Neuroendocrine and neurophysiological effects of interleukin 6 in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 29186541
- PMCID: PMC6199533
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex391
Neuroendocrine and neurophysiological effects of interleukin 6 in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
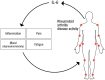
RA is a chronic, systemic, autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation and degradation of the joints, causing significant negative impact on quality of life. In addition to joint disease, symptoms and co-morbidities associated with RA-namely pain, fatigue and mood disorders-are often as debilitating as the disease itself. The pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-6 plays a critical role in RA-associated pathology. However, a greater understanding of the translational effects of IL-6 outside of the immune system is needed. This review discusses our current understanding of emerging aspects of IL-6 in RA-associated pain, fatigue and mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. This review also describes the clinical effects of IL-6 inhibition on these symptoms and co-morbidities in patients with RA.
Figures


References
-
- Gibofsky A. Overview of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Manag Care 2012;18:S295–302. - PubMed
-
- Singh JA, Saag KG, Bridges SL Jr. et al. 2015 American College of Rheumatology guideline for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016;68:1–26. - PubMed
-
- Radovits BJ, Fransen J, Al Shamma S. et al. Excess mortality emerges after 10 years in an inception cohort of early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res 2010;62:362–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

