Histamine H2 Receptor Polymorphisms, Myocardial Transcripts, and Heart Failure (from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and Beta-Blocker Effect on Remodeling and Gene Expression Trial)
- PMID: 29191567
- PMCID: PMC5742297
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2017.10.016
Histamine H2 Receptor Polymorphisms, Myocardial Transcripts, and Heart Failure (from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and Beta-Blocker Effect on Remodeling and Gene Expression Trial)
Abstract
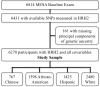
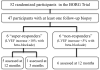
Myocardial H2 receptor activation contributes to heart failure (HF) in preclinical models, and H2 receptor antagonists are associated with decreased HF incidence. This study evaluated whether H2 histamine receptor (HRH2) single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are associated with HF incidence and whether myocardial transcript abundance is associated with HF recovery. The association of SNPs in HRH2 with incident HF was characterized using Cox proportional hazards regression among participants in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Differences in myocardial HRH2 transcripts were characterized in participants with dilated cardiomyopathy comparing 6 "super-responders" with 6 nonresponders to β blockade in the Beta-Blocker Effect on Remodeling and Gene Expression Trial. In MESA, no candidate SNP was associated with HF in black, Hispanic, or white participants. The rs2241562 minor allele was present only in Chinese participants and the adjusted HF hazard among those with 1 or more copies of this allele was 3.7, 95% confidence interval 1.0 to 13.4. In BORG, super-responders to β blockade had higher levels of myocardial HRH2 transcript at baseline compared with nonresponders (fragments per kilobase per transcript per million mapped reads: Variant 2, 5.5 ± 1.1 compared with 3.2 ± 0.8 in nonresponders, p = 0.002; Variant 1 + 2, 32.1 ± 7.4 compared with 23.3 ± 4.2 in nonresponders, p = 0.04). In conclusion, the presence of a minor allele at rs2241562 was associated with increased HF incidence in Chinese participants. Differences in myocardial HRH2 transcript abundance were seen in participants with dilated cardiomyopathy who responded to β blockade. These observations support the hypothesis that HRH2 is involved in the pathogenesis of HF.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bild DE, Bluemke DA, Burke GL, Detrano R, Diez Roux AV, Folsom AR, Greenland P, Jacob DR, Kronmal R, Liu K, Nelson JC, O’Leary D, Saad MF, Shea S, Szklo M, Tracy RP. Multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis: objectives and design. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;156:871–881. - PubMed
-
- MESA Manual of Operations: Field Center and Laboratory Procedures. mesa-nhlbiorg. Available at: http://www.mesa-nhlbi.org/manuals.aspx. Accessed March 17, 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- L30 HL110124/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002317/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL048013/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL125725/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065226/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007822/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR000421/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL071118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC065226/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous