Chronic exposure to a glyphosate-containing pesticide leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and increased reactive oxygen species production in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 29190595
- PMCID: PMC5803312
- DOI: 10.1016/j.etap.2017.11.005
Chronic exposure to a glyphosate-containing pesticide leads to mitochondrial dysfunction and increased reactive oxygen species production in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
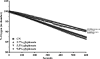
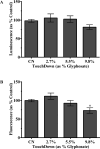
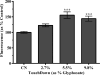
Glyphosate-containing herbicides are among the most widely-used in the world. Although glyphosate itself is relatively non-toxic, growing evidence suggests that commercial herbicide formulations may lead to increased oxidative stress and mitochondrial inhibition. In order to assess these mechanisms in vivo, we chronically (24h) exposed Caenorhabditis elegans to various concentrations of the glyphosate-containing herbicide TouchDown (TD). Following TD exposure, we evaluated the function of specific mitochondrial electron transport chain complexes. Initial oxygen consumption studies demonstrated inhibition in mid- and high-TD concentration treatment groups compared to controls. Results from tetramethylrhodamine ethyl ester and ATP assays indicated reductions in the proton gradient and ATP levels, respectively. Additional studies were designed to determine whether TD exposure resulted in increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Data from hydrogen peroxide, but not superoxide or hydroxyl radical, assays showed statistically significant increases in this specific ROS. Taken together, these data indicate that exposure of Caenorhabditis elegans to TD leads to mitochondrial inhibition and hydrogen peroxide production.
Keywords: C. elegans; Glyphosate; Herbicide; Hydrogen peroxide; Mitochondrial inhibition; Reactive oxygen species.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Allen MT, Levy LS. Parkinson's Disease and Pesticide Exposure: A New Assessment. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2013;43:515–534. - PubMed
-
- Bailey DC, Todt CE, Orfield SE, Denney RD, Snapp IB, Negga R, Montgomery KM, Bailey AC, Pressley AS, Traynor WL, Fitsanakis VA. Caenorhabditis elegans Chronically Exposed to a Mn/Zn Ethylene-bis-Dithiocarbamate Fungicide Show Mitochondrial Complex I Inhibition and Increased Reactive Oxygen Species. Neurotoxicology. 2016;56:170–179. - PubMed
-
- Baltazar MT, Dinis-Oliveira RJ, de Lourdes Bastos M, Tsatsakis AM, Duarte JA, Carvalho F. Pesticides Exposure as Etiological Factors of Parkinson's Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Mechanistic Approach. Toxicol Lett. 2014;230:85–103. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

