The presynaptic scaffolding protein Piccolo organizes the readily releasable pool at the calyx of Held
- PMID: 29194628
- PMCID: PMC5899986
- DOI: 10.1113/JP274885
The presynaptic scaffolding protein Piccolo organizes the readily releasable pool at the calyx of Held
Abstract
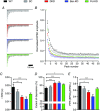
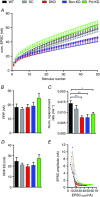
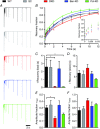
Key points: Bassoon and Piccolo do not mediate basal synaptic vesicle release at a high-frequency synapse. Knockdown of Bassoon increases short-term depression at the calyx of Held. Both Bassoon and Piccolo have shared functions in synaptic vesicle replenishment during high-frequency synaptic transmission. Piccolo organizes the readily releasable pool of synaptic vesicles. It safeguards a fraction of them to be not immediately available for action potential-induced release. This enables the synapse to sustain high-frequency synaptic transmission over long periods.
Abstract: Synaptic vesicles (SVs) are released at the active zone (AZ), a specialized region of the presynaptic plasma membrane organized by a highly interconnected network of multidomain proteins called the cytomatrix of the active zone (CAZ). Two core components of the CAZ are the large, highly homologous scaffolding proteins Bassoon and Piccolo, whose function is not well understood. To investigate their role in synaptic transmission, we established the small hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated in vivo knockdown (KD) of Bassoon and Piccolo at the rat calyx of Held synapse. KD of Bassoon and Piccolo, separately or simultaneously, did not affect basic SV release. However, short-term depression (STD) was prominently increased by the KD of Bassoon, whereas KD of Piccolo only had a minor effect. The observed alterations in STD were readily explained by reduced SV replenishment in synapses deficient in either of the proteins. Thus, the regulation of SV refilling during ongoing synaptic activity is a shared function of Bassoon and Piccolo, although Bassoon appears to be more efficient. Moreover, we observed the recruitment of slowly-releasing SVs of the readily-releasable pool (RRP), which are normally not available for action potential-induced release, during high-frequency stimulation in Piccolo-deficient calyces. Therefore, the results obtained in the present study suggest a novel and specific role for Piccolo in the organization of the subpools of the RRP.
Keywords: active zone; replenishment; synaptic vesicles.
© 2017 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology © 2017 The Physiological Society.
Figures



Comment in
-
Allegro giusto: piccolo, bassoon and clarinet set the tempo of vesicle pool replenishment.J Physiol. 2018 Apr 15;596(8):1315-1316. doi: 10.1113/JP275704. Epub 2018 Mar 25. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29446080 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Targeted three-dimensional immunohistochemistry reveals localization of presynaptic proteins Bassoon and Piccolo in the rat calyx of Held before and after the onset of hearing.J Comp Neurol. 2010 Apr 1;518(7):1008-29. doi: 10.1002/cne.22260. J Comp Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20127803
-
Piccolo Promotes Vesicle Replenishment at a Fast Central Auditory Synapse.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2017 Oct 25;9:14. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2017.00014. eCollection 2017. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29118709 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly of active zone precursor vesicles: obligatory trafficking of presynaptic cytomatrix proteins Bassoon and Piccolo via a trans-Golgi compartment.J Biol Chem. 2006 Mar 3;281(9):6038-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508784200. Epub 2005 Dec 21. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16373352
-
Molecular organization and assembly of the presynaptic active zone of neurotransmitter release.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006;43:49-68. doi: 10.1007/400_012. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2006. PMID: 17068967 Review.
-
Role of Bassoon and Piccolo in Assembly and Molecular Organization of the Active Zone.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2016 Jan 12;7:19. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2015.00019. eCollection 2015. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 26793095 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Effect on Hippocampal Synaptic Facilitation by the Presynaptic Protein Mover.Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2019 Nov 15;11:30. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2019.00030. eCollection 2019. Front Synaptic Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31803042 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Synaptic Vesicle Exo- and Endocytosis.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 4;10(7):1593. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071593. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35884898 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presynaptic Cytomatrix Proteins.Adv Neurobiol. 2023;33:23-42. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-34229-5_2. Adv Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37615862
-
Rebuilding essential active zone functions within a synapse.Neuron. 2022 May 4;110(9):1498-1515.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2022.01.026. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Neuron. 2022. PMID: 35176221 Free PMC article.
-
A Multiple Piccolino-RIBEYE Interaction Supports Plate-Shaped Synaptic Ribbons in Retinal Neurons.J Neurosci. 2019 Apr 3;39(14):2606-2619. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2038-18.2019. Epub 2019 Jan 29. J Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30696732 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altrock WD, tom Dieck S, Sokolov M, Meyer AC, Sigler A, Brakebusch C, Fässler R, Richter K, Boeckers TM, Potschka H, Brandt C, Löscher W, Grimberg D, Dresbach T, Hempelmann A, Hassan H, Balschun D, Frey JU, Brandstätter JH, Garner CC, Rosenmund C & Gundelfinger ED (2003). Functional inactivation of a fraction of excitatory synapses in mice deficient for the active zone protein bassoon. Neuron 37, 787–800. - PubMed
-
- Borst JG & Soria van Hoeve J (2012). The calyx of held synapse: from model synapse to auditory relay. Annu Rev Physiol 74, 199–224. - PubMed
-
- Davydova D, Marini C, King C, Klueva J, Bischof F, Romorini S, Montenegro‐Venegas C, Heine M, Schneider R, Schröder MS, Altrock WD, Henneberger C, Rusakov DA, Gundelfinger ED & Fejtova A (2014). Bassoon specifically controls presynaptic P/Q‐type Ca(2+) channels via RIM‐binding protein. Neuron 82, 181–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

