Evaluation of Inulin Replacing Chitosan in a Polyurethane/Polysaccharide Material for Pb2+ Removal
- PMID: 29186073
- PMCID: PMC6150026
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22122093
Evaluation of Inulin Replacing Chitosan in a Polyurethane/Polysaccharide Material for Pb2+ Removal
Abstract
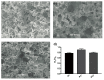
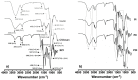
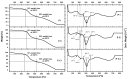
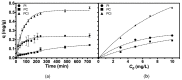
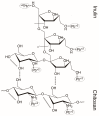
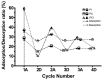
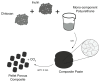
Downstream waste from industry and other industrial processes could increase concentration of heavy metals in water. These pollutants are commonly removed by adsorption because it is an effective and economical method. Previously, we reported adsorption capacity of a chitosan/polyurethane/titanium dioxide (TiO₂) composite for three ions in a dynamic wastewater system. There, increasing the chitosan concentration in composite increased the cation removal as well; however, for ratios higher than 50% of chitosan/TiO₂, the manufacturing cost increased significantly. In this work, we address the manufacturing cost problem by proposing a new formulation of the composite. Our hypothesis is that inulin could replace chitosan in the composite formulation, either wholly or in part. In this exploratory research, three blends were prepared with a polyurethane matrix using inulin or/and chitosan. Adsorption was evaluated using a colorimetric method and the Langmuir and Freundlich models. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra, scanning electron microscopy (SEM) micrographs, differential scanning calorimetry and thermogravimetric analysis curves were obtained to characterize blends. Results indicate that blends are suitable for toxic materials removal (specifically lead II, Pb2+). Material characterization indicates that polysaccharides were distributed in polyurethane's external part, thus improving adsorption. Thermal degradation of materials was found above 200 °C. Comparing the blends data, inulin could replace chitosan in part and thereby improve the cost efficiency and scalability of the production process of the polyurethane based-adsorbent. Further research with different inulin/chitosan ratios in the adsorbent and experiments with a dynamic system are justified.
Keywords: composite; heavy metals; lead pollution; polysaccharide; wastewater treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Biodegradable polymer based ternary blends for removal of trace metals from simulated industrial wastewater.Int J Biol Macromol. 2016 Feb;83:198-208. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.09.050. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016. PMID: 26432371
-
Improved waste-sourced biocomposite for simultaneous removal of crude oil and heavy metals from synthetic and real oilfield-produced water.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Nov;25(31):31407-31420. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3136-2. Epub 2018 Sep 8. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30196464
-
Adsorption Studies of Lead(II) from aqueous solution onto Nanochitosan /Polyurethane /Polypropylene glycol ternary blends.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Nov;104(Pt B):1436-1448. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.06.004. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. PMID: 28602992
-
Recent advances in chitosan-based nanocomposites for adsorption and removal of heavy metal ions.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jun;270(Pt 2):132386. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.132386. Epub 2024 May 15. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38754671 Review.
-
Versatile nature of hetero-chitosan based derivatives as biodegradable adsorbent for heavy metal ions; a review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2017 Dec;105(Pt 1):190-203. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.07.008. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017. PMID: 28735891 Review.
Cited by
-
Magnetized inulin by Fe3O4 as a bio-nano adsorbent for treating water contaminated with methyl orange and crystal violet dyes.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 20;12(1):22034. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26652-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36539589 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Chitosan on the Chemical Structure, Morphology, and Selected Properties of Polyurethane/Chitosan Composites.Polymers (Basel). 2020 May 25;12(5):1205. doi: 10.3390/polym12051205. Polymers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32466336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation and Characterization of New Sol-Gel Hybrid Inulin-TEOS Adsorbent.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Apr 15;13(8):1295. doi: 10.3390/polym13081295. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33921052 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient and Fast Removal of Oils from Water Surfaces via Highly Oleophilic Polyurethane Composites.Toxics. 2021 Aug 5;9(8):186. doi: 10.3390/toxics9080186. Toxics. 2021. PMID: 34437504 Free PMC article.
-
Titanate-polyurethane-chitosan ternary nanocomposite as an efficient coating for steel against corrosion.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 19;14(1):30562. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81104-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39702766 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed J.K., Ahmaruzzaman M. A review on potential usage of industrial waste materials for binding heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. J. Water Process Eng. 2016;10:39–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jwpe.2016.01.014. - DOI
-
- Wismer T., Dabvt D.V.M. Small Animal Toxicology. 3rd ed. Elsevier Inc.; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2013. Lead. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

