Copy number variation meta-analysis reveals a novel duplication at 9p24 associated with multiple neurodevelopmental disorders
- PMID: 29191242
- PMCID: PMC5709845
- DOI: 10.1186/s13073-017-0494-1
Copy number variation meta-analysis reveals a novel duplication at 9p24 associated with multiple neurodevelopmental disorders
Abstract
Background: Neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders represent a wide spectrum of heterogeneous yet inter-related disease conditions. The overlapping clinical presentations of these diseases suggest a shared genetic etiology. We aim to identify shared structural variants spanning the spectrum of five neuropsychiatric disorders.
Methods: We investigated copy number variations (CNVs) in five cohorts, including schizophrenia (SCZ), bipolar disease (BD), autism spectrum disorders (ASD), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and depression, from 7849 cases and 10,799 controls. CNVs were called based on intensity data from genome-wide SNP arrays and CNV frequency was compared between cases and controls in each disease cohort separately. Meta-analysis was performed via a gene-based approach. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) was employed to validate novel significant loci.
Results: In our meta-analysis, two genes containing CNVs with exonic overlap reached genome-wide significance threshold of meta P value < 9.4 × 10-6 for deletions and 7.5 × 10-6 for duplications. We observed significant overlap between risk CNV loci across cohorts. In addition, we identified novel significant associations of DOCK8/KANK1 duplications (meta P value = 7.5 × 10-7) across all cohorts, and further validated the CNV region with qPCR.
Conclusions: In the first large scale meta-analysis of CNVs across multiple neurodevelopmental/psychiatric diseases, we uncovered novel significant associations of structural variants in the locus of DOCK8/KANK1 shared by five diseases, suggesting common etiology of these clinically distinct neurodevelopmental conditions.
Keywords: Copy number variation; DOCK8; Gene-based analysis; Meta-analysis; Neuropsychiatric disorders; Quantitative PCR.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All cohorts in our study were from published datasets. Study protocols used in each cohort have been approved by corresponding Institutional Review Board or equivalent committees, and written informed consent was given from each participant or parent. Our research complies with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Dr. Nadine Cohen is a former employee of Janssen Research & Development. Drs. Dai Wang and Qingqin Li are current employees of Janssen Research & Development. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests. Funding for this study included sponsored research to The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia by Janssen Research & Development, LLC.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
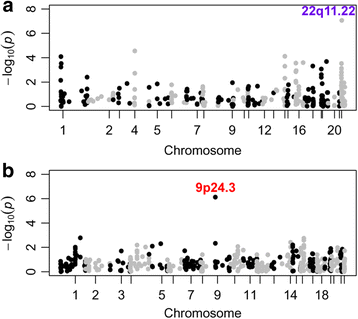
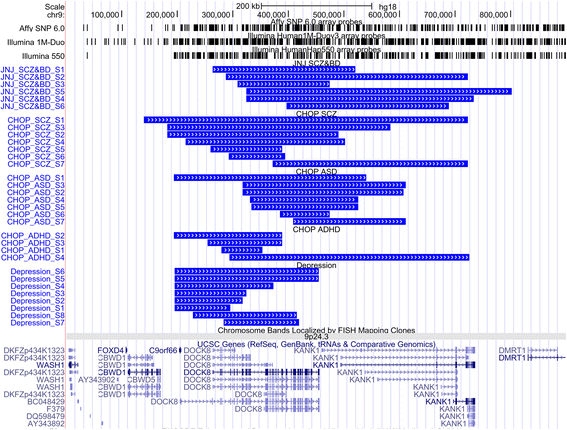
Comment in
-
Mapping a shared genetic basis for neurodevelopmental disorders.Genome Med. 2017 Dec 14;9(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s13073-017-0503-4. Genome Med. 2017. PMID: 29241461 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Lee SH, Ripke S, Neale BM, Faraone SV, Purcell SM, Perlis RH, Mowry BJ, Thapar A, Goddard ME, et al. Genetic relationship between five psychiatric disorders estimated from genome-wide SNPs. Nat Genet. 2013;45(9):984–94. doi: 10.1038/ng.2711. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Biomedical Graduate Studies training grant/University of Pennsylvania
- sponsored research to The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia/Janssen Research and Development
- an Institutional Development Award to the Center for Applied Genomics/Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
- R01 MH097284/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01MH097284-01/National Institute of Mental Health
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

