Long-Term Clinical Outcomes after Early Initiation of RRT in Critically Ill Patients with AKI
- PMID: 29196304
- PMCID: PMC5827600
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2017060694
Long-Term Clinical Outcomes after Early Initiation of RRT in Critically Ill Patients with AKI
Abstract
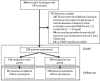
Whether earlier initiation of RRT in critically ill patients with AKI can improve outcomes remains debated. We examined follow-up data from a large clinical trial to prospectively investigate the long-term outcomes associated with the timing of RRT initiation in such patients. We extended the follow-up of patients in the Early Versus Delayed Initiation of RRT in Critically Ill Patients with AKI (ELAIN) Trial from 90 days to 1 year after randomization for 230 (99.6%) patients. The primary outcome was a composite of major adverse kidney events (persistent renal dysfunction, dialysis dependence, and mortality) at 1 year. Secondary outcomes included inflammatory markers. Overall, 72 of 111 (64.9%) and 106 of 119 (89.1%) patients met the primary outcome in the early (stage 2 AKI) and delayed (stage 3 AKI) initiation groups, respectively (odds ratio [OR] with early initiation, 0.23; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 0.11 to 0.45; P< 0.001). The early initiation group had a 1-year all-cause mortality rate (56 of 111 [50.2%]) significantly lower than that of the delayed initiation group (83 of 119 [69.8%]; absolute difference, -19.6%; 95% CI, -32.0% to -7.2%; P<0.01). After 1 year, 16 of 55 (29.1%) and 23 of 36 (63.9%) surviving patients in the early and delayed groups, respectively, failed to recover renal function (absolute difference, -34.8%; 95% CI, -54.6% to -15.0%; P=0.001). In conclusion, early initiation of RRT in these critically ill patients with AKI significantly reduced the occurrence of major adverse kidney events, reduced mortality, and enhanced renal recovery at 1 year.
Keywords: acute renal failure; hemodialysis; survival.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


References
-
- Hoste EA, Bagshaw SM, Bellomo R, Cely CM, Colman R, Cruz DN, Edipidis K, Forni LG, Gomersall CD, Govil D, Honoré PM, Joannes-Boyau O, Joannidis M, Korhonen AM, Lavrentieva A, Mehta RL, Palevsky P, Roessler E, Ronco C, Uchino S, Vazquez JA, Vidal Andrade E, Webb S, Kellum JA: Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: The multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med 41: 1411–1423, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Uchino S: The epidemiology of acute renal failure in the world. Curr Opin Crit Care 12: 538–543, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Star RA: Treatment of acute renal failure. Kidney Int 54: 1817–1831, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Liaño F, Junco E, Pascual J, Madero R, Verde E; The Madrid Acute Renal Failure Study Group : The spectrum of acute renal failure in the intensive care unit compared with that seen in other settings. Kidney Int Suppl 66: S16–S24, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Chertow GM, Christiansen CL, Cleary PD, Munro C, Lazarus JM: Prognostic stratification in critically ill patients with acute renal failure requiring dialysis. Arch Intern Med 155: 1505–1511, 1995 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

