Multimodal profiling of single-cell morphology, electrophysiology, and gene expression using Patch-seq
- PMID: 29189773
- PMCID: PMC6422019
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2017.120
Multimodal profiling of single-cell morphology, electrophysiology, and gene expression using Patch-seq
Abstract
Neurons exhibit a rich diversity of morphological phenotypes, electrophysiological properties, and gene-expression patterns. Understanding how these different characteristics are interrelated at the single-cell level has been difficult because of the lack of techniques for multimodal profiling of individual cells. We recently developed Patch-seq, a technique that combines whole-cell patch-clamp recording, immunohistochemistry, and single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) to comprehensively profile single neurons from mouse brain slices. Here, we present a detailed step-by-step protocol, including modifications to the patching mechanics and recording procedure, reagents and recipes, procedures for immunohistochemistry, and other tips to assist researchers in obtaining high-quality morphological, electrophysiological, and transcriptomic data from single neurons. Successful implementation of Patch-seq allows researchers to explore the multidimensional phenotypic variability among neurons and to correlate gene expression with phenotype at the level of single cells. The entire procedure can be completed in ∼2 weeks through the combined efforts of a skilled electrophysiologist, molecular biologist, and biostatistician.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING FINANCIAL INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
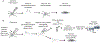
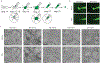



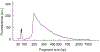

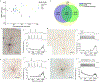
References
Key References
-
- Cadwell CR & Tolias AS (2016) Correlating cellular morphology, physiology, and gene expression using Patch-Seq. In: Using single-cell genomics to analyze neurons, glia, and circuits. (McCarroll S, ed) pp. 41–51. San Diego, CA: Society for Neuroscience.
References
-
- Tang F et al., mRNA-Seq whole-transcriptome analysis of a single cell. Nature methods 6, 377–382 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Picelli S et al., Smart-seq2 for sensitive full-length transcriptome profiling in single cells. Nature methods 10, 1096–1098 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Hashimshony T, Wagner F, Sher N, Yanai I, CEL-Seq: single-cell RNA-Seq by multiplexed linear amplification. Cell Rep 2, 666–673 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

