Post-transcriptional Regulation of Genes Related to Biological Behaviors of Gastric Cancer by Long Noncoding RNAs and MicroRNAs
- PMID: 29187891
- PMCID: PMC5706018
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.22076
Post-transcriptional Regulation of Genes Related to Biological Behaviors of Gastric Cancer by Long Noncoding RNAs and MicroRNAs
Abstract
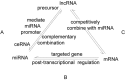
Noncoding RNAs play critical roles in regulating protein-coding genes and comprise two major classes: long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs). LncRNAs regulate gene expression at transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and epigenetic levels via multiple action modes. LncRNAs can also function as endogenous competitive RNAs for miRNAs and indirectly regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally. By binding to the 3'-untranslated regions (3'-UTR) of target genes, miRNAs post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression. Herein, we conducted a review of post-transcriptional regulation by lncRNAs and miRNAs of genes associated with biological behaviors of gastric cancer.
Keywords: gastric cancer; lncRNAs; miRNAs; ncRNAs; post-transcriptional regulation..
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Interplay Between Long Noncoding RNAs and MicroRNAs in Cancer.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1819:75-92. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8618-7_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30421400
-
Genome-wide prediction of cauliflower miRNAs and lncRNAs and their roles in post-transcriptional gene regulation.Planta. 2021 Sep 14;254(4):72. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03689-y. Planta. 2021. PMID: 34519918
-
Short and Long Noncoding RNAs Regulate the Epigenetic Status of Cells.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Sep 20;29(9):832-845. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7262. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018. PMID: 28847161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer: Pathogenesis and clinical implications.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jan 21;22(3):1213-23. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1213. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26811659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs, Long Noncoding RNAs, and Their Functions in Human Disease.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1617:1-25. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7046-9_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28540673 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Significance of microRNA-196b-5p in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and its Potential Molecular Mechanism.J Cancer. 2019 Aug 29;10(22):5355-5370. doi: 10.7150/jca.29293. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31632480 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-130a-3p inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and TMZ resistance in glioblastoma by targeting Sp1.Am J Transl Res. 2019 Dec 15;11(12):7272-7285. eCollection 2019. Am J Transl Res. 2019. PMID: 31934277 Free PMC article.
-
LINC01619 promotes non-small cell lung cancer development via regulating PAX6 by suppressing microRNA-129-5p.Am J Transl Res. 2020 Jun 15;12(6):2538-2553. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32655789 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation on neurobiological changes in Alzheimer's disease (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2022 Apr;25(4):109. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12625. Epub 2022 Feb 4. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 35119081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-135a suppresses migration of gastric cancer cells by targeting TRAF5-mediated NF-κB activation.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Feb 1;12:975-984. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S189976. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 30774383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Esteller M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12:861–74. - PubMed
-
- Bushati N, Cohen SM. microRNA functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:175–205. - PubMed
-
- He L, Hannon GJ. MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 2004;5:522–31. - PubMed
-
- Covarrubias AA, Reyes JL. Post-transcriptional gene regulation of salinity and drought responses by plant microRNAs. Plant Cell Environ. 2010;33:481–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

