Counter-intuitive influence of Himalayan river morphodynamics on Indus Civilisation urban settlements
- PMID: 29184098
- PMCID: PMC5705636
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-01643-9
Counter-intuitive influence of Himalayan river morphodynamics on Indus Civilisation urban settlements
Abstract
Urbanism in the Bronze-age Indus Civilisation (~4.6-3.9 thousand years before the present, ka) has been linked to water resources provided by large Himalayan river systems, although the largest concentrations of urban-scale Indus settlements are located far from extant Himalayan rivers. Here we analyse the sedimentary architecture, chronology and provenance of a major palaeochannel associated with many of these settlements. We show that the palaeochannel is a former course of the Sutlej River, the third largest of the present-day Himalayan rivers. Using optically stimulated luminescence dating of sand grains, we demonstrate that flow of the Sutlej in this course terminated considerably earlier than Indus occupation, with diversion to its present course complete shortly after ~8 ka. Indus urban settlements thus developed along an abandoned river valley rather than an active Himalayan river. Confinement of the Sutlej to its present incised course after ~8 ka likely reduced its propensity to re-route frequently thus enabling long-term stability for Indus settlements sited along the relict palaeochannel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

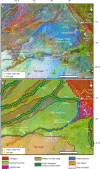
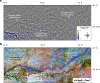







Similar articles
-
On the existence of a perennial river in the Harappan heartland.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 20;9(1):17221. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53489-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31748611 Free PMC article.
-
Reorganization of the western Himalayan river system after five million years ago.Nature. 2005 Dec 15;438(7070):1001-3. doi: 10.1038/nature04379. Nature. 2005. PMID: 16355221
-
Lipid residues in pottery from the Indus Civilisation in northwest India.J Archaeol Sci. 2021 Jan;125:105291. doi: 10.1016/j.jas.2020.105291. J Archaeol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33519031 Free PMC article.
-
Fluvial landscapes of the Harappan civilization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Jun 26;109(26):E1688-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1112743109. Epub 2012 May 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22645375 Free PMC article.
-
Large observational bias on discharge in the Indus River since 1970s.Sci Rep. 2018 Nov 23;8(1):17291. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35600-3. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30470822 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Modelling water levels of northwestern India in response to improved irrigation use efficiency.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 10;10(1):13452. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70416-0. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32778800 Free PMC article.
-
Automated detection of archaeological mounds using machine-learning classification of multisensor and multitemporal satellite data.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 4;117(31):18240-18250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005583117. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32690717 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral river erosion impacts the preservation of Neolithic enclosures in alluvial plains.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 2;13(1):16566. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43849-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37783939 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting Settlement Contemporaneity and Exploring Stability and Instability: Case Studies from the Indus Civilization.J Field Archaeol. 2019 Sep 30;45(1):1-15. doi: 10.1080/00934690.2019.1664848. J Field Archaeol. 2019. PMID: 33239833 Free PMC article.
-
On the existence of a perennial river in the Harappan heartland.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 20;9(1):17221. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53489-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31748611 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams, R. M. Heartland of Cities. Surveys of Ancient Settlement and Land use on the Central Floodplain of the Euphrates. (University of Chicago, Chicago, 1981).
-
- Macklin MG, Lewin J. The rivers of civilization. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2015;114:228–244. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.02.004. - DOI
-
- Morozova GS. A review of Holocene avulsions of the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers and possible effects on the evolution of civilizations in lower Mesopotamia. Geoarchaeol. Int. J. 2005;20:401–423. doi: 10.1002/gea.20057. - DOI
-
- Jotheri J, Allen MB, Wilkinson TJ. Holocene avulsions of the Euphrates River in the Najaf area of Western Mesopotamia: impacts on human settlement patterns. Geoarchaeology. 2015;31:175–193. doi: 10.1002/gea.21548. - DOI
-
- Slingerland R, Smith ND. River avulsions and their deposits. Annu. Rev. Earth. Planet. Sci. 2004;32:257–285. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.32.101802.120201. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

