Experiences using and organizing HIV self-testing
- PMID: 29194120
- PMCID: PMC5758403
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001705
Experiences using and organizing HIV self-testing
Abstract
Objective: HIV self-testing (HIVST) is now officially recommended by the WHO, yet much of HIVST evidence to date has focused on quantitative data and hypothetical concerns. Effective scale-up of HIVST in diverse local contexts requires qualitative data from experiences using and organizing HIVST. This qualitative systematic review aims to appraise and synthesize research evidence on experiences using and organizing HIVST.
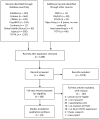
Methods: We conducted a systematic search of seven primary literature databases, four gray literature sources, and reference lists reporting qualitative evidence on HIVST. Data extraction and thematic analysis were used to synthesize findings. Quality of studies was assessed using the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme tool. Confidence in review findings was evaluated using the Confidence in the Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative Research approach. The review protocol was registered (CRD42015027607).
Results: From 1266 potential articles, we included 18. Four studies were conducted in low-income countries, three in middle-income countries, 10 in high-income countries, and one in multiple countries. Generally, HIVST increased capacity to reach priority populations and expanded opportunities for service delivery. Self-testing was preferred to facility-based testing due to increased convenience and confidentiality, especially among stigmatized populations. HIVST decreased test-associated stigma compared with facility-based testing. HIVST generally empowered people because it provided greater control over individual testing needs. At the same time, HIVST rarely allowed husbands to coerce their wives to test.
Conclusions: This review suggests that HIVST should be offered as an additional HIV testing option to expand testing and empower testers. Adapting national policies to incorporate HIVST will be necessary to guide scale-up.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no competing interests.
References
-
- UNAIDS. 90-90-90-An ambitious treatment target to help end the AIDS epidemic. Geneva: 2014.
-
-
UNAIDS 2016 estimates
-
-
- WHO. Guidelines on HIV self-testing and partner notification: supplement to consolidated guidelines on HIV testing services. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical