VDJ gene usage among B-cell receptors in ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation determined by RNA-seq Transcriptomic analysis
- PMID: 29183295
- PMCID: PMC5706410
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-017-0770-8
VDJ gene usage among B-cell receptors in ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation determined by RNA-seq Transcriptomic analysis
Abstract
Background: Studies on B-cell subtypes and V(D)J gene usage of B-cell receptors in kidney transplants are scarce. This study aimed to investigate V(D)J gene segment usage in ABO-incompatible (ABOi) kidney transplant (KT) patients compared to that in ABO-compatible (ABOc) KT patients.
Methods: We selected 16 ABOi KT patients with accommodation (ABOiA), 6 ABOc stable KT patients (ABOcS), and 6 ABOi KT patients with biopsy-proven acute antibody-mediated rejection (ABOiR) at day 10, whose graft tissue samples had been stored in the biorepository between 2010 and 2014. Complete transcriptomes of graft tissues were sequenced and analyzed through RNA sequencing (RNA-seq). The international ImMunoGeneTics information system (IMGT®) was used for in-depth comparison of V(D)J gene segment usage.
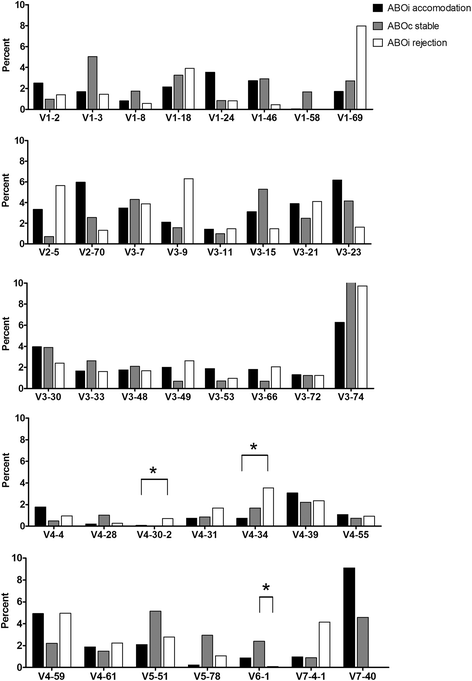
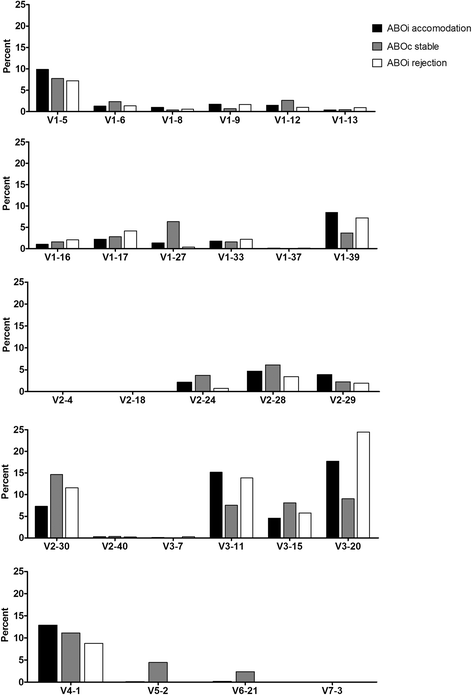
Results: The mean age of the 28 KT recipients was 43.3 ± 12.8 years, and 53.6% were male. By family, IGHV3, IGHJ4, IGLV2, and IGLJ3 gene segments were most frequently used in all groups, and their usage was not statistically different among the three patient groups. While IGKV3 was most frequently used in both the ABOiA and ABOiR groups, IGKV1 was most commonly used in the ABOcS group. In addition, while IGKJ1 was most commonly used in the ABOiA and ABOcS groups, IGKJ4 was most frequently used in the ABOiR group. According to individual gene segments, IGHV4-34 and IGHV4-30-2 were more commonly used in the ABOiR group than in the ABOiA group, and IGHV6-1 was more commonly used in the ABOcS group than in the ABOiR group. IGLV7-43 was more commonly used in the ABOcS group than in the ABOi group. However, technical variability, small sample size, and potential confounding effects of Rituximab or HLA mismatching are limitations of our study.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that RNA-seq transcriptomic analyses can provide information on the V(D)J gene usage of B-cell receptors and the mechanisms of accommodation and immune reaction in ABOi KT.
Keywords: ABO incompatible kidney transplantation; B cell receptor; RNA-seq; VDJ usage.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The running of a biorepository of graft tissue samples of KT patients (H-1102-082-353) and this study (H-1412-029-631) were performed with approval from the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital, and evidence of a personally signed and dated informed consent document indicating that the subject had been informed of all pertinent aspects of the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
VDJ Gene Usage of B Cell Receptors in Peripheral Blood of ABO-incompatible Kidney Transplantation Patients.Transplant Proc. 2018 May;50(4):1056-1062. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2018.01.047. Transplant Proc. 2018. PMID: 29731065
-
Acute Rejection and Infectious Complications in ABO- and HLA-Incompatible Kidney Transplantations.Ann Transplant. 2020 Oct 6;25:e927420. doi: 10.12659/AOT.927420. Ann Transplant. 2020. PMID: 33020465 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome of ABO Blood Type-Incompatible Living-Related Donor Kidney Transplantation Under a Contemporary Immunosuppression Strategy in Japan.Transplant Proc. 2020 Jul-Aug;52(6):1700-1704. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.01.152. Epub 2020 May 21. Transplant Proc. 2020. PMID: 32448659
-
Advancement in preoperative desensitization therapy for ABO incompatible kidney transplantation recipients.Transpl Immunol. 2023 Oct;80:101899. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2023.101899. Epub 2023 Jul 9. Transpl Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37433394 Review.
-
Clinical outcomes after ABO-incompatible renal transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Lancet. 2019 May 18;393(10185):2059-2072. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32091-9. Epub 2019 Apr 18. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 31006573
Cited by
-
Immunoglobulin and T cell receptor repertoire changes induced by a prototype vaccine against Chagas disease in naïve rhesus macaques.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Jun 1;31(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01050-5. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38824576 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Assessment of Kidney Allografts: Are We Closer to a Daily Routine?Physiol Res. 2020 Apr 30;69(2):215-226. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934278. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Physiol Res. 2020. PMID: 32199018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of antibody and T cell receptor repertoires in Trypanosoma cruzi infected rhesus macaques and host response to infection.J Biomed Sci. 2025 Jun 18;32(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12929-025-01152-8. J Biomed Sci. 2025. PMID: 40533759 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

