Lean leadership attributes: a systematic review of the literature
- PMID: 29187082
- PMCID: PMC5868554
- DOI: 10.1108/JHOM-12-2016-0245
Lean leadership attributes: a systematic review of the literature
Abstract
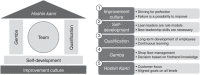
Purpose Emphasis on quality and reducing costs has led many health-care organizations to reconfigure their management, process, and quality control infrastructures. Many are lean, a management philosophy with roots in manufacturing industries that emphasizes elimination of waste. Successful lean implementation requires systemic change and strong leadership. Despite the importance of leadership to successful lean implementation, few researchers have probed the question of ideal leadership attributes to achieve lean thinking in health care. The purpose of this paper is to provide insight into applicable attributes for lean leaders in health care. Design/methodology/approach The authors systematically reviewed the literature on principles of leadership and, using Dombrowski and Mielke's (2013) conceptual model of lean leadership, developed a parallel theoretical model for lean leadership in health care. Findings This work contributes to the development of a new framework for describing leadership attributes within lean management of health care. Originality/value The summary of attributes can provide a model for health-care leaders to apply lean in their organizations.
Keywords: Healthcare; Leadership; Management; Management attitudes.
Figures
References
-
- Aij K.H., Aernoudts R.L. and Joosten G. (2015), “Manager traits and quality-of-care performance in hospitals”, Leadership in Health Services, Vol. 28 No. 3, pp. 200-215. - PubMed
-
- Aij K.H., Visse M. and Widdershoven G.A. (2015), “Lean leadership: an ethnographic study”, Leadership in Health Services, Vol. 28 No. 2, pp. 119-134. - PubMed
-
- Al-Balushi S., Sohal A.S., Singh P.J., Al Hajri A., Al Farsi Y.M. and Al Abri R. (2014), “Readiness factors for lean implementation in healthcare settings – a literature review”, Journal of Health Organization and Management, Vol. 28 No. 2, pp. 135-153. - PubMed
-
- Albrecht S.L. and Andreetta M. (2011), “The influence of empowering leadership, empowerment and engagement on affective commitment and turnover intentions in community health service workers: test of a model”, Leadership in Health Services, Vol. 24 No. 3, pp. 228-237.
-
- Angood P. and Shannon D. (2014), “Unique benefits of physician leadership – an American perspective”, Leadership in Health Services, Vol. 27 No. 4, pp. 272-282.
Further reading
-
- Aziz R.F. and Hafez S.M. (2013), “Applying lean thinking in construction and performance improvement”, Alexandria Engineering Journal, Vol. 52 No. 4, pp. 679-695.
-
- Bennett D. (2003), “Lean enterprise value: insights from MIT’s lean aerospace initiative. By Earll Murman”, R&D Management, Vol. 33 No. 3, p. 359.
-
- Bortolotti T., Boscari S. and Danese P. (2015), “Successful lean implementation: organizational culture and soft lean practices”, International Journal of Production Economics, Vol. 160, pp. 182-201.
-
- Cattaneo C., Galizzi G. and Bassani G. (2012), “Efficiency as a domain of health care systems: a phenomenographic approach”, Annual Review of Health Care Management: Strategy and Policy Perspectives on Reforming Health Systems, Vol. 13, pp. 161-188. - PubMed
-
- Craven A. (2009), “An interview with Susan Hodgetts MIHM MBA BEd Med, Chief Executive: Institute of Healthcare Management, UK”, Leadership in Health Services, Vol. 22 No. 1, pp. 1-4.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources