Decreasing Delirium through Music (DDM) in critically ill, mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit: study protocol for a pilot randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 29187230
- PMCID: PMC5708104
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-017-2324-6
Decreasing Delirium through Music (DDM) in critically ill, mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit: study protocol for a pilot randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Delirium is a highly prevalent and morbid syndrome in intensive care units (ICUs). Changing the stressful environment within the ICU via music may be an effective and a scalable way to reduce the burden of delirium.
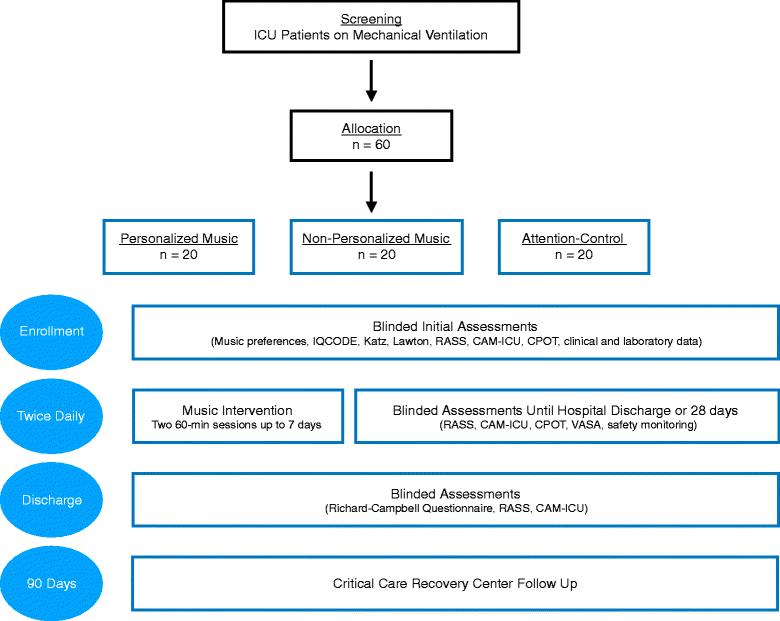
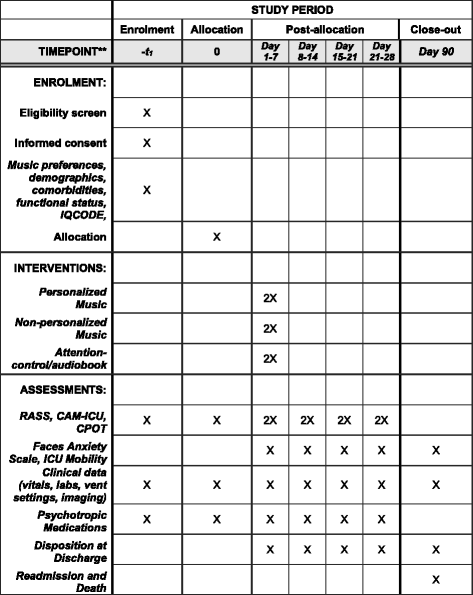
Methods/design: The Decreasing Delirium through Music (DDM) study is a three-arm, single-blind, randomized controlled feasibility trial. Sixty patients admitted to the ICU with respiratory failure requiring mechanical ventilation will be randomized to one of three arms (20 participants per arm): (1) personalized music, (2) non-personalized relaxing music, or (3) attention-control. Music preferences will be obtained from all enrolled participants or their family caregivers. Participants will receive two 1-h audio sessions a day through noise-cancelling headphones and mp3 players. Our primary aim is to determine the feasibility of the trial design (recruitment, adherence, participant retention, design and delivery of the music intervention). Our secondary aim is to estimate the potential effect size of patient-preferred music listening in reducing delirium, as measured by the Confusion Assessment Method for the ICU (CAM-ICU). Participants will receive twice daily assessments for level of sedation and presence of delirium. Enrolled participants will be followed in the hospital until death, discharge, or up to 28 days, and seen in the Critical Care Recovery Clinic at 90 days.
Discussion: DDM is a feasibility trial to provide personalized and non-personalized music interventions for critically ill, mechanically ventilated patients. Our trial will also estimate the preliminary efficacy of music interventions on reducing delirium incidence and severity.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, Identifier: NCT03095443 . Registered on 23 March 2017.
Keywords: Critical care; Delirium; Music.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The DDM Trial received Indiana University’s Institutional Review Board approval (IRB 1608887741A003).
For participants deemed eligible for enrollment, the patient and/or their legal representative are approached for consent.
Consent for publication
Consent forms for the trial include consent for publication of results in peer-reviewed journals.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Miller RR, Ely EW, editors. Delirium and cognitive dysfunction in the intensive care unit. Seminars in respiratory and critical care medicine. New York: Thieme; 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

