Testosterone Attenuates Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell-Mediated Airway Inflammation
- PMID: 29186686
- PMCID: PMC5731254
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.110
Testosterone Attenuates Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell-Mediated Airway Inflammation
Abstract
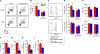
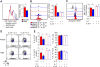
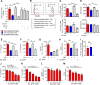
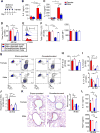
Sex hormones regulate many autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, including asthma. As adults, asthma prevalence is 2-fold greater in women compared to men. The number of group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2) is increased in patients with asthma, and we investigate how testosterone attenuates ILC2 function. In patients with moderate to severe asthma, we determine that women have an increased number of circulating ILC2 compared to men. ILC2 from adult female mice have increased IL-2-mediated ILC2 proliferation versus ILC2 from adult male mice, as well as pre-pubescent females and males. Further, 5α-dihydrotestosterone, a hormone downstream of testosterone, decreases lung ILC2 numbers and IL-5 and IL-13 expression from ILC2. In vivo, testosterone attenuated Alternaria-extract-induced IL-5+ and IL-13+ ILC2 numbers and lung eosinophils by intrinsically decreasing lung ILC2 numbers, as well as by decreasing expression of IL-33 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), ILC2-stimulating cytokines. Collectively, these findings provide a foundational understanding of sexual dimorphism in ILC2 function.
Keywords: asthma; innate lymphoid cells; sex hormones; testosterone.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Agarwal R. Severe asthma with fungal sensitization. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2011;11:403–413. - PubMed
-
- American Lung Association. Trends in Asthma Morbidity and Mortality 2012
-
- Barlow JL, Bellosi A, Hardman CS, Drynan LF, Wong SH, Cruickshank JP, McKenzie AN. Innate IL-13-producing nuocytes arise during allergic lung inflammation and contribute to airways hyperreactivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129:191–198. e191–194. - PubMed
-
- Busse WW, Israel E, Nelson HS, Baker JW, Charous BL, Young DY, Vexler V, Shames RS Daclizumab Asthma Study, G. Daclizumab improves asthma control in patients with moderate to severe persistent asthma: a randomized, controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;178:1002–1008. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

