Urine cell-free microRNA as biomarkers for transitional cell carcinoma
- PMID: 29187235
- PMCID: PMC5708087
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-017-2950-9
Urine cell-free microRNA as biomarkers for transitional cell carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: MicroRNA (miRNA) are short nucleotide strands with a regulatory function in the cell. Several miRNAs have been shown to be useful as biomarkers for different neoplasms. The aim of this project was to assess whether levels of miRNA in cell free urine could be used as a biomarker in transitional cell carcinoma (TCC).
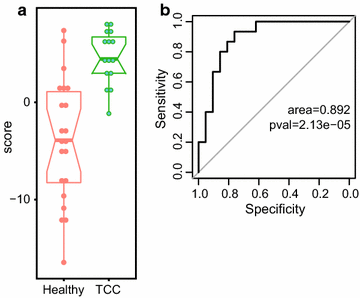
Results: cDNA libraries were produced based on small RNAs in urine samples of fourteen TCC patients and twenty healthy volunteers. Resulting reads were deep sequenced on Illumina HiSeq sequencer with the intent of characterizing cell free urine miRNA profiles. A statistically significant difference was found for a single miRNA; miR-210 was > sixfold higher in the TCC group compared to the control group. Furthermore, we were able to produce a diagnostic score by summing of standardized levels of overexpressed miRNA. This score was considerably higher in TCC patients with a sensitivity of 0.93, specificity of 0.76 and negative predictive value > 0.97.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Extracellular RNA; Transitional cell carcinoma; Urothelial carcinoma; microRNA.
Figures

References
-
- Lotan Y. Clinical presentation, diagnosis, and staging of bladder cancer. Waltham: UpToDate.com; 2014.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

