Phosphorylated exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils exacerbate pathology and induce neuronal dysfunction in mice
- PMID: 29184069
- PMCID: PMC5705684
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-15813-8
Phosphorylated exogenous alpha-synuclein fibrils exacerbate pathology and induce neuronal dysfunction in mice
Abstract
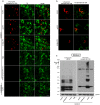
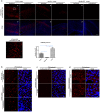
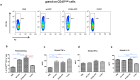
Approximately 90% of alpha-synuclein (α-Synuclein) deposited in Lewy bodies is phosphorylated at serine 129 suggesting that the accumulation of phosphorylated α-Synuclein is critical in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. However, in vivo experiments addressing the role of phosphorylated α-Synuclein in the progression of Parkinson's disease have produced equivocal data. To clarify a role of Ser129 phosphorylation of α-Synuclein in pathology progression we performed stereotaxic injections targeting the mouse striatum with three fibrilar α-Synuclein types: wt-fibrils, phosphorylated S129 fibrils and, phosphorylation incompetent, S129A fibrils. Brain inoculation of all three fibrilar types caused seeding of the endogenous α-Synuclein. However, phosphorylated fibrils triggered the formation of more α-Synuclein inclusions in the Substantia Nigra pars compacta (SNpc), exacerbated pathology in the cortex and caused dopaminergic neuronal loss and fine motor impairment as early as 60 days post injection. Phosphorylated fibril injections also induced early changes in the innate immune response including alterations in macrophage recruitment and IL-10 release. Our study further shows that S129 phosphorylation facilitated α-Synuclein fibril uptake by neurons. Our results highlight the role of phosphorylated fibrilar α-Synuclein in pathology progression in vivo and suggest that targeting phosphorylated α-Synuclein assemblies might be important for delaying inclusion formation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Propagation of pathological α-synuclein in marmoset brain.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2017 Feb 2;5(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40478-017-0413-0. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2017. PMID: 28148299 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral defects associated with amygdala and cortical dysfunction in mice with seeded α-synuclein inclusions.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Feb;134:104708. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104708. Epub 2019 Dec 16. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 31837424 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms underlying extensive Ser129-phosphorylation in α-synuclein aggregates.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2017 Jun 15;5(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s40478-017-0452-6. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2017. PMID: 28619113 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Ser129 phosphorylation of α-synuclein in neurodegeneration of Parkinson's disease: a review of in vivo models.Rev Neurosci. 2013;24(2):115-23. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2012-0071. Rev Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23314528 Review.
-
Initiation and propagation of α-synuclein aggregation in the nervous system.Mol Neurodegener. 2020 Mar 6;15(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s13024-020-00368-6. Mol Neurodegener. 2020. PMID: 32143659 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stress-inducible phosphoprotein 1 (HOP/STI1/STIP1) regulates the accumulation and toxicity of α-synuclein in vivo.Acta Neuropathol. 2022 Nov;144(5):881-910. doi: 10.1007/s00401-022-02491-8. Epub 2022 Sep 19. Acta Neuropathol. 2022. PMID: 36121476 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Parkinson's Disease With the Alpha-Synuclein Protein.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Apr 23;11:356. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00356. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32390826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha-synuclein pathology in the "weaver" mouse, a genetic model of dopaminergic denervation.MicroPubl Biol. 2024 Mar 13;2024:10.17912/micropub.biology.001156. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.001156. eCollection 2024. MicroPubl Biol. 2024. PMID: 38550606 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic basis for receptor-mediated pathological α-synuclein fibril cell-to-cell transmission in Parkinson's disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jun 29;118(26):e2011196118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2011196118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34172566 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha-synuclein-induced stress sensitivity renders the Parkinson's disease brain susceptible to neurodegeneration.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024 Jun 17;12(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s40478-024-01797-w. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024. PMID: 38886854 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

