Photodynamic Priming Mitigates Chemotherapeutic Selection Pressures and Improves Drug Delivery
- PMID: 29187403
- PMCID: PMC5771811
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1700
Photodynamic Priming Mitigates Chemotherapeutic Selection Pressures and Improves Drug Delivery
Abstract
Physiologic barriers to drug delivery and selection for drug resistance limit survival outcomes in cancer patients. In this study, we present preclinical evidence that a subtumoricidal photodynamic priming (PDP) strategy can relieve drug delivery barriers in the tumor microenvironment to safely widen the therapeutic window of a nanoformulated cytotoxic drug. In orthotopic xenograft models of pancreatic cancer, combining PDP with nanoliposomal irinotecan (nal-IRI) prevented tumor relapse, reduced metastasis, and increased both progression-free survival and 1-year disease-free survival. PDP enabled these durable improvements by targeting multiple tumor compartments to (i) increase intratumoral drug accumulation by >10-fold, (ii) increase the duration of drug exposure above a critical therapeutic threshold, and (iii) attenuate surges in CD44 and CXCR4 expression, which mediate chemoresistance often observed after multicycle chemotherapy. Overall, our results offer preclinical proof of concept for the effectiveness of PDP to minimize risks of tumor relapse, progression, and drug resistance and to extend patient survival.Significance: A biophysical priming approach overcomes key treatment barriers, significantly reduces metastases, and prolongs survival in orthotopic models of human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res; 78(2); 558-71. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
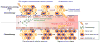
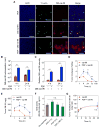
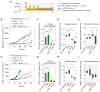

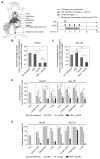
References
-
- Holohan C, Van Schaeybroeck S, Longley DB, Johnston PG. Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:714–26. - PubMed
-
- Adiseshaiah PP, Crist RM, Hook SS, McNeil SE. Nanomedicine strategies to overcome the pathophysiological barriers of pancreatic cancer. Nature reviews Clinical oncology. 2016;13:750–65. - PubMed
-
- Garrido-Laguna I, Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer: from state-of-the-art treatments to promising novel therapies. Nature reviews Clinical oncology. 2015;12:319–34. - PubMed
-
- Minchinton AI, Tannock IF. Drug penetration in solid tumours. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:583–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

