Metformin activates type I interferon signaling against HCV via activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase
- PMID: 29190886
- PMCID: PMC5696152
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20248
Metformin activates type I interferon signaling against HCV via activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase
Abstract
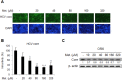
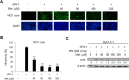
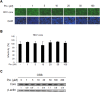
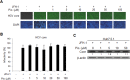
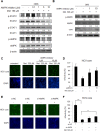
Activation of the type I interferon (IFN) signaling pathway is essential for the eradication of hepatitis C virus (HCV). Metformin can activate adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) to reduce insulin resistance. Cross talks between AMPK and IFN signaling remain unclear. To understand the influence of metformin on the type I IFN signaling pathway and HCV infection, the full-length HCV replicon OR6 cells and the infectious HCV clones JFH1 were used to assess the anti-HCV effect of the insulin sensitizers, metformin and pioglitazone. Immunofluorescence staining and the immunoblotting of HCV viral protein demonstrated that metformin, but not pioglitazone, inhibited HCV replication in OR-6 and JFH-1-infected Huh 7.5.1 cells. Immunoblotting data showed that metformin activated the phosphorylation of STAT-1 and STAT-2 in OR-6 and JFH-1 infected Huh 7.5.1 cells. Metformin enhanced the phosphorylation of AMPK, and the metformin-activated IFN signaling was down-regulated by AMPK inhibitor. After treatment of AMPK inhibitor, the level of HCV core protein decreased by metformin can be rescued. In conclusion, metformin activates type I interferon signaling and inhibits the replication of HCV via activation of AMPK.
Keywords: AMPK; hepatits C virus; interferon; metformin.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kao JH, Chen DS. Changing disease burden of hepatocellular carcinoma in the Far East and Southeast Asia. Liver Int. 2005;25:696–703. - PubMed
-
- Santantonio T, Wiegand J, Gerlach JT. Acute hepatitis C: current status and remaining challenges. J Hepatol. 2008;49:625–633. - PubMed
-
- Fattovich G, Stroffolini T, Zagni I, Donato F. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: incidence and risk factors. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:S35–S50. - PubMed
-
- Shintani Y, Fujie H, Miyoshi H, Tsutsumi T, Tsukamoto K, Kimura S, Moriya K, Koike K. Hepatitis C virus infection and diabetes: direct involvement of the virus in the development of insulin resistance. Gastroenterology. 2004;126:840–848. - PubMed
-
- Sheikh MY, Choi J, Qadri I, Friedman JE, Sanyal AJ. Hepatitis C virus infection: molecular pathways to metabolic syndrome. Hepatology. 2008;47:2127–2133. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

