Neurofascin antibodies in autoimmune, genetic, and idiopathic neuropathies
- PMID: 29187518
- PMCID: PMC5754648
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004773
Neurofascin antibodies in autoimmune, genetic, and idiopathic neuropathies
Abstract
Objective: To measure the frequency, persistence, isoform specificity, and clinical correlates of neurofascin antibodies in patients with peripheral neuropathies.
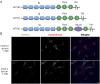
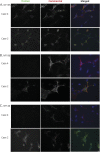
Methods: We studied cohorts of patients with Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) or chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) (n = 59), genetic neuropathy (n = 111), and idiopathic neuropathy (n = 43) for immunoglobulin (Ig) G and IgM responses to 3 neurofascin (NF) isoforms (NF140, NF155, and NF186) using cell-based assays.
Results: Neurofascin antibodies were more common in patients with GBS/CIDP (14%, 8 of 59) compared to genetic neuropathy controls (3%, 3 of 111, p = 0.01). Seven percent (3 of 43) of patients with idiopathic neuropathy also had neurofascin antibodies. NF155 IgG4 antibodies were associated with CIDP refractory to IV immunoglobulin but responsive to rituximab, and some of these patients had an acute onset resembling GBS. NF186 IgG and IgM to either isoform were less specific. A severe form of CIDP, approaching a locked-in state, was seen in a patient with antibodies recognizing all 3 neurofascin isoforms.
Conclusions: Neurofascin antibodies were 4 times more frequent in autoimmune neuropathy samples compared to genetic neuropathy controls. Persistent IgG4 responses to NF155 correlated with severe CIDP resistant to usual treatments but responsive to rituximab. IgG4 antibodies against the common domains shared by glial and axonal isoforms may portend a particularly severe but treatable neuropathy. The prognostic implications of neurofascin antibodies in a subset of idiopathic neuropathy patients and transient IgM responses in GBS require further investigation.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
References
-
- Devaux JJ, Odaka M, Yuki N. Nodal proteins are target antigens in Guillain-Barre syndrome. J Periph Nerv Syst 2012;17:62–71. - PubMed
-
- Querol L, Nogales-Gadea G, Rojas-Garcia R, et al. Antibodies to contactin-1 in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Ann Neurol 2013;73:370–380. - PubMed
-
- Kamamura N, Yamasaki R, Yonekawa T, et al. Anti-neurofascin antibody in patients with combined central and peripheral demyelination. Neurology 2013;81:714–722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
