Airway Mucus and Asthma: The Role of MUC5AC and MUC5B
- PMID: 29186064
- PMCID: PMC5742801
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm6120112
Airway Mucus and Asthma: The Role of MUC5AC and MUC5B
Abstract
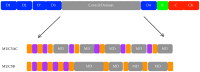
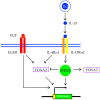
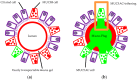
Asthma is characterized by mucus abnormalities. Airway epithelial hyperplasia and metaplasia result in changes in stored and secreted mucin and the production of a pathologic mucus gel. Mucus transport is impaired, culminating in mucus plugging and airway obstruction-a major cause of morbidity in asthma. The polymeric mucins MUC5AC and MUC5B are integral components of airway mucus. MUC5AC and MUC5B gene expression is altered in asthma, and recent work sheds light on their contribution to asthma pathogenesis. Herein, we review our current understanding of the role of MUC5AC and MUC5B in mucus dysfunction in asthma.
Keywords: MUC5AC; MUC5B; asthma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

