Acquisition of EGFR TKI resistance and EMT phenotype is linked with activation of IGF1R/NF-κB pathway in EGFR-mutant NSCLC
- PMID: 29190911
- PMCID: PMC5696177
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.21170
Acquisition of EGFR TKI resistance and EMT phenotype is linked with activation of IGF1R/NF-κB pathway in EGFR-mutant NSCLC
Abstract
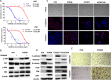
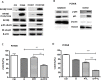
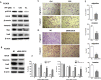
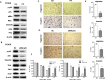
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is clinically associated with acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) in non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC). However, the mechanisms promoting EMT in EGFR TKI-resistant NSCLC have not been fully elucidated. Previous studies have suggested that IGF1R signaling is involved in both acquired EGFR TKI resistance in NSCLC and induction of EMT in some types of tumor. In this study, we further explored the role of the IGF1R signaling in the acquisition of EMT phenotype associated with EGFR TKI resistance in mutant-EGFR NSCLC. Compared to gefitinib-sensitive parental cells, gefitinib-resistant (GR) cells displayed an EMT phenotype associated with increased migration and invasion abilities with the concomitant activation of IGF1R and NF-κB p65 signaling. Inhibition of IGF1R or p65 using pharmacological inhibitor or specific siRNA partially restored sensitivity to gefitinib with the concomitant reversal of EMT in GR cells. Conversely, exogenous IGF1 induced both gefitinib resistance and accompanying EMT in parental cells. We also demonstrated that IGF1R could phosphorylate downstream Akt and Erk to activate NF-κB p65. Taken together, our findings indicate that activation of IGF1R/Akt/Erk/NF-κB signaling is linked to the acquisition of EGFR TKI resistance and EMT phenotype in EGFR-mutant NSCLC and could be a novel therapeutic target for advanced NSCLC.
Keywords: EGFR TKI resistance; EMT; IGF1R; NF-κB; NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST We declare that we have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Implication of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in IGF1R-induced resistance to EGFR-TKIs in advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 29;6(42):44332-45. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6293. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26554308 Free PMC article.
-
Intratumoral Heterogeneity in EGFR-Mutant NSCLC Results in Divergent Resistance Mechanisms in Response to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition.Cancer Res. 2015 Oct 15;75(20):4372-83. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0377. Epub 2015 Aug 17. Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26282169 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the IGF1R pathway potentially mediates acquired resistance to mutant-selective 3rd-generation EGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 19;7(16):22005-15. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8013. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26980747 Free PMC article.
-
The role of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016 Apr;5(2):172-82. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2016.04.07. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27186512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic strategy for advanced EGFR mutant non-small-cell lung carcinoma.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013 Dec;88(3):477-93. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2013.06.009. Epub 2013 Jul 31. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23911281 Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of Acquired Resistance towards EGFR Inhibitor Gefitinib in a Patient-Derived Xenograft Model of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Subsequent Molecular Characterization.Cells. 2019 Jul 18;8(7):740. doi: 10.3390/cells8070740. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31323891 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical importance of long non‑coding RNA LINC00460 expression in EGFR‑mutant lung adenocarcinoma.Int J Oncol. 2020 Jan;56(1):243-257. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4919. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Int J Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31789388 Free PMC article.
-
Repositioning Aspirin to Treat Lung and Breast Cancers and Overcome Acquired Resistance to Targeted Therapy.Front Oncol. 2020 Jan 14;9:1503. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01503. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31993373 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging application of genomics-guided therapeutics in personalized lung cancer treatment.Ann Transl Med. 2018 May;6(9):160. doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.05.02. Ann Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29911108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic silencing of miR-483-3p promotes acquired gefitinib resistance and EMT in EGFR-mutant NSCLC by targeting integrin β3.Oncogene. 2018 Aug;37(31):4300-4312. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0276-2. Epub 2018 May 2. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29717264 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, Lindeman N, Gale CM, Zhao X, Christensen J, Kosaka T, Holmes AJ, Rogers AM, et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 2007;316:1039–43. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Jänne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, Johnson BE, Eck MJ, Tenen DG, Halmos B. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:786–92. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi S, Ji H, Yuza Y, Meyerson M, Wong KK, Tenen DG, Halmos B. An alternative inhibitor overcomes resistance caused by a mutation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Cancer Res. 2005;65:7096–101. - PubMed
-
- Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D, Digumarthy S, Turke AB, Fidias P, Bergethon K, Shaw AT, Gettinger S, Cosper AK, Akhavanfard S, Heist RS, Temel J, et al. Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:75ra26. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

