Functional Foods and Lifestyle Approaches for Diabetes Prevention and Management
- PMID: 29194424
- PMCID: PMC5748760
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9121310
Functional Foods and Lifestyle Approaches for Diabetes Prevention and Management
Abstract
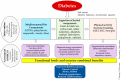
Functional foods contain biologically active ingredients associated with physiological health benefits for preventing and managing chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). A regular consumption of functional foods may be associated with enhanced anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, insulin sensitivity, and anti-cholesterol functions, which are considered integral to prevent and manage T2DM. Components of the Mediterranean diet (MD)-such as fruits, vegetables, oily fish, olive oil, and tree nuts-serve as a model for functional foods based on their natural contents of nutraceuticals, including polyphenols, terpenoids, flavonoids, alkaloids, sterols, pigments, and unsaturated fatty acids. Polyphenols within MD and polyphenol-rich herbs-such as coffee, green tea, black tea, and yerba maté-have shown clinically-meaningful benefits on metabolic and microvascular activities, cholesterol and fasting glucose lowering, and anti-inflammation and anti-oxidation in high-risk and T2DM patients. However, combining exercise with functional food consumption can trigger and augment several metabolic and cardiovascular protective benefits, but it is under-investigated in people with T2DM and bariatric surgery patients. Detecting functional food benefits can now rely on an "omics" biological profiling of individuals' molecular, genetics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, but is under-investigated in multi-component interventions. A personalized approach for preventing and managing T2DM should consider biological and behavioral models, and embed nutrition education as part of lifestyle diabetes prevention studies. Functional foods may provide additional benefits in such an approach.
Keywords: Mediterranean diet; bariatric surgery; functional food; green tea; nutrition counselling; physical activity; polyphenols; type 2 diabetes mellitus; yerba mate.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest or otherwise is declared as part of this work.
Figures
References
-
- WHO World Health Organization (WHO) Global Report on Diabetes. [(accessed on 9 October 2017)];2016 Available online: http://www.who.int/diabetes/global-report/en/
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas. [(accessed on 12 September 2017)]; 2015-7th Edition. Available online: http://www.diabetesatlas.org/
-
- Tuomilehto J., Lindstrom J., Eriksson J.G., Valle T.T., Hamalainen H., Ilanne-Parikka P., Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi S., Laakso M., Louheranta A., Rastas M., et al. Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001;344:1343–1350. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200105033441801. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pan X.R., Li G.W., Hu Y.H., Wang J.X., Yang W.Y., An Z.X., Hu Z.X., Lin J., Xiao J.Z., Cao H.B., et al. Effects of diet and exercise in preventing NIDDM in people with impaired glucose tolerance. The Da Qing IGT and Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care. 1997;20:537–544. doi: 10.2337/diacare.20.4.537. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

