Chemical Composition and Labeling of Substances Marketed as Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators and Sold via the Internet
- PMID: 29183075
- PMCID: PMC5820696
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2017.17069
Chemical Composition and Labeling of Substances Marketed as Selective Androgen Receptor Modulators and Sold via the Internet
Erratum in
-
Omitted Conflict of Interest Disclosures.JAMA. 2018 Feb 20;319(7):724. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.0613. JAMA. 2018. PMID: 29466569 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: Recent reports have described the increasing use of nonsteroidal selective androgen receptor modulators, which have not been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), to enhance appearance and performance. The composition and purity of such products is not known.
Objective: To determine the chemical identity and the amounts of ingredients in dietary supplements and products marketed and sold through the internet as selective androgen receptor modulators and compare the analyzed contents with product labels.
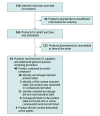
Design and setting: Web-based searches were performed from February 18, 2016, to March 25, 2016, using the Google search engine on the Chrome and Internet Explorer web browsers to identify suppliers selling selective androgen receptor modulators. The products were purchased and the identities of the compounds and their amounts were determined from April to August 2016 using chain-of-custody and World Anti-Doping Association-approved analytical procedures. Analytical findings were compared against the label information.
Exposures: Products marketed and sold as selective androgen receptor modulators.
Main outcomes and measures: Chemical identities and the amount of ingredients in each product marketed and sold as selective androgen receptor modulators.
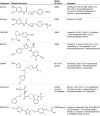
Results: Among 44 products marketed and sold as selective androgen receptor modulators, only 23 (52%) contained 1 or more selective androgen receptor modulators (Ostarine, LGD-4033, or Andarine). An additional 17 products (39%) contained another unapproved drug, including the growth hormone secretagogue ibutamoren, the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-δ agonist GW501516, and the Rev-ErbA agonist SR9009. Of the 44 tested products, no active compound was detected in 4 (9%) and substances not listed on the label were contained in 11 (25%). In only 18 of the 44 products (41%), the amount of active compound in the product matched that listed on the label. The amount of the compounds listed on the label differed substantially from that found by analysis in 26 of 44 products (59%).
Conclusions and relevance: In this limited investigation involving chemical analyses of 44 products marketed as selective androgen receptor modulators and sold via the internet, most products contained unapproved drugs and substances. Only 52% contained selective androgen receptor modulators and many were inaccurately labeled.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
The Public Health Consequences of Performance-Enhancing Substances: Who Bears Responsibility?JAMA. 2017 Nov 28;318(20):1983-1984. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.17111. JAMA. 2017. PMID: 29183050 No abstract available.
References
-
- Westerman ME, Charchenko CM, Ziegelmann MJ, Bailey GC, Nippoldt TB, Trost L. Heavy testosterone use among bodybuilders: an uncommon cohort of illicit substance users. Mayo Clin Proc. 2016;91(2):175-182. - PubMed
-
- Pope HG Jr, Khalsa JH, Bhasin S. Body image disorders and abuse of anabolic-androgenic steroids among men. JAMA. 2017;317(1):23-24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

