Myc Cooperates with Ras by Programming Inflammation and Immune Suppression
- PMID: 29195074
- PMCID: PMC5720393
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.013
Myc Cooperates with Ras by Programming Inflammation and Immune Suppression
Abstract
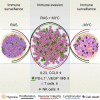
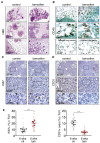
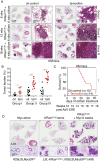
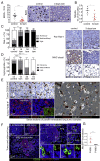
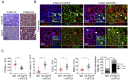
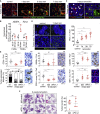
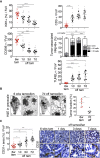
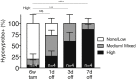
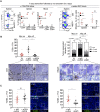
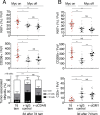
The two oncogenes KRas and Myc cooperate to drive tumorigenesis, but the mechanism underlying this remains unclear. In a mouse lung model of KRasG12D-driven adenomas, we find that co-activation of Myc drives the immediate transition to highly proliferative and invasive adenocarcinomas marked by highly inflammatory, angiogenic, and immune-suppressed stroma. We identify epithelial-derived signaling molecules CCL9 and IL-23 as the principal instructing signals for stromal reprogramming. CCL9 mediates recruitment of macrophages, angiogenesis, and PD-L1-dependent expulsion of T and B cells. IL-23 orchestrates exclusion of adaptive T and B cells and innate immune NK cells. Co-blockade of both CCL9 and IL-23 abrogates Myc-induced tumor progression. Subsequent deactivation of Myc in established adenocarcinomas triggers immediate reversal of all stromal changes and tumor regression, which are independent of CD4+CD8+ T cells but substantially dependent on returning NK cells. We show that Myc extensively programs an immune suppressive stroma that is obligatory for tumor progression.
Keywords: CCL9; IL-23; Myc; NK cells; Ras; immune suppression; inflammation; lung cancer; oncogene cooperation; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Andres A.C., van der Valk M.A., Schönenberger C.A., Flückiger F., LeMeur M., Gerlinger P., Groner B. Ha-ras and c-myc oncogene expression interferes with morphological and functional differentiation of mammary epithelial cells in single and double transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1988;2:1486–1495. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

