BmILF and i-motif structure are involved in transcriptional regulation of BmPOUM2 in Bombyx mori
- PMID: 29194483
- PMCID: PMC5829645
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx1207
BmILF and i-motif structure are involved in transcriptional regulation of BmPOUM2 in Bombyx mori
Abstract
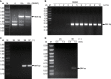
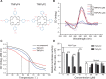
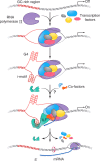
Guanine-rich and cytosine-rich DNA can form four-stranded DNA secondary structures called G-quadruplex (G4) and i-motif, respectively. These structures widely exist in genomes and play important roles in transcription, replication, translation and protection of telomeres. In this study, G4 and i-motif structures were identified in the promoter of the transcription factor gene BmPOUM2, which regulates the expression of the wing disc cuticle protein gene (BmWCP4) during metamorphosis. Disruption of the i-motif structure by base mutation, anti-sense oligonucleotides (ASOs) or inhibitory ligands resulted in significant decrease in the activity of the BmPOUM2 promoter. A novel i-motif binding protein (BmILF) was identified by pull-down experiment. BmILF specifically bound to the i-motif and activated the transcription of BmPOUM2. The promoter activity of BmPOUM2 was enhanced when BmILF was over-expressed and decreased when BmILF was knocked-down by RNA interference. This study for the first time demonstrated that BmILF and the i-motif structure participated in the regulation of gene transcription in insect metamorphosis and provides new insights into the molecular mechanism of the secondary structures in epigenetic regulation of gene transcription.
Figures




References
-
- Ruvkun G., Finney M.. Regulation of transcription and cell identity by POU domain proteins. Cell. 1991; 64:475–478. - PubMed
-
- Herr W., Sturm R.A., Clerc R.G., Corcoran L.M., Baltimore D., Sharp P.A., Ingraham H.A., Rosenfeld M.G., Finney M., Ruvkun G. et al. The POU domain: a large conserved region in the mammalian pit-1, oct-1, oct-2, and Caenorhabditis elegans unc-86 gene products. Genes Dev. 1988; 2:1513–1516. - PubMed
-
- Ryan A.K., Rosenfeld M.G.. POU domain family values: flexibility, partnerships, and developmental codes. Genes Dev. 1997; 11:1207–1225. - PubMed
-
- Andersen B., Rosenfeld M.G.. POU domain factors in the neuroendocrine system: lessons from developmental biology provide insights into human disease. Endocr. Rev. 2001; 22:2–35. - PubMed
-
- Komiyama T., Johnson W.A., Luo L., Jefferis G.S.. From lineage to wiring specificity POU domain transcription factors control precise connections of Drosophila olfactory projection neurons. Cell. 2003; 112:157–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

