Active thermodynamic contrast imaging for label-free tumor detection in a murine xenograft tumor model
- PMID: 29188098
- PMCID: PMC5695948
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.8.005013
Active thermodynamic contrast imaging for label-free tumor detection in a murine xenograft tumor model
Abstract
Passive thermal imaging provides a limited differentiation between a tumor and neighboring tissue based on the temperature difference. We propose active thermodynamic contrast imaging (ATCI) with convection thermal modulators to provide more physiologically relevant parameters with high contrast such as the rate of temperature change, and thermal recovery time for tumor detection with a murine xenograft tumor model. With early stage tumors, we found the average rate of temperature change was higher in the tumor (0.22 ± 0.06 [Formula: see text]/sec) than that of neighboring tissue (0.13 ± 0.01 [Formula: see text]/sec) with heating modulation. With established tumors (volume > 100 mm3), this tendency was greater. On the other hand, the thermal recovery time was shorter in tumor tissue (τ = 7.30 ± 0.59 sec) than that of neighboring tissue (τ = 11.91 ± 2.22 sec). We also found distinct thermal contrast with cooling modulation. These data suggest ATCI is a potential tumor detection modality for clinical application with its inherently label-free and physiology-based approach. Furthermore, this strategy may find applications in endoscopic tumor detection in the future.
Keywords: (040.3060) Infrared; (110.2970) Image detection systems; (170.3880) Medical and biological imaging; (170.4580) Optical diagnostics for medicine.
Figures

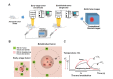
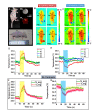
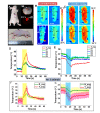
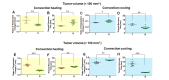
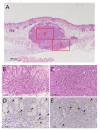
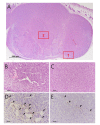
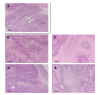
References
-
- Diakides N. A., “Infrared Imaging: An Emerging Technology in Medicine,” IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 17(4), 17–18 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Maldague X. P., Nondestructive evaluation of materials by infrared thermography (Springer Science & Business Media, 2012)
-
- Ng E.-K., “A review of thermography as promising non-invasive detection modality for breast tumor,” Int. J. Therm. Sci. 48(5), 849–859 (2009).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
