Sterol 27-hydroxylase gene dosage and the antiatherosclerotic effect of Rifampicin in mice
- PMID: 29191818
- PMCID: PMC5784176
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20171162
Sterol 27-hydroxylase gene dosage and the antiatherosclerotic effect of Rifampicin in mice
Abstract
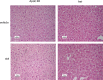
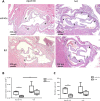
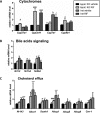
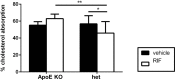
Sterol 27-hydroxylase (CYP27A1) catalyzes the hydroxylation of cholesterol to 27-hydroxycholesterol (27-OHC) and regulates cholesterol homeostasis. In Cyp27a1/ Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) double knockout (KO) mice fed with Western diet (WD), the atherosclerotic phenotype found in ApoE KO mice was reversed. As protective mechanism, up-regulation of Cyp3a11 and Cyp7a1 was proposed. Cyp27a1 heterozygote/ApoE KO (het) mice, with reduced Cyp27a1 expression and normal levels of Cyp7a1 and Cyp3a11, developed more severe lesions than ApoE KO mice. To analyze the contribution of Cyp3a11 to the protection of atherosclerosis development, Cyp3a11 was induced by Rifampicin (RIF) in ApoE KO and het mice. Males were fed with WD and treated daily with RIF (10 mg/kg ip) or vehicle for 4 weeks. Atherosclerosis was quantified in the aortic valve. Plasma lipids and 27-hydroxycholesterol (27-OHC), expression of cytochromes P450 and genes involved in cholesterol transport and bile acids (BAs) signaling in liver and intestine, and intestinal cholesterol absorption were analyzed. RIF increased expression of hepatic but not intestinal Cyp3a11 4-fold in both genotypes. In ApoE KO mice treated with RIF, we found a 2-fold decrease in plasma cholesterol, and a 2-fold increase in high-density lipoprotein/low-density lipoprotein ratio and CY27A1 activity. Intestinal cholesterol absorption remained unchanged and atherosclerotic lesions decreased approximately 3-fold. In het mice, RIF had no effect on plasma lipids composition, CYP27A1 activity, and atherosclerotic plaque development, despite a reduction in cholesterol absorption. In conclusion, the antiatherogenic effect of Cyp3a11 induction by RIF was also dependent on Cyp27a1 expression.
Keywords: 27-hydroxycholesterol; ApoE knock out mice; Western diet.
© 2018 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Downregulation of Cyp7a1 by Cholic Acid and Chenodeoxycholic Acid in Cyp27a1/ApoE Double Knockout Mice: Differential Cardiovascular Outcome.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Oct 28;11:586980. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.586980. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 33193099 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Cyp27A1 gene dosage on atherosclerosis development in ApoE-knockout mice.FASEB J. 2014 Mar;28(3):1198-209. doi: 10.1096/fj.13-233791. Epub 2013 Dec 10. FASEB J. 2014. PMID: 24327605 Free PMC article.
-
Bile Acid Homeostasis in a Cholesterol 7α-Hydroxylase and Sterol 27-Hydroxylase Double Knockout Mouse Model.Hepatology. 2019 Jul;70(1):389-402. doi: 10.1002/hep.30612. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 30864232 Free PMC article.
-
Cytochrome P450s in the synthesis of cholesterol and bile acids--from mouse models to human diseases.FEBS J. 2012 May;279(9):1516-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08432.x. Epub 2011 Dec 22. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22111624 Review.
-
Cholesterol-metabolizing cytochromes P450.Drug Metab Dispos. 2006 Apr;34(4):513-20. doi: 10.1124/dmd.105.008789. Epub 2006 Jan 24. Drug Metab Dispos. 2006. PMID: 16434543 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial Cholesterol Metabolites in a Bile Acid Synthetic Pathway Drive Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Revised "Two-Hit" Hypothesis.Cells. 2023 May 20;12(10):1434. doi: 10.3390/cells12101434. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37408268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
27-Hydroxycholesterol-Induced Dysregulation of Cholesterol Metabolism Impairs Learning and Memory Ability in ApoE ε4 Transgenic Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 1;23(19):11639. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911639. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bjorkhem I. (1992) Mechanism of degradation of the steroid side chain in the formation of bile acids. J. Lipid Res. 33, 455–471 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

