An invasive herbivore structures plant competitive dynamics
- PMID: 29187604
- PMCID: PMC5719370
- DOI: 10.1098/rsbl.2017.0374
An invasive herbivore structures plant competitive dynamics
Abstract
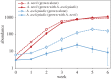
Species interactions are central to our understanding of ecological communities, but may change rapidly with the introduction of invasive species. Invasive species can alter species interactions and community dynamics directly by having larger detrimental effects on some species than others, or indirectly by changing the ways in which native species compete among themselves. We tested the direct and indirect effects of an invasive aphid herbivore on a native aphid species and two host milkweed species. The invasive aphid caused a 10-fold decrease in native aphid populations, and a 30% increase in plant mortality (direct effects). The invasive aphid also increased the strength of interspecific competition between the two native plant hosts (indirect effects). By investigating the role that indirect effects play in shaping species interactions in native communities, our study highlights an understudied component of species invasions.
Keywords: aphid; competition; herbivory; invasive species; milkweed; species interactions.
© 2017 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Mooney HA, Hobbs RJ. 2000. Invasive species in a changing world. Washington, DC: Island Press.
-
- Sakai AK, et al. 2001. The population biology of invasive species. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 32, 305–332. (doi:10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.32.081501.114037) - DOI
-
- Gandhi KJ, Herms DA. 2010. Direct and indirect effects of alien insect herbivores on ecological processes and interactions in forests of eastern North America. Biol. Invasions 12, 389–405. (doi:10.1007/s10530-009-9627-9) - DOI
-
- Kenis M, Auger-Rozenberg M-A, Roques A, Timms L, Péré C, Cock MJ, Settele J, Augustin S, Lopez-Vaamonde C. 2009. Ecological effects of invasive alien insects. Biol. Invasions 11, 21–45. (doi:10.1007/s10530-008-9318-y) - DOI
-
- Carson WP, Root RB. 2000. Herbivory and plant species coexistence: community regulation by an outbreaking phytophagous insect. Ecol. Monogr. 70, 73–99. (doi:10.1890/0012-9615(2000)070[0073:HAPSCC]2.0.CO;2) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
