Temporal changes in retinal vascular parameters associated with successful panretinal photocoagulation in proliferative diabetic retinopathy: A prospective clinical interventional study
- PMID: 29193789
- PMCID: PMC6099241
- DOI: 10.1111/aos.13617
Temporal changes in retinal vascular parameters associated with successful panretinal photocoagulation in proliferative diabetic retinopathy: A prospective clinical interventional study
Abstract
Purpose: We aimed to investigate changes in retinal vascular geometry over time after panretinal photocoagulation (PRP) in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR).
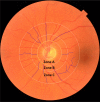
Methods: Thirty-seven eyes with PDR were included. Wide-field fluorescein angiography (Optomap, Optos PLC., Dunfermline, Scotland, UK) was used to diagnose PDR at baseline and to assess activity at follow-up month three and six. At each time-point, a trained grader measured retinal vessel geometry on optic disc (OD) centred images using semiautomated software (SIVA, Singapore I Vessel Assessment, National University of Singapore, Singapore) according to a standardized protocol.
Results: At baseline, the mean age and duration of diabetes were 52.8 and 22.3 years, and 65% were male. Mean HbA1c was 69.9 mmol/mol, and blood pressure was 155/84 mmHg. Of the 37 eyes with PDR, eight (22%) eyes had progression at month three and 13 (35%) progressed over six months. Baseline characteristics, including age, sex, duration of diabetes, HbA1c, blood pressure, vessel geometric variables and total amount of laser energy delivered did not differ by progression status. However, compared to patients with progression of PDR, patients with favourable treatment outcome had alterations in the retinal arteriolar structures from baseline to month six (calibre, 154.3 μm versus 159.5 μm, p = 0.04, tortuosity 1.12 versus 1.10, p = 0.04) and in venular structures from baseline to month three (fractal dimension 1.490 versus 1.499, p = 0.04, branching coefficient (BC) 1.32 versus 1.37, p = 0.01).
Conclusion: In patients with PDR, successful PRP leads to alterations in the retinal vascular structure. However, baseline retinal vascular geometry characteristics did not predict treatment outcome.
Keywords: NAVILAS; SIVA; clinical; computer-assisted; humans; panretinal photocoagulation; proliferative diabetic retinopathy; prospective; retinal vessel geometry.
© 2017 The Authors. Acta Ophthalmologica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica Foundation.
Figures
References
-
- Armstrong RA (2013): Statistical guidelines for the analysis of data obtained from one or both eyes. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 33: 7–14. - PubMed
-
- Broe R, Rasmussen ML, Frydkjaer‐Olsen U et al. (2014a): Retinal vessel calibers predict long‐term microvascular complications in type 1 diabetes: the danish cohort of pediatric diabetes 1987 (DCPD1987). Diabetes 63: 3906–3914. - PubMed
-
- Broe R, Rasmussen ML, Frydkjaer‐Olsen U, Olsen BS, Mortensen HB, Peto T & Grauslund J (2014b): Retinal vascular fractals predict long‐term microvascular complications in type 1 diabetes mellitus: the Danish Cohort of Pediatric Diabetes 1987 (DCPD1987). Diabetologia 57: 2215–2221. - PubMed
-
- Cheung CY, Hsu W, Lee ML et al. (2010a): A new method to measure peripheral retinal vascular caliber over an extended area. Microcirculation 17: 495–503. - PubMed
-
- Cheung N, Mitchell P & Wong TY (2010b): Diabetic retinopathy. Lancet 376: 124–136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

