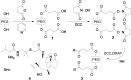
Synthesis, characterization and in vitro release performance of the pegylated valnemulin prodrug
- PMID: 29187697
- PMCID: PMC5797878
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.17-0434
Synthesis, characterization and in vitro release performance of the pegylated valnemulin prodrug
Abstract
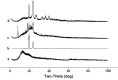
Valnemulin, successfully developed by Sandoz in 1984, is a new generation derivative of pleuromutilin related to tiamulin. Valnemulin has low water-solubility, a short half-life period, low bioavailability, and instability. The application of valnemulin was restricted. Therefore, finding a more moderate delivery system is necessary to improve the shortcomings of valnemulin. The purpose of the study was to improve the strong stability and the irritation caused by of valnemulin hydrochloride power through pegylated-valnemulin prodrug mode. The prepared pegylated-valnemulin prodrug was characterized and evaluated by in vitro release performance under buffer solutions with pH levels of 7.4 and 3.6. The loading rate of valnemulin in PEG-succinic-valnemulin prodrug was determined by ultraviolet spectrophotometer and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). HPLC with evaporative light scattering detector was applied to determine the amount of PEG-succinic acid. The loading rate of valnemulin in PEG-succinic-valnemulin prodrug was 6.46%. PEG-succinic-valnemulin prodrug demonstrated a satisfactory solubility of valnemulin with 523 mg·ml-1 and excellent stability verified by the stability experiment. The result of the in vitro release test showed that the prepared PEG-valnemulin prodrug has controlled release ability and the release rate of valnemulin from PEG-valnemulin prodrug with a pH of 7.4 was 64.98%, which was higher than that of pH3.6 with release rate of 31.90%. Therefore, the prepared PEG-succinic-valnemulin prodrug has great application potential.
Keywords: PEG; prodrug; release; valnemulin; valnemulin hydrochloride.
Figures
References
-
- Chandrashekar B. N., Swamy B. E. K., Pandurangachar M., Shankar S. S., Gilbert O., Manjunatha J. G., Sherigara B. S.2010. Electrochemical oxidation of dopamine at polyethylene glycol modified carbon paste electrode: A cyclic voltammetric study. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 5: 578–592.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources