Defining Radiation-Induced Hepatic Toxicity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy
- PMID: 29187892
- PMCID: PMC5706019
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.21561
Defining Radiation-Induced Hepatic Toxicity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy
Abstract
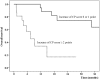
The definition and criteria of radiation-induced hepatic toxicity (RIHT) in hepatocellular carcinoma patients vary among studies. Therefore, the reported rates of RIHT differ among studies, and this causes confusion. In this study, we evaluated RIHT using several laboratory and clinical parameters, and analyzed which criterion is more correlated with RT and survival. Forty-five HCC patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy were included for the analysis. All patients had unresectable HCC and Child-Pugh (CP) class A or B baseline liver function. A median total dose of 45 Gy was delivered by CyberKnife in 3 fractions. For individual laboratory parameter, ≥ grade 2 toxicity development of bilirubin, albumin, or prothrombin time by Common Terminology Criteria of Adverse Effects (CTCAE) was correlated with mean liver dose and survival. However, serum transaminases had no correlation with liver mean dose and survival, and were rather affected by other local treatments. Compared to the CTCAE, the increase in the CP score of 2 points or more was better correlated with liver failure and overall survival, and it was not affected by other local treatments or tumor progression. We concluded RIHT was better defined by the change in the CP score rather than the CTCAE in patients treated by stereotactic body radiotherapy for HCC.
Keywords: Child-Pugh score; Hepatocellular carcinoma; radiation therapy; radiation-induced liver disease; stereotactic body radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of CyberKnife stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma on hepatic toxicity.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Nov 18;9:7169-7175. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S112290. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27920555 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective cohort study of hepatic toxicity after stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma.Radiother Oncol. 2018 Oct;129(1):136-142. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2018.02.031. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Radiother Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29548558 Clinical Trial.
-
Dose-volumetric parameters predicting radiation-induced hepatic toxicity in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007 Jan 1;67(1):225-31. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2006.08.015. Epub 2006 Oct 23. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007. PMID: 17056199
-
Stereotactic body radiation therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma: Optimal treatment strategies based on liver segmentation and functional hepatic reserve.Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2015 Nov-Dec;20(6):417-24. doi: 10.1016/j.rpor.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2015. PMID: 26696781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiation-induced hypothyroidism after treatment of head and neck cancer.Dan Med J. 2016 Mar;63(3):B5213. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 26931197 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic Analysis of Radiation-Induced Acute Liver Damage in a Rabbit Model.Dose Response. 2019 Nov 29;17(4):1559325819889508. doi: 10.1177/1559325819889508. eCollection 2019 Oct-Dec. Dose Response. 2019. PMID: 31827415 Free PMC article.
-
Gut microbiome dysbiosis in patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma after extended hepatectomy liver failure.Ann Transl Med. 2022 May;10(10):549. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-1958. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35722392 Free PMC article.
-
Radiotherapy plus anti-PD1 versus radiotherapy for hepatic toxicity in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.Radiat Oncol. 2023 Aug 4;18(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13014-023-02309-1. Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37542246 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a nomogram for radiation-induced hepatic toxicity after intensity modulated radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2024 Jun 1;54(6):699-707. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyae024. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38376811 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Current Trends and Controversies.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Jan 1;17:1533033818790217. doi: 10.1177/1533033818790217. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 30068240 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines. management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56:908–43. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous