IL-35 recombinant protein reverses inflammatory bowel disease and psoriasis through regulation of inflammatory cytokines and immune cells
- PMID: 29193791
- PMCID: PMC5783847
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13428
IL-35 recombinant protein reverses inflammatory bowel disease and psoriasis through regulation of inflammatory cytokines and immune cells
Abstract
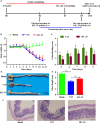
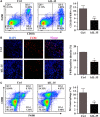
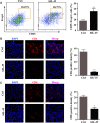
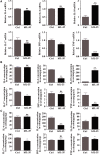
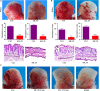
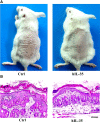
Interleukin-35 (IL-35), a member of the IL-12 family, functions as a new anti-inflammatory factor involved in arthritis, psoriasis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and other immune diseases. Although IL-35 can significantly prevent the development of inflammation in many diseases, there have been no early studies accounting for the role of IL-35 recombinant protein in IBD and psoriasis. In this study, we assessed the therapeutic potential of IL-35 recombinant protein in three well-known mouse models: the dextransulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis mouse model, the keratin14 (K14)-vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A)-transgenic (Tg) psoriasis mouse model and the imiquimod (IMQ)-induced psoriasis mouse model. Our results indicated that IL-35 recombinant protein can slow down the pathologic process in DSS-induced acute colitis mouse model by decreasing the infiltrations of macrophages, CD4+ T and CD8+ T cells and by promoting the infiltration of Treg cells. Further analysis demonstrated that IL-35 recombinant protein may regulate inflammation through promoting the secretion of IL-10 and inhibiting the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-α and IL-17 in acute colitis model. In addition, lower dose of IL-35 recombinant protein could achieve long-term treatment effects as TNF-α monoclonal antibody did in the psoriasis mouse. In summary, the remarkable therapeutic effects of IL-35 recombinant protein in acute colitis and psoriasis mouse models indicated that IL-35 recombinant protein had a variety of anti-inflammatory effects and was expected to become an effective candidate drug for the treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: IL-35 recombinant protein; immunoregulation; inflammatory bowel disease; psoriasis.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-35 Decelerates the Inflammatory Process by Regulating Inflammatory Cytokine Secretion and M1/M2 Macrophage Ratio in Psoriasis.J Immunol. 2016 Sep 15;197(6):2131-44. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1600446. Epub 2016 Aug 15. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27527600
-
Toll-Like Receptor 7 Agonist-Induced Dermatitis Causes Severe Dextran Sulfate Sodium Colitis by Altering the Gut Microbiome and Immune Cells.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Sep 25;7(1):135-156. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2018.09.010. eCollection 2019. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 30510995 Free PMC article.
-
Restoration of mucosal integrity and epithelial transport function by concomitant anti-TNFα treatment in chronic DSS-induced colitis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2018 Aug;96(8):831-843. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1658-1. Epub 2018 Jun 20. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018. PMID: 29967942
-
IL-19 as a potential therapeutic in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases.Curr Pharm Des. 2011 Nov;17(34):3776-80. doi: 10.2174/138161211798357845. Curr Pharm Des. 2011. PMID: 22103848 Review.
-
Role of Inflammation in the Development of Colorectal Cancer.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2021;21(1):77-90. doi: 10.2174/1871530320666200909092908. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2021. PMID: 32901590 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation between Serum IL-35 Levels and Bone Loss in Postmenopausal Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Aug 26;2019:9139145. doi: 10.1155/2019/9139145. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31534439 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of IL-35 by Lactococcus lactis Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 20;9:2691. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02691. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30515168 Free PMC article.
-
Lower serum interleukin-22 and interleukin-35 levels are associated with disease status in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020 Feb;26(2):251-259. doi: 10.1111/cns.13198. Epub 2019 Jul 24. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020. PMID: 31342670 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for targeting cytokines in inflammatory bowel disease.Nat Rev Immunol. 2024 Aug;24(8):559-576. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01008-6. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38486124 Review.
-
Interleukin 35 induced Th2 and Tregs bias under normal conditions in mice.PeerJ. 2018 Sep 21;6:e5638. doi: 10.7717/peerj.5638. eCollection 2018. PeerJ. 2018. PMID: 30258726 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Choi J, Leung PS, Bowlus C, et al IL‐35 and autoimmunity: a comprehensive perspective. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015; 49: 327–32. - PubMed
-
- Collison LW, Workman CJ, Kuo TT, et al The inhibitory cytokine IL‐35 contributes to regulatory T‐cell function. Nature. 2007; 450: 566–9. - PubMed
-
- Ye S, Wu J, Zhou L, et al Interleukin‐35: the future of hyperimmune‐related diseases? J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013; 33: 285–91. - PubMed
-
- Guan SY, Leng RX, Khan MI, et al Interleukin‐35: a potential therapeutic agent for autoimmune diseases. Inflammation. 2017; 40: 303–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

