Thermodynamic secrets of multidrug resistance: A new take on transport mechanisms of secondary active antiporters
- PMID: 29193407
- PMCID: PMC5818768
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.3355
Thermodynamic secrets of multidrug resistance: A new take on transport mechanisms of secondary active antiporters
Abstract
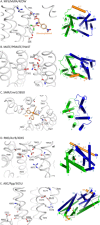
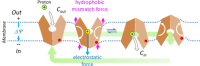
Multidrug resistance (MDR) presents a growing challenge to global public health. Drug extrusion transporters play a critical part in MDR; thus, their mechanisms of substrate recognition are being studied in great detail. In this work, we review common structural features of key transporters involved in MDR. Based on our membrane potential-driving hypothesis, we propose a general energy-coupling mechanism for secondary-active antiporters. This putative mechanism provides a common framework for understanding poly-specificity of most-if not all-MDR transporters.
Keywords: energy coupling; exporters; membrane potential; multidrug resistance; titratable residue.
© 2017 The Protein Society.
Figures
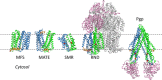

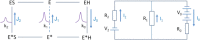
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

