [Docetaxel plus cisplatin versus 5‐fluorouracil plus cisplatin as first‐line treatment for metastatic esophageal squamous patients: a prospective multicenter, randomized controlled clinical study]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03002064 (first received 23 December 2016).
NCT03006432 {published data only}
-
- NCT03006432. Phase III randomised trial to evaluate folfox with or without docetaxel (TFOX) as 1st line chemotherapy for locally advanced or metastatic oesophago‐gastric carcinoma (GASTFOX) [Essai de phase iii randomise evaluant le folfox avec ou sans docetaxel (tfox) en 1ère ligne de chimiotherapie des adenocarcinomes oeso‐gastriques localement avances ou metastatiques]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03006432 (first received 30 December 2016).
NCT03019588 {published data only}
-
- NCT03019588. Efficacy and safety study of pembrolizumab (MK‐3475) versus paclitaxel in Asian participants with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma who progressed after first‐line therapy with platinum and fluoropyrimidine (MK‐3475‐063/KEYNOTE‐063) [A phase III, randomized, open‐label clinical trial of pembrolizumab (MK‐3475) versus paclitaxel in Asian subjects with advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma who progressed after first‐line therapy with platinum and fluoropyrimidine]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03019588 (first received 12 January 2017).
NCT03042611 {published data only}
-
- Kang YK, Boku N, Kang WK, Yoon HH, Cascinu S, Al‐Batran SE, et al. A prospective, randomized, double‐blinded, placebo‐controlled, phase III study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of apatinib plus best supportive care (BSC) compared to placebo plus BSC in patients with advanced or metastatic gastric cancer: The ANGEL study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 3 Feb 2017 [Epub ahead of print]; Vol. 35, issue 15. [DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.35.15_suppl.TPS4138] - DOI
NCT03168594 {published data only}
-
- NCT03168594. Study to compare irinotecan combined with cisplatin (IP) versus etoposide combined with cisplatin (EP) in advanced and metastatic gastrointestinal pancreatic and esophageal neuroendocrine carcinoma [A randomized, controlled phase II study to compare irinotecan combined with cisplatin (IP) versus etoposide combined with cisplatin (EP) in advanced and metastatic gastrointestinal pancreatic and esophageal neuroendocrine carcinoma]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03168594 (first received 30 May 2017).
NCT03189719 {published data only}
-
- NCT03189719. First‐line esophageal carcinoma study with chemo vs. chemo plus pembrolizumab (MK‐3475‐590/KEYNOTE‐590) [A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled phase III clinical trial of pembrolizumab (MK‐3475) in combination with cisplatin and 5‐fluorouracil versus placebo in combination with cisplatin and 5‐fluorouracil as first‐line treatment in subjects with advanced/metastatic esophageal carcinoma (KEYNOTE‐590)]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03189719 (first received 16 June 2017).
NCT03279601 {published data only}
-
- NCT03279601. Study to compare capecitabine combined with dacarbazine (CAPDTIC) versus capecitabine combined temozolomide (CAPTEM) in advanced and metastatic gastrointestinal pancreatic and esophageal neuroendocrine tumor [A randomized, controlled phase II study to compare capecitabine combined with dacarbazine (CAPDTIC) versus capecitabine combined temozolomide (CAPTEM) in advanced and metastatic gastrointestinal pancreatic and esophageal neuroendocrine tumor]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03279601 (first received 12 September 2017).
NCT03281369 {published data only}
-
- NCT03281369. A study of multiple immunotherapy‐based treatment combinations in patients with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer (G/GEJ) (UMBRELLA) [A phase Ib/II, open‐label, multicenter, randomized, umbrella study evaluating the efficacy and safety of multiple immunotherapy‐based treatment combinations in patients with locally advanced unresectable or metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer (morpheus‐gastric cancer)]. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03281369 (first received 13 September 2017).
Ohtsu 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ohtsu A, Tabernero J, Bang YJ, Fuchs CS, Sun L, Wang Z, et al. KEYNOTE‐061: pembrolizumab (MK‐3475) versus paclitaxel as second‐line therapy for advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma. Annals of Oncology 2015;26(9 Suppl):ix69.
Shah 2017b {published data only}
-
- Shah MA, Metges JP, Chun PY, Smith V, Maltzman JD, Wainberg ZA. A phase II, open‐label, randomized study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of GS‐5745 combined with nivolumab versus nivolumab alone in subjects with unresectable or recurrent gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2017;35(15 Suppl):TPS4141.
Tabernero 2013 {published data only}
-
- Tabernero J, Hoff PM, Shen L, Ohtsu A, Yu R, Eng‐Wong J, Kang YK. Pertuzumab (P) with trastuzumab (T) and chemotherapy (CTX) in patients (pts) with HER2‐positive metastatic gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer: an international phase III study (JACOB). Journal of Clinical Oncology 2013;31(15 Suppl):TPS4150.
Tabernero 2016 {published data only}
-
- Tabernero J, Bang YJ, Fuchs CS, Ohtsu A, Kher U, Lam B, et al. KEYNOTE‐062: Phase III study of pembrolizumab (MK‐3475) alone or in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone as first‐line therapy for advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2016;34(4):TPS185.
Toshihiko 2016 {published data only}
-
- Toshihiko D, Jaafar B, Lin S, Peter E, Ruixue W, Ildiko C, et al. Pembrolizumab versus physician‐choice chemotherapy for previously treated patients with advanced/metastatic squamous or adenocarcinoma of the esophagus or Siewert I adenocarcinoma of the esophagogastric junction (EGJ): randomized, phase 3 KEYNOTE‐18. Annals of Oncology 2016;27(2 Suppl):i81.
Additional references
Aaronson 1993
-
- Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, et al. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ‐C30: a quality‐of‐life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 1993;85(5):365‐76. - PubMed
Altman 2001
Amdal 2013
-
- Amdal CD, Jacobsen A, Guren MGN, Bjordal K. Patient‐reported outcomes evaluating palliative radiotherapy and chemotherapy in patients with oesophageal cancer: a systematic review. Acta Oncologica 2013;52(4):679–90. - PubMed
Arnold 2015
-
- Arnold M, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J, Forman D. Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological subtype in 2012. Gut 2015;64(3):381‐7. - PubMed
Bennett 2012
Blazeby 2001
-
- Blazeby JM. Measurement of outcome. Surgical Oncology 2001;10(3):127‐33. - PubMed
Blazeby 2003
-
- Blazeby JM, Conroy T, Hammerlid E, Fayers P, Sezer O, Koller M, et al. Clinical and psychometric validation of an EORTC questionnaire module, the EORTC QLQ‐OES18, to assess quality of life in patients with oesophageal cancer. European Journal of Cancer 2003;39(10):1384‐94. - PubMed
Blazeby 2004
-
- Blazeby JM, Conroy T, Bottomley A, Vickery C, Arraras J, Sezer O, et al. Clinical and psychometric validation of a questionnaire module, the EORTC QLQ‐STO 22, to assess quality of life in patients with gastric cancer. European Journal of Cancer 2004;40(15):2260‐8. - PubMed
Chau 2009
-
- Chau I, Norman AR, Cunningham D, Oates J, Hawkins R, Iveson T, et al. The impact of primary tumour origins in patients with advanced oesophageal, oesophago‐gastric junction and gastric adenocarcinoma ‐ 025EF individual patient data from 1775 patients in four randomised controlled trials. Annals of Oncology 2009;20(5):885‐91. - PubMed
Common Toxicity Criteria 4.0
-
- National Cancer Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events v 4.0. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute; 2009 May. NIH publication #09‐7473.
Cook 2009
Edgren 2013
-
- Edgren G, Adami HO, Vainio EW, Nyren O. A global assessment of the oesophageal adenocarcinoma epidemic. Gut 2013;62(10):1406‐14. - PubMed
Enzinger 2003
-
- Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Medical progress ‐ Esophageal cancer. New England Journal of Medicine 2003;349(23):2241‐52. - PubMed
EuroQol 1990
-
- EuroQol group. EuroQol‐‐a new facility for the measurement of health‐related quality of life. Health Policy 1990;16(3):199‐208. - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Howlader 2014
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Garshell J, Miller D, Altekruse SF, et al. editors. SEER Cancer Statistics Review 1975‐2011. Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute; 2014 April. [http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2011/]
Hur 2013
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJ, Gavaghan DJ, et al. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?. Controlled Clinical Trials 1996;17(1):1‐12. - PubMed
Lin 2013
Machin 1997
-
- Machin D, Stenning SP, Parmar MKP. Thirty years of Medical Research Council randomised trials in solid tumors. Journal of Clinical Oncology 1997;9(2):100–14. - PubMed
Marsman 2005
-
- Marsman WA, Tytgat GNJ, Kate FJW, Lanschot JJB. Differences and similarities of adenocarcinomas of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction. Journal of Surgical Oncology 2005;92(3):160‐8. - PubMed
Mohammad 2015
-
- Mohammad NH, ter Veer E, Ngai L, Mali R, Oijen MG, Laarhoven HW. Optimal first‐line chemotherapeutic treatment in patients with locally advanced or metastatic esophagogastric carcinoma: triplet versus doublet chemotherapy: a systematic literature review and meta‐analysis. Cancer Metastasis Reviews 2015;34(3):429‐41. - PMC - PubMed
Moher 2009
Ocama 2008
Parmar 1998
-
- Parmar MKB, Torri V, Steward L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta‐analysis of the published literature for survival endpoints. Statistics in Medicine 1998;17(28):15–34. - PubMed
R 2014 [Computer program]
-
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Version 3.1.2. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing, 2014.
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Shah 2011
Somdyala 2010
-
- Somdyala NIM, Bradshaw D, Gelderblom WCA, Parkin DM. Cancer incidence in a rural population of South Africa, 1998‐2002. International Journal of Cancer 2010;127(10):2420‐9. - PubMed
Wagner 2010
White 2009
-
- White RE, Parker RK, Fitzwater JW, Kasepoi Z, Topazian M. Stents as sole therapy for oesophageal cancer: a prospective analysis of outcomes after placement. Lancet Oncology 2009;10(3):240‐6. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Homs 2003
-
- Homs MYV, Gaast A, Siersema PD, Steyerberg EW, Kuipers EJ. Chemotherapy for metastatic carcinoma of the esophagus and gastric cardia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004063] - DOI
Homs 2006
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

