Adiposity QTL Adip20 decomposes into at least four loci when dissected using congenic strains
- PMID: 29194435
- PMCID: PMC5711020
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188972
Adiposity QTL Adip20 decomposes into at least four loci when dissected using congenic strains
Abstract
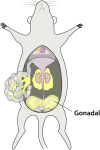
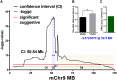
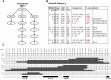
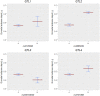
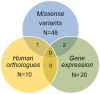
An average mouse in midlife weighs between 25 and 30 g, with about a gram of tissue in the largest adipose depot (gonadal), and the weight of this depot differs between inbred strains. Specifically, C57BL/6ByJ mice have heavier gonadal depots on average than do 129P3/J mice. To understand the genetic contributions to this trait, we mapped several quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for gonadal depot weight in an F2 intercross population. Our goal here was to fine-map one of these QTLs, Adip20 (formerly Adip5), on mouse chromosome 9. To that end, we analyzed the weight of the gonadal adipose depot from newly created congenic strains. Results from the sequential comparison method indicated at least four rather than one QTL; two of the QTLs were less than 0.5 Mb apart, with opposing directions of allelic effect. Different types of evidence (missense and regulatory genetic variation, human adiposity/body mass index orthologues, and differential gene expression) implicated numerous candidate genes from the four QTL regions. These results highlight the value of mouse congenic strains and the value of this sequential method to dissect challenging genetic architecture.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Reed DR, Bachmanov AA, Tordoff MG. Forty mouse strain survey of body composition. Physiol Behav. 2007;91(5):593–600. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2007.03.026 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reed DR, Duke FF, Ellis HK, Rosazza MR, Lawler MP, Alarcon LK, et al. Body fat distribution and organ weights of 14 common strains and a 22-strain consomic panel of rats. Physiol Behav. 2011;103:523–9. Epub 2011/04/21. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.04.006 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fried SK, Lee MJ, Karastergiou K. Shaping fat distribution: New insights into the molecular determinants of depot- and sex-dependent adipose biology. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2015;23(7):1345–52. doi: 10.1002/oby.21133 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eppig JT, Bult CJ, Kadin JA, Richardson JE, Blake JA, Anagnostopoulos A, et al. The Mouse Genome Database (MGD): from genes to mice—a community resource for mouse biology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33(Database issue):D471–5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki113 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Drinkwater NR, Gould MN. The long path from QTL to gene. PLoS Genet. 2012;8(9):e1002975 doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002975 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

