Experimental design and quantitative analysis of microbial community multiomics
- PMID: 29187204
- PMCID: PMC5708111
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-017-1359-z
Experimental design and quantitative analysis of microbial community multiomics
Abstract
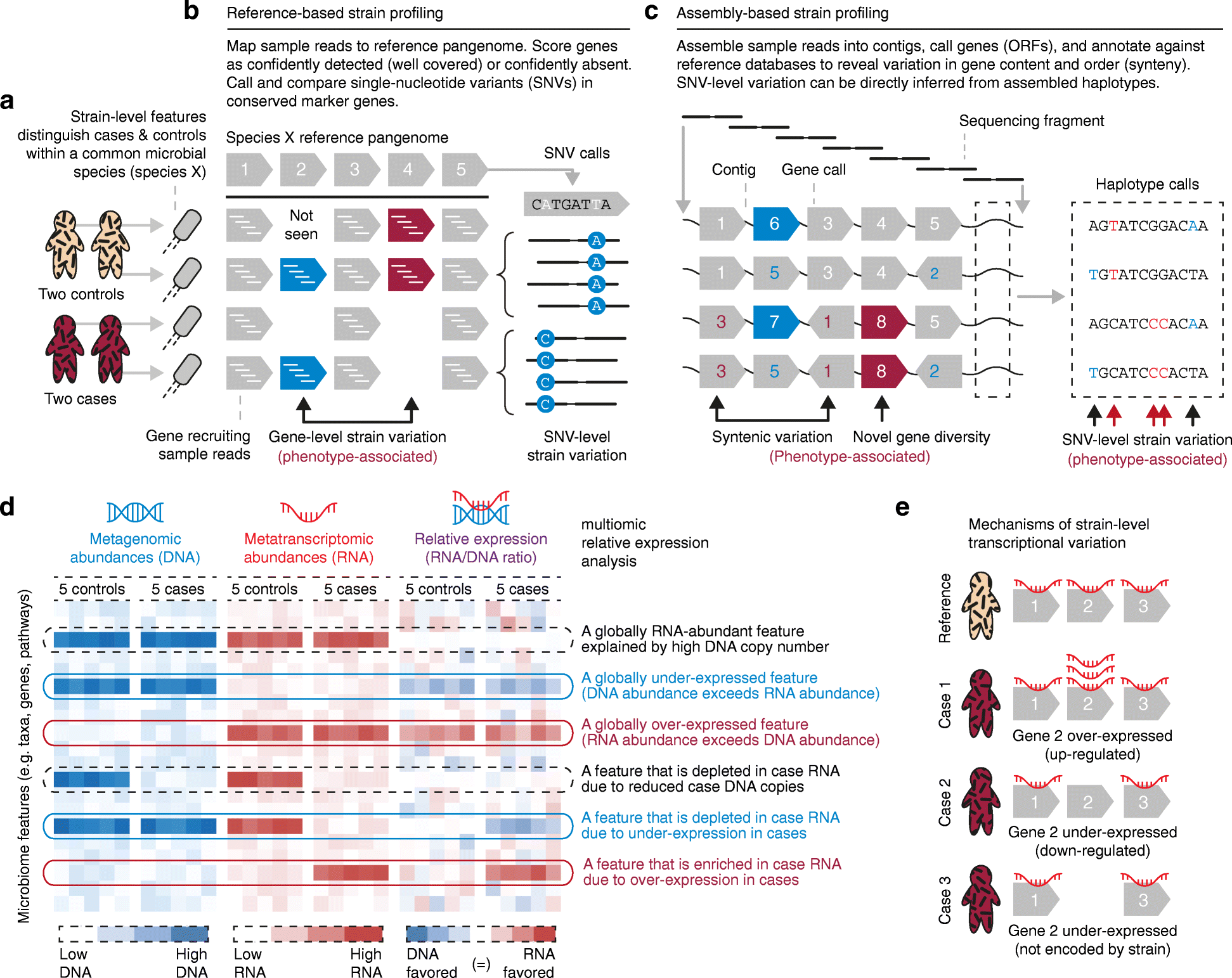
Studies of the microbiome have become increasingly sophisticated, and multiple sequence-based, molecular methods as well as culture-based methods exist for population-scale microbiome profiles. To link the resulting host and microbial data types to human health, several experimental design considerations, data analysis challenges, and statistical epidemiological approaches must be addressed. Here, we survey current best practices for experimental design in microbiome molecular epidemiology, including technologies for generating, analyzing, and integrating microbiome multiomics data. We highlight studies that have identified molecular bioactives that influence human health, and we suggest steps for scaling translational microbiome research to high-throughput target discovery across large populations.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

