Discovery and Biological Evaluation of Potent and Selective N-Methylene Saccharin-Derived Inhibitors for Rhomboid Intramembrane Proteases
- PMID: 29185711
- PMCID: PMC6040592
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b01066
Discovery and Biological Evaluation of Potent and Selective N-Methylene Saccharin-Derived Inhibitors for Rhomboid Intramembrane Proteases
Abstract
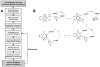
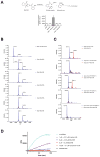
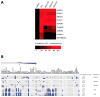
Rhomboids are intramembrane serine proteases and belong to the group of structurally and biochemically most comprehensively characterized membrane proteins. They are highly conserved and ubiquitously distributed in all kingdoms of life and function in a wide range of biological processes, including epidermal growth factor signaling, mitochondrial dynamics, and apoptosis. Importantly, rhomboids have been associated with multiple diseases, including Parkinson's disease, type 2 diabetes, and malaria. However, despite a thorough understanding of many structural and functional aspects of rhomboids, potent and selective inhibitors of these intramembrane proteases are still not available. In this study, we describe the computer-based rational design, chemical synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel N-methylene saccharin-based rhomboid protease inhibitors. Saccharin inhibitors displayed inhibitory potency in the submicromolar range, effectiveness against rhomboids both in vitro and in live Escherichia coli cells, and substantially improved selectivity against human serine hydrolases compared to those of previously known rhomboid inhibitors. Consequently, N-methylene saccharins are promising new templates for the development of rhomboid inhibitors, providing novel tools for probing rhomboid functions in physiology and disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Monocyclic β-lactams are selective, mechanism-based inhibitors of rhomboid intramembrane proteases.ACS Chem Biol. 2011 Apr 15;6(4):325-35. doi: 10.1021/cb100314y. Epub 2011 Jan 12. ACS Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 21175222 Free PMC article.
-
General and Modular Strategy for Designing Potent, Selective, and Pharmacologically Compliant Inhibitors of Rhomboid Proteases.Cell Chem Biol. 2017 Dec 21;24(12):1523-1536.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2017.09.007. Epub 2017 Oct 26. Cell Chem Biol. 2017. PMID: 29107700 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery and validation of 2-styryl substituted benzoxazin-4-ones as a novel scaffold for rhomboid protease inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018 May 1;28(8):1417-1422. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.02.017. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2018. PMID: 29463448
-
Inhibitors of rhomboid proteases.Biochimie. 2016 Mar;122:38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.07.007. Epub 2015 Jul 10. Biochimie. 2016. PMID: 26166068 Review.
-
Emerging role of rhomboid family proteins in mammalian biology and disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Dec;1828(12):2840-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.03.025. Epub 2013 Apr 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23562403 Review.
Cited by
-
A combination of solid-state NMR and MD simulations reveals the binding mode of a rhomboid protease inhibitor.Chem Sci. 2021 Sep 1;12(38):12754-12762. doi: 10.1039/d1sc02146j. eCollection 2021 Oct 6. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34703562 Free PMC article.
-
4-Oxo-β-lactams as Covalent Inhibitors of the Mitochondrial Intramembrane Protease PARL.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024 Nov 14;15(12):2101-2106. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.4c00384. eCollection 2024 Dec 12. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024. PMID: 39691509
-
Activity-Based Protein Profiling of RHBDL4 Reveals Proteolysis of the Enzyme and a Distinct Inhibitor Profile.ACS Chem Biol. 2024 Aug 16;19(8):1674-1682. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.4c00273. Epub 2024 Jul 23. ACS Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 39041925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Puente XS, Sanchez LM, Overall CM, Lopez-Otin C. Human and mouse proteases: a comparative genomic approach. Nat Rev Genet. 2003;4:544–558. - PubMed
-
- Egeblad M, Werb Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:161–174. - PubMed
-
- Lichtenthaler SF, Haass C, Steiner H. Regulated intramembrane proteolysis–lessons from amyloid precursor protein processing. J Neurochem. 2011;117:779–796. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

