Development of a GAL4-VP16/UAS trans-activation system for tissue specific expression in Medicago truncatula
- PMID: 29186192
- PMCID: PMC5706680
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188923
Development of a GAL4-VP16/UAS trans-activation system for tissue specific expression in Medicago truncatula
Abstract
Promoters with tissue-specific activity are very useful to address cell-autonomous and non cell autonomous functions of candidate genes. Although this strategy is widely used in Arabidopsis thaliana, its use to study tissue-specific regulation of root symbiotic interactions in legumes has only started recently. Moreover, using tissue specific promoter activity to drive a GAL4-VP16 chimeric transcription factor that can bind short upstream activation sequences (UAS) is an efficient way to target and enhance the expression of any gene of interest. Here, we developed a collection of promoters with different root cell layers specific activities in Medicago truncatula and tested their abilities to drive the expression of a chimeric GAL4-VP16 transcription factor in a trans-activation UAS: β-Glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene system. By developing a binary vector devoted to modular Golden Gate cloning together with a collection of adapted tissue specific promoters and coding sequences we could test the activity of four of these promoters in trans-activation GAL4/UAS systems and compare them to "classical" promoter GUS fusions. Roots showing high levels of tissue specific expression of the GUS activity could be obtained with this trans-activation system. We therefore provide the legume community with new tools for efficient modular Golden Gate cloning, tissue specific expression and a trans-activation system. This study provides the ground work for future development of stable transgenic lines in Medicago truncatula.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
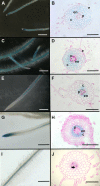
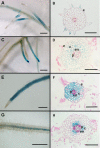
References
-
- Doyle JJ. Phylogenetic perspectives on the origins of nodulation. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2011;24(11):1289–95. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-05-11-0114 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gaulin E, Jacquet C, Bottin A, Dumas B. Root rot disease of legumes caused by Aphanomyces euteiches. Mol Plant Pathol. 2007;8(5):539–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2007.00413.x . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vailleau F, Sartorel E, Jardinaud MF, Chardon F, Genin S, Huguet T, et al. Characterization of the interaction between the bacterial wilt pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum and the model legume plant Medicago truncatula. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2007;20(2):159–67. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-20-2-0159 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brand AH, Perrimon N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 1993;118(2):401–15. . - PubMed
-
- Moore I, Samalova M, Kurup S. Transactivated and chemically inducible gene expression in plants. Plant J. 2006;45(4):651–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02660.x . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

