Virtually increased acceptance angle for efficient estimation of spatially resolved reflectance in the subdiffusive regime: a Monte Carlo study
- PMID: 29188088
- PMCID: PMC5695938
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.8.004872
Virtually increased acceptance angle for efficient estimation of spatially resolved reflectance in the subdiffusive regime: a Monte Carlo study
Abstract
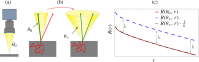
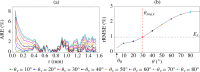
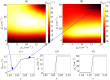
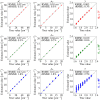
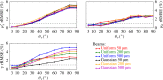
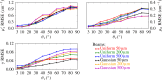
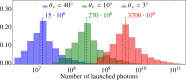
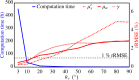
Light propagation in biological tissues is frequently modeled by the Monte Carlo (MC) method, which requires processing of many photon packets to obtain adequate quality of the observed backscattered signal. The computation times further increase for detection schemes with small acceptance angles and hence small fraction of the collected backscattered photon packets. In this paper, we investigate the use of a virtually increased acceptance angle for efficient MC simulation of spatially resolved reflectance and estimation of optical properties by an inverse model. We devise a robust criterion for approximation of the maximum virtual acceptance angle and evaluate the proposed methodology for a wide range of tissue-like optical properties and various source configurations.
Keywords: (110.4234) Multispectral and hyperspectral imaging; (160.4760) Optical properties; (170.3660) Light propagation in tissues; (170.3880) Medical and biological imaging; (170.3890) Medical optics instrumentation; (170.5280) Photon migration; (170.7050) Turbid media.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Estimation of optical properties by spatially resolved reflectance spectroscopy in the subdiffusive regime.J Biomed Opt. 2016 Sep 1;21(9):95003. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.21.9.095003. J Biomed Opt. 2016. PMID: 27653934
-
Efficient estimation of subdiffusive optical parameters in real time from spatially resolved reflectance by artificial neural networks.Opt Lett. 2018 Jun 15;43(12):2901-2904. doi: 10.1364/OL.43.002901. Opt Lett. 2018. PMID: 29905719
-
Analysis of relative error in perturbation Monte Carlo simulations of radiative transport.J Biomed Opt. 2023 Jun;28(6):065001. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.28.6.065001. Epub 2023 Jun 7. J Biomed Opt. 2023. PMID: 37293394 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Monte Carlo modeling of light transport in tissues.J Biomed Opt. 2013 May;18(5):50902. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.18.5.050902. J Biomed Opt. 2013. PMID: 23698318 Review.
-
Principles, developments, and applications of spatially resolved spectroscopy in agriculture: a review.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Jan 10;14:1324881. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1324881. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 38269139 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Two-term scattering phase function for photon transport to model subdiffuse reflectance in superficial tissues.Biomed Opt Express. 2023 Jan 13;14(2):751-770. doi: 10.1364/BOE.476461. eCollection 2023 Feb 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2023. PMID: 36874481 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Usenik P., Bürmen M., Fidler A., Pernuš F., Likar B., “Automated Classification and Visualization of Healthy and Diseased Hard Dental Tissues by Near-Infrared Hyperspectral Imaging,” Appl. Spectrosc. 66, 1067–1074 (2012).10.1366/11-06460 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
