Factors Associated With Documentation of Obesity in the Inpatient Setting
- PMID: 29183918
- PMCID: PMC5703768
- DOI: 10.1542/hpeds.2017-0100
Factors Associated With Documentation of Obesity in the Inpatient Setting
Abstract
Objectives: Childhood obesity is rarely identified in hospitalized pediatric patients despite the high prevalence of obesity and potential for associated morbidity. The purpose of this study was to identify specific patient characteristics associated with the documentation of obesity and related weight management recommendations in the inpatient setting.
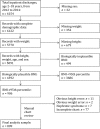
Methods: Retrospective chart review was conducted on all pediatric patients ages 2 to 18 years old and discharged between January 1, 2012, and December 31, 2014, to determine the following: (1) if obesity was noted in the clinical documentation of those with a BMI ≥95th percentile; and (2) if those with documented obesity had evidence of an obesity-specific management plan. Using χ2 and multivariable logistic regression, we determined patient characteristics associated with the documentation of obesity and presence of a management plan.
Results: Only 26% (214 of 809) of inpatients with obesity had documentation of weight status. The odds of obesity documentation were higher in patients with comorbid cholelithiasis, severe obesity, and older age. Of those with obesity documentation, 23% (49 of 214) had an obesity management plan. Comorbid sleep apnea and admission to a surgical service with a pediatric hospital medicine consult were significantly associated with the presence of an obesity management plan.
Conclusions: Increased efforts are necessary to improve obesity diagnosis and management in younger children who have not yet developed comorbidities. Additionally, the role of pediatric hospitalists as consultants for surgical patients should be further explored as a tool for addressing obesity during inpatient hospitalization.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
-
- Krebs NF, Jacobson MS; American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition. Prevention of pediatric overweight and obesity. Pediatrics. 2003;112(2):424–430 - PubMed
-
- Barlow SE, Bobra SR, Elliott MB, Brownson RC, Haire-Joshu D. Recognition of childhood overweight during health supervision visits: does BMI help pediatricians? Obesity (Silver Spring). 2007;15(1):225–232 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical