Novel molecular imaging ligands targeting matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 for imaging of unstable atherosclerotic plaques
- PMID: 29190653
- PMCID: PMC5708805
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187767
Novel molecular imaging ligands targeting matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 for imaging of unstable atherosclerotic plaques
Abstract
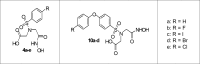
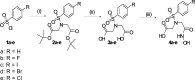
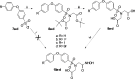
Molecular imaging of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) may allow detection of atherosclerotic lesions vulnerable to rupture. In this study, we develop a novel radiolabelled compound that can target gelatinase MMP subtypes (MMP2/9) with high selectivity and inhibitory potency. Inhibitory potencies of several halogenated analogues of MMP subtype-selective inhibitors (N-benzenesulfonyliminodiacetyl monohydroxamates and N-halophenoxy-benzenesulfonyl iminodiacetyl monohydroxamates) were in the nanomolar range for MMP2/9. The analogue with highest inhibitory potency and selectivity was radiolabelled with [123I], resulting in moderate radiochemical yield, and high radiochemical purity. Biodistribution studies in mice, revealed stabilization in blood 1 hour after intravenous bolus injection. Intravenous infusion of the radioligand and subsequent autoradiography of excised aortas showed tracer uptake in atheroprone mice. Distribution of the radioligand showed co-localization with MMP2/9 immunohistochemical staining. In conclusion, we have developed a novel selective radiolabeled MMP2/9 inhibitor, suitable for single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging that effectively targets atherosclerotic lesions in mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
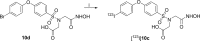

References
-
- Naghavi M, Libby P, Falk E, Casscells SW, Litovsky S, Rumberger J, et al. From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient: a call for new definitions and risk assessment strategies: Part I. Circulation 2003; 108(14): 1664–72. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000087480.94275.97 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Finn AV, Gold HK, Tulenko TN, et al. Atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability to rupture: angiogenesis as a source of intraplaque hemorrhage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005; 25(10): 2054–61. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000178991.71605.18 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ohshima S, Petrov A, Fujimoto S, Zhou J, Azure M, Edwards DS, et al. Molecular imaging of matrix metalloproteinase expression in atherosclerotic plaques of mice deficient in apolipoprotein e or low-density-lipoprotein receptor. J Nucl Med 2009; 50(4): 612–7. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.108.055889 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hugenberg V, Breyholz HJ, Riemann B, Hermann S, Schober O, Schafers M, et al. A new class of highly potent matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors based on triazole-substituted hydroxamates: (radio)synthesis and in vitro and first in vivo evaluation. J Med Chem 2012; 55(10): 4714–27. doi: 10.1021/jm300199g - DOI - PubMed
-
- Matusiak N, van Waarde A, Bischoff R, Oltenfreiter R, van de Wiele C, Dierckx RA, et al. Probes for non-invasive matrix metalloproteinase-targeted imaging with PET and SPECT. Curr Pharm Des 2013; 19(25): 4647–72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

