Epigenetic Therapy Ties MYC Depletion to Reversing Immune Evasion and Treating Lung Cancer
- PMID: 29195073
- PMCID: PMC5808406
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.022
Epigenetic Therapy Ties MYC Depletion to Reversing Immune Evasion and Treating Lung Cancer
Abstract
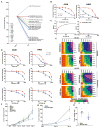
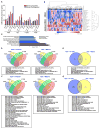
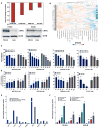
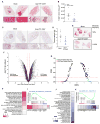
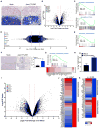
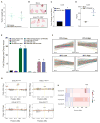
Combining DNA-demethylating agents (DNA methyltransferase inhibitors [DNMTis]) with histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACis) holds promise for enhancing cancer immune therapy. Herein, pharmacologic and isoform specificity of HDACis are investigated to guide their addition to a DNMTi, thus devising a new, low-dose, sequential regimen that imparts a robust anti-tumor effect for non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Using in-vitro-treated NSCLC cell lines, we elucidate an interferon α/β-based transcriptional program with accompanying upregulation of antigen presentation machinery, mediated in part through double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) induction. This is accompanied by suppression of MYC signaling and an increase in the T cell chemoattractant CCL5. Use of this combination treatment schema in mouse models of NSCLC reverses tumor immune evasion and modulates T cell exhaustion state towards memory and effector T cell phenotypes. Key correlative science metrics emerge for an upcoming clinical trial, testing enhancement of immune checkpoint therapy for NSCLC.
Keywords: HDAC; ITF-2357; MYC; NSCLC; azacitidine; immune response; lung cancer; memory T cells.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Combination immuno-oncology therapy with immune checkpoint blockers targeting PD-L1, PD-1 or CTLA4 and epigenetic drugs targeting MYC and immune evasion for precision medicine.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Mar;10(3):1294-1299. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.03.62. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 29708143 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

