Mesenchymal lineage cells and their importance in B lymphocyte niches
- PMID: 29183783
- PMCID: PMC11488667
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2017.11.018
Mesenchymal lineage cells and their importance in B lymphocyte niches
Abstract
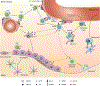
Early B lymphopoiesis occurs in the bone marrow and is reliant on interactions with numerous cell types in the bone marrow microenvironment, particularly those of the mesenchymal lineage. Each cellular niche that supports the distinct stages of B lymphopoiesis is unique. Different cell types and signaling molecules are important for the progressive stages of B lymphocyte differentiation. Cells expressing CXCL12 and IL-7 have long been recognized as having essential roles in facilitating progression through stages of B lymphopoiesis. Recently, a number of other factors that extrinsically mediate B lymphopoiesis (positively or negatively) have been identified. In addition, the use of transgenic mouse models to delete specific genes in mesenchymal lineage cells has further contributed to our understanding of how B lymphopoiesis is regulated in the bone marrow. This review will cover the current understanding of B lymphocyte niches in the bone marrow and key extrinsic molecules and signaling pathways involved in these niches, with a focus on how mesenchymal lineage cells regulate B lymphopoiesis.
Keywords: B lymphocytes; B lymphopoiesis; Mesenchymal cells; Osteoblasts; Osteoclasts.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
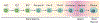

References
-
- Sims NA and Gooi JH, Bone remodeling: Multiple cellular interactions required for coupling of bone formation and resorption. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2008. 19(5): p. 444–51. - PubMed
-
- Hardy RR, B-1 B cell development. J Immunol, 2006. 177(5): p. 2749–54. - PubMed
-
- Nagasawa T, Microenvironmental niches in the bone marrow required for B-cell development. Nat Rev Immunol, 2006. 6(2): p. 107–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

