Mineral particles stimulate innate immunity through neutrophil extracellular traps containing HMGB1
- PMID: 29192209
- PMCID: PMC5709501
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-16778-4
Mineral particles stimulate innate immunity through neutrophil extracellular traps containing HMGB1
Abstract
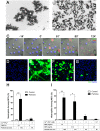
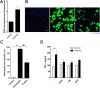
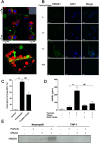
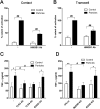
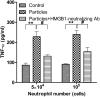
Calcium phosphate-based mineralo-organic particles form spontaneously in the body and may represent precursors of ectopic calcification. We have shown earlier that these particles induce activation of caspase-1 and secretion of IL-1β by macrophages. However, whether the particles may produce other effects on immune cells is unclear. Here, we show that these particles induce the release of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in a size-dependent manner by human neutrophils. Intracellular production of reactive oxygen species is required for particle-induced NET release by neutrophils. NETs contain the high-mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1), a DNA-binding protein capable of inducing secretion of TNF-α by a monocyte/macrophage cell line and primary macrophages. HMGB1 functions as a ligand of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 on macrophages, leading to activation of the MyD88 pathway and TNF-α production. Furthermore, HMGB1 is critical to activate the particle-induced pro-inflammatory cascade in the peritoneum of mice. These results indicate that mineral particles promote pro-inflammatory responses by engaging neutrophils and macrophages via signaling of danger signals through NETs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

