Chip-based digital PCR as a novel detection method for quantifying microRNAs in acute myocardial infarction patients
- PMID: 29188800
- PMCID: PMC6289362
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2017.136
Chip-based digital PCR as a novel detection method for quantifying microRNAs in acute myocardial infarction patients
Abstract
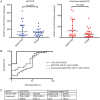
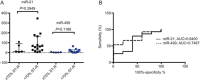
miRNAs have shown promise as potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction (AMI). However, the current used quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) allows solely for relative expression of nucleic acids and it is susceptible to day-to-day variability, which has limited the validity of using the miRNAs as biomarkers. In this study we explored the technical qualities and diagnostic potential of a new technique, chip-based digital PCR, in quantifying the miRNAs in patients with AMI and ischaemia-reperfusion injury (I/R). In a dilution series of synthetic C.elegans-miR-39, chip-based digital PCR displayed a lower coefficient of variation (8.9% vs 46.3%) and a lower limit of detection (0.2 copies/μL vs 1.1 copies/μL) compared with qRT-PCR. In the serum collected from 24 patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and 20 patients with stable coronary artery disease (CAD) patients after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), we used qRT-PCR and multiplexed chip-based digital PCR to quantify the serum levels of miRNA-21 and miRNA-499 as they have been validated in AMI in prior studies. In STEMI, I/R injury was assessed via measurement of ST-segment resolution (ST-R). Chip-based digital PCR revealed a statistical significance in the difference of miR-21 levels between stable CAD and STEMI groups (118.8 copies/μL vs 59 copies/μL; P=0.0300), whereas qRT-PCR was unable to reach significance (136.4 copies/μL vs 122.8 copies/μL; P=0.2273). For miR-499 levels, both chip-based digital PCR and qRT-PCR revealed statistically significant differences between stable CAD and STEMI groups (2 copies/μL vs 8.5 copies/μL, P=0.0011; 0 copies/μL vs 19.4 copies/μL; P<0.0001). There was no association between miR-21/499 levels and ST-R post-PCI. Our results show that the chip-based digital PCR exhibits superior technical qualities and promises to be a superior method for quantifying miRNA levels in the circulation, which may become a more accurate and reproducible method for directly quantifying miRNAs, particularly for use in large multi-centre clinical trials.
Keywords: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; chip-based digital PCR; ichaemia-reperfusion injury; micro-RNAs; qRT-PCR.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Droplet digital PCR as a novel detection method for quantifying microRNAs in acute myocardial infarction.Int J Cardiol. 2018 Apr 15;257:247-254. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.10.111. Int J Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29506703
-
A multiplexed ion-exchange membrane-based miRNA (MIX·miR) detection platform for rapid diagnosis of myocardial infarction.Lab Chip. 2021 Oct 12;21(20):3876-3887. doi: 10.1039/d1lc00685a. Lab Chip. 2021. PMID: 34546237 Free PMC article.
-
miR-941 as a promising biomarker for acute coronary syndrome.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017 Aug 22;17(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12872-017-0653-8. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017. PMID: 28830367 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-152-5p and miR-3681-5p function as potential biomarkers for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2022 Jun 22;77:100038. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2022.100038. eCollection 2022. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2022. PMID: 35751950 Free PMC article.
-
API expert consensus document on management of ischemic heart disease.J Assoc Physicians India. 2006 Jun;54:469-80. J Assoc Physicians India. 2006. PMID: 16909697 Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of microRNA-202-3p protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through activation of TGF-β1/Smads signaling pathway by targeting TRPM6.Cell Cycle. 2019 Mar;18(5):621-637. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1580494. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Cell Cycle. 2019. Retraction in: Cell Cycle. 2022 Apr;21(7):759. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2022.2046797. PMID: 30810438 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A systematic review of miRNAs as biomarkers for chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity in breast cancer patients reveals potentially clinically informative panels as well as key challenges in miRNA research.Cardiooncology. 2022 Sep 7;8(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s40959-022-00142-1. Cardiooncology. 2022. PMID: 36071532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extraction-Free Absolute Quantification of Circulating miRNAs by Chip-Based Digital PCR.Biomedicines. 2022 Jun 8;10(6):1354. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061354. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740375 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases: the beats never stop.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018 Jul;39(7):1065-1067. doi: 10.1038/aps.2018.43. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018. PMID: 29926843 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Release and Detection of microRNA by Combining Magnetic Hyperthermia and Electrochemistry Modules on a Microfluidic Chip.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Dec 29;21(1):185. doi: 10.3390/s21010185. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33383936 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

