Testing differential use of payoff-biased social learning strategies in children and chimpanzees
- PMID: 29187629
- PMCID: PMC5740275
- DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2017.1751
Testing differential use of payoff-biased social learning strategies in children and chimpanzees
Abstract
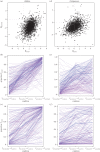
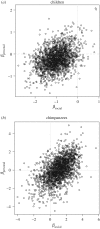
Various non-human animal species have been shown to exhibit behavioural traditions. Importantly, this research has been guided by what we know of human culture, and the question of whether animal cultures may be homologous or analogous to our own culture. In this paper, we assess whether models of human cultural transmission are relevant to understanding biological fundamentals by investigating whether accounts of human payoff-biased social learning are relevant to chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes). We submitted 4- and 5-year-old children (N = 90) and captive chimpanzees (N = 69) to a token-reward exchange task. The results revealed different forms of payoff-biased learning across species and contexts. Specifically, following personal and social exposure to different tokens, children's exchange behaviour was consistent with proportional imitation, where choice is affected by both prior personally acquired and socially demonstrated token-reward information. However, when the socially derived information regarding token value was novel, children's behaviour was consistent with proportional observation; paying attention to socially derived information and ignoring their prior personal experience. By contrast, chimpanzees' token choice was governed by their own prior experience only, with no effect of social demonstration on token choice, conforming to proportional reservation. We also find evidence for individual- and group-level differences in behaviour in both species. Despite the difference in payoff strategies used, both chimpanzees and children adopted beneficial traits when available. However, the strategies of the children are expected to be the most beneficial in promoting flexible behaviour by enabling existing behaviours to be updated or replaced with new and often superior ones.
Keywords: cultural transmission bias; culture; payoff bias; social learning; social learning strategies.
© 2017 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no completing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Galef BG Jr, Whiten A. 2017. The comparative psychology of social learning. In APA handbook of comparative psychology (ed. Call J.), pp. 411–440. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
-
- Vale GL, Dean LG, Whiten A. In press. Culture in nonhuman animals. In Wiley international encyclopedia of anthropology (ed. Callan H.). New York, NY: Wiley-Blackwell.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
