Characteristics and risk factors of rheumatoid arthritis in the United States: an NHANES analysis
- PMID: 29188142
- PMCID: PMC5703145
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.4035
Characteristics and risk factors of rheumatoid arthritis in the United States: an NHANES analysis
Abstract
Background: We examined the United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database to determine factors associated with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in adults 20 to 55 years of age.
Methods: NHANES data collected between 2007 and 2014, excluding the 2011-2012 period, were used. Subjects were divided into those with and without RA. Demographic, clinical, and lifestyle factors were compared between the groups.
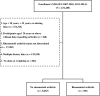
Results: After applying inclusion/exclusion criteria, 8,789 persons were included in the study (8,483 without RA, 306 with RA). Multivariable analysis indicated that advanced age (odds ratio [OR] = 1.09, 95% CI [1.07-1.11], P < 0.001), regular smoking (OR = 2.19, 95% CI [1.49-3.21], P < 0.001), diabetes (OR = 2.00, 95% CI [1.35-2.95], P = 0.001), obesity (reference, normal or underweight; OR = 3.31, 95% CI [2.05-5.36], P < 0.001), and osteoporosis (OR = 3.68, 95% CI [1.64-8.22], P = 0.002) were positively associated with RA. Covered by health insurance (OR = 1.81, 95% CI [1.12-2.93], P = 0.016) and living in poverty (OR = 2.96, 95% CI [1.88-4.65], P < 0.001) were also associated with having RA. Mexican American, Hispanic white or other Hispanic ethnicity (reference, non-Hispanic white; OR = 0.54, 95% CI [0.31-0.96], P = 0.036), appropriate sleep duration (about 6-11 h, OR = 0.46, 95% CI [0.32-0.65], P < 0.001), and insufficient vitamin A intake (reference, recommended; OR = 0.70, 95% CI [0.50-0.98], P = 0.036) were negatively associated with RA.
Discussion: Some factors associated with RA are potentially modifiable.
Keywords: NHANES; National health and nutrition examination survey; Rheumatoid arthritis; Risk factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham 3rd CO, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Cohen MD, Combe B, Costenbader KH, Dougados M, Emery P, Ferraccioli G, Hazes JM, Hobbs K, Huizinga TW, Kavanaugh A, Kay J, Kvien TK, Laing T, Mease P, Menard HA, Moreland LW, Naden RL, Pincus T, Smolen JS, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Symmons D, Tak PP, Upchurch KS, Vencovsky J, Wolfe F, Hawker G. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis and Rheumatism. 2010;62:2569–2581. doi: 10.1002/art.27584. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Begovich AB, Carlton VE, Honigberg LA, Schrodi SJ, Chokkalingam AP, Alexander HC, Ardlie KG, Huang Q, Smith AM, Spoerke JM, Conn MT, Chang M, Chang SY, Saiki RK, Catanese JJ, Leong DU, Garcia VE, McAllister LB, Jeffery DA, Lee AT, Batliwalla F, Remmers E, Criswell LA, Seldin MF, Kastner DL, Amos CI, Sninsky JJ, Gregersen PK. A missense single-nucleotide polymorphism in a gene encoding a protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTPN22) is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. American Journal of Human Genetics. 2004;75:330–337. doi: 10.1086/422827. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources