Monkeys share the neurophysiological basis for encoding sound periodicities captured by the frequency-following response with humans
- PMID: 29192170
- PMCID: PMC5709359
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-16774-8
Monkeys share the neurophysiological basis for encoding sound periodicities captured by the frequency-following response with humans
Abstract
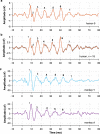
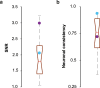
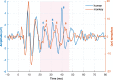
The extraction and encoding of acoustical temporal regularities are fundamental for human cognitive auditory abilities such as speech or beat entrainment. Because the comparison of the neural sensitivity to temporal regularities between human and animals is fundamental to relate non-invasive measures of auditory processing to their neuronal basis, here we compared the neural representation of auditory periodicities between human and non-human primates by measuring scalp-recorded frequency-following response (FFR). We found that rhesus monkeys can resolve the spectrotemporal structure of periodic stimuli to a similar extent as humans by exhibiting a homologous FFR potential to the speech syllable /da/. The FFR in both species is robust and phase-locked to the fundamental frequency of the sound, reflecting an effective neural processing of the fast-periodic information of subsyllabic cues. Our results thus reveal a conserved neural ability to track acoustical regularities within the primate order. These findings open the possibility to study the neurophysiology of complex sound temporal processing in the macaque subcortical and cortical areas, as well as the associated experience-dependent plasticity across the auditory pathway in behaving monkeys.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Kraus, N., Anderson, S. & White-Schwoch T. The Frequency-Following Response: A Window into Human Communication (eds Kraus, N. et al.) Ch. 1, 1–15 (Springer-Nature, 2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

